![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
201 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
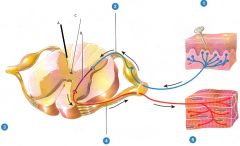
Label all the numbers and letters
|
1) Sensory receptor
2) Sensory neuron 3) Integrating center 4) Motor Neuron 5) Effector A) Spinal cord integrator B) Interneuron C) Central Canal |
|
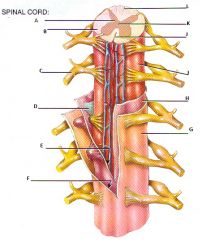
Label this spinal cord
|
A: Gray matter, B: White matter, C: Spinal nerve, D: Denticulate ligament, E: Subarachnoid space, F: Subdural space, G: Dura mater, H: Arachnoid mater, I: Pia mater, J: Anterior median fissure, K: Central canal, L: Posterior median sulcus
|
|
|
Most superficial layer of the meninges
|
Dura mater
|
|
|
Meninge that is composed of dense irregular connective tissue
|
Dura mater
|
|
|
space between the dura mater and the wall of the vertebral canal
|
Epidural space
|
|
|
What is epidural space filled with?
|
Adipose and areolar connective tissues
|
|
|
middle layer of the meninges
|
Arachnoid
|
|
|
Which of the meninges has an avascular covering?
|
Arachnoid mater
|
|
|
What is the space between the dura mater and the arachnoid matter?
|
Subdural space
|
|
|
What is the subdural space filled with?
|
interstitial fluid
|
|
|
What is the inner most or deep layer of the meninges
|
Pia mater
|
|
|
Which of the meninges is composed of a thin transparent connective tissue that adheres to the surface of the spinal cord
|
Pia mater
|
|
|
What are thinkenings of the pia mater that project laterally and fuse with the arachnoid and dura mater?
|
Denticulate ligaments
|
|
|
What is the space between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater?
|
Subarachnoid space
|
|
|
In adults how far does the spinal cord extend?
|
From the medulla oblongata to the superior border of the 2nd lumbar vertebra
|
|
|
How far does the spinal cord extend in a new born?
|
from the medulla oblongata to the 3rd or 4th lumbar vertebrae
|
|
|
What is a tail-like array of roots of spinal nerves at the inferior end of the spinal cord?
|
Cauda equine
|
|
|
What is the non nervous fibrous tissue of the spinal cord that extends inferiorly from conus medullaris to the coccyx?
|
Filum terminale
|
|
|
Where does the cervical enlargement extend to?
|
4th cervical vertebrae to the 1st thoracic vertebrae
|
|
|
How far does the lumbar enlargement extend to?
|
from the 9th to 12th thoracic vertebrae
|
|
|
What is the name of the plexus that goes to the arm?
|
Brachial
|
|
|
Why does the thoracic have no nerve plexus?
|
Those nerves go directly to their target without branching
|
|
|
Define a reflex
|
Extremely rapid response involving skeletal muscles in order to remove your body for obnoxious stimuli
|
|
|
Are motor neurons ventral or dorsal?
|
ventral
|
|
|
Are sensory neurons ventral or dorsal?
|
dorsal
|
|
|
How can you tell if spinal nerve is dorsal or ventral?
|
Dorsal side is a little swollen
|
|
|
What are the four somatic spinal reflexes?
|
Stretch, tendon, flexor, crossed extensor
|
|
|
Nerves in the CNS are referred to as _____.
|
tracts
|
|
|
What defines a stretch reflex?
|
Monosynaptic and ipsilateral
|
|
|
What defines a tendon reflex?
|
polysynaptic and ipsilateral
|
|
|
What defines a Flexor (withdrawal) reflex?
|
polysynaptic, intersegmental, and ipsilateral
|
|
|
What defines a crossed extensor reflex?
|
polysynaptic, intersegmental, and contralateral
|
|
|
How many pairs of spinal nerves arise from the spinal cord?
|
31
|
|
|
How are the segments of the spinal nerves based?
|
location
|
|
|
How many pairs of nerves are in the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal segments?
|
8, 12, 5, 5, 1
|
|
|
What are roots?
|
bundles of axons that connect the spinal nerves to the spinal cord
|
|
|
What is a commissure?
|
acts like a bridge, the horizontal part of the H
|
|
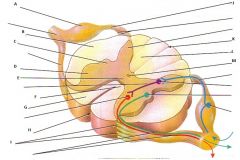
Label the following parts.
|
A: Posterior (dorsal) root ganglion, B: Lateral white column, C: lateral gray horn, D: Anterior gray horn, E: Gray commissure, F: Anterior white commissure, G: Anterior white column, H: Anterior median fissure, I: Anterior rootlets, J: Posterior (dorsal) root of spinal nerve, K:Posterior median sulcus, L: Posterior white column, M: central canal
|
|
|
What are the regions that gray matter is divided into called?
