![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Citric Acid Cycle (krebs Cycle)
|
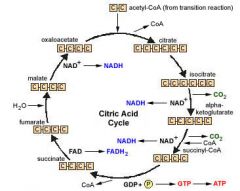
|
|
|
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
|
e- passed from one component to the next in a series of redox reactions
|
|
|
Heterotroph
|
Consumers (animals)
|
|
|
Autotroph
|
Producers (plants)
|
|
|
Anaerobic Respiration
|
use something other than O2 as final acceptor of an ETC
|
|
|
Oxidation
|
loss of electrons
|
|
|
Reduction
|
Gain of electrons
|
|
|
Cellular Respiration
|
process where living things obtain energy from organic molecules and release waste products,
|
|
|
Photon
|
massless particle that travel in waves and move at the speed of light.
|
|
|
Glycolysis
|
glucose broken down into 2 pyruvate molecules(w/ 3 carbons each) producing a net gain of 2 ATP and 2 NADH,
|
|
|
Chemiosmosis
|
Energy stored in H+ gradient is used to synthesize ATP from ADP and Pi.
|
|
|
fermentation
|
breakdown of organic molecules to harness energy without any net oxidation
|
|
|
Substrate Level Phosphorylation
|
energy rich substrate that provides the energy to make ATP.
|
|
|
Oxidative Phosphorylation
|
organic molecules oxidized, e- carriers (NAD+, FAD) are reduced. NADH, FADH2 reduce ETC. e- pump H+ into inter membrane. E powers ATP synthesis.
|

