![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Organic Chemistry |
the study of carbon compounds (organic compounds) |
|
|
Hydrocarbons |
organic molecules consisting of only C and H |
|
|
List the four ways that carbon skeletons can vary. |
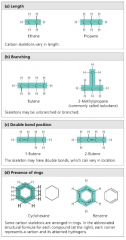
1. Length 2. Branching 3. Bond types/location 4. Rings |
|
|
Isomer |
one of several compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and therefore different properties |
|
|
List the three types of isomers. |
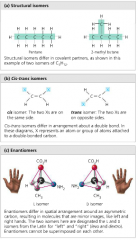
|
|
|
Structural Isomers |
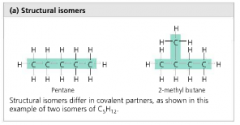
isomers that differ in covalent partners |
|
|
Cis-Trans Isomers (Geometric Isomers) |
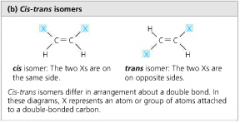
isomers that differ in arrangement about an inflexible double bond cis - X groups on same side trans - X groups of different sides |
|
|
Enantiomers |
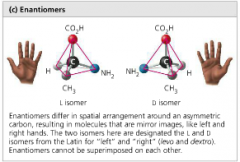
isomers that differ in spatial arrangement around asymmetric C that appear as mirror images to each other |
|
|
Functional Groups |
a specific confirguration of atoms commonly attached to the carbon skeletons of organic molecules and involved in chemical reactions |
|
|
Name 7 functional groups. |
1. Hydroxyl group (-OH) 2. Carbonyl group (C=O) 3. Carboxyl group (-COOH) 4. Amino group (-NH2) 5. Sulfhydryl group (-SH) 6. Phosphate group (-OPO3 (2-)) 7. Methyl group (-CH3) |
|
|
Hydroxyl group |
-OH Compound Name: Alcohol polar; forms H bonds with water to dissolve compounds like sugar |
|
|
Carbonyl group |
C=O Compound Name: Ketone (if within skeleton) or Aldehyde (if at end of skeleton) |
|
|
Carboxyl group |
-COOH Compound Name: carboxylic (organic) acid acts as an acid due to high polarity of O-H bond |
|
|
Amino group |
-NH2 Compound Name: Amine acts as a base |
|
|
Sulfhydryl group |
-SH Compound name: Thiol two molecules with -SH groups can react and form a "cross-link" to stabilize protein structures |
|
|
Phosphate group |
-OPO3 (-2) Compound name: Organic phosphate contributes a negative charge to molecule; allows molecule to react with water and release energy |
|
|
Methyl group |
-CH3 Compound name: Methylated compound affects the expression of genes when on DNA or on proteins bound to DNA; affects shape/function of sex hormones |
|
|
Adenosine Triphosphate |
ATP an adenine-containing nucleoside triphosphate that releases free energy when phosphate bonds are hydrolyzed; used to drive endergonic reactions in cells |
|
|
ATP Reaction |
(P)(P)(P)[A] +H2O -> (P1) + (P)(P)[A] + Energy ATP and water react to form an inorganic phosphate (P1), ADP, and energy |
|
|
Both _______ and _______ groups are always found in amino acids. |
Both -COOH (carboxyl) and -NH2 (amine) groups are always found in amino acids. |
|
|
The chemical group that is involved in regulating DNA is the ________ group. |
The chemical group that is involved in regulating DNA is the methyl (-CH3) group. |
|
|
The chemical group that helps stabilize protein structure is the __________. |
The chemical group that helps stabilize protein structure is the sulfhydryl group (-SH). |
|
|
All functional groups are (hydrophobic/hydrophillic) and thus (increase/decrease) an organic compound's water solubility. |
All functional groups are hydrophillic and thus increase an organic compound's water solubility. |