|
Horns
|
|
|
What do the anterior or ventral gray horns contain?
|
cell bodies somatic and motor neurons
|
|
|
What do the dorsal gray horns contain?
|
somatic and autonomic sensory nuclei
|
|
|
What do the lateral gray horns contain? And where are they in the lateral horns?
|
autonomic motor neurons, on the very edge
|
|
|
Where are the lateral gray horns found in the spinal cord? What regions?
|
thoracic, upper lumbar, and sacral segments
|
|
|
What are the regions that white matter is divided into called?
|
columns
|
|
|
What are the two principal functions of the spinal cord?
|
nerve impulse propagation and information integration
|
|
|
What does the name of a tract indicate?
|
it's origin: where it begins and ends
|
|
|
Information integration is used for what?
|
reflex and reflex arc
|
|
|
What are the four different types of reflexes?
|
Spinal, Cranial, Somatic, and Autonomic
|
|
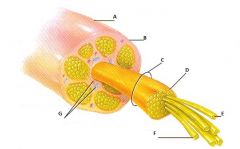
Label all parts
|
A: Spinal nerve, B: Epineurium, C: Fascicle, D: Perineurium, E: Axon, F: Endoneurium, G: Blood vessels
|
|
|
What are the names of the two dura maters of the brain?
|
periosteal and meningeal
|
|
|
What is the outer layer of the dura mater?
|
periosteal
|
|
|
What is the dura mater that is connected to the dura mater of the spinal cord?
|
meningeal
|
|
|
What is the inner layer of the dura mater?
|
meningeal
|
|
|
What is the falx cerebri?
|
located between the two cerebral hemispheres
|
|
|
What is the falx cerebelli?
|
located between the two cerebral hemispheres
|
|
|
Where is the tentorium cerebelli?
|
between the cerebrum and cerebellum
|
|
|
What absorbs the CSF?
|
Arachnoid villi
|
|
|
What meninx has a lot of blood vessels?
|
pia
|
|
|
What structure secretes CSF?
|
ependymal cells in the choird plexus
|
|
|
What is a ventricle?
|
cavity in the brain filled with CSF
|
|
|
What is the choirod plexus composed of?
|
cluster of capillaries surrounded by ependymal cells
|
|
|
What is the tube that connects the lateral ventricles to the 3rd ventricle?
|
interventricular foramen
|
|
|
What is the tube that connects the 3rd ventricle to the 4th?
|
cerebral aqueduct
|
|
|
What are the three holes that the CSF comes out of at the base of the brain?
|
lateral aperatures and a median aperature
|
|
|
About how many ml of CSF do adults have?
|
150ml
|
|
|
CSF is like plasma except that the CSF has _____________
|
less proteins and more electrolytes
|
|
|
What is a rami?
|
spinal nerves that go short distances after passing through the invertebral foramen then break into branches
|
|
|
What does the posterior (dorsal) ramus supply?
|
deep nerves of the back and skin of the back
|
|
|
What does the anterior (ventral) ramus supply?
|
muscles and structures of the upper and lower limbs and the skin of the lateral and ventral sides
|
|
|
What does the meningeal branch supply?
|
renters the vertebral canal through the invertebral foramen and supplies the vertebrae, ligaments, blood vessels, and meninges
|
|
|
Which rami does not go directly to the body structures?
|
anterior
|
|
|
What section of the anterior rami does go directly to the body structures?
|
T1-T12
|
|
|
What are the names of the plexuses?
|
cervical, brachial, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
|
|
|
What is a dermatome?
|
area of the skin that provides sensory input to the CNS via the posterior or dorsal roots of one pair of spianl nerves via cranial nerve V
|
|
|
Which spinal nerve is not connected to a dermatome?
|
C1
|
|
|
What disease is caused be an acute infection of the PNS?
|
shingles
|
|
|
What virus causes shingles?
|
Herpes zoster
|
|
|
What does shingles look like?
|
pain, discoloration of the skin and blisters
|
|
|
What causes polio?
|
poiliovirus
|
|
|
What characterizes polio?
|
fever, severe headache, stiff neck and back, deep muscle pain and weakness, and loss of certain somatic reflexes
|
|
|
Does polio attack the PNS or the CNS?
|
PNS
|
|
|
Why does polio cause paralysis?
|
poliovirus destroys motor neuron cell bodies
|
|
|
What is meningitis?
|
inflammation and infection of the menenges
|
|
|
How is meningitis usually treated?
|
antibiotic
|
|
|
What is the branching inside the cerebellum called?
|
Arbor vitae (tree of life)
|
|
|
What are the two types of meningitis, and what is it caused by?
|
spinal and cranial, bacteria or a virus
|
|
|
How does CSF circulate?
|
through equal secretion and absorption
|
|
|
What are the three main ways that CSF contributes to homeostais?
|
Mechanical, Chemical, Circulation
|
|
|
When the CSF leaves through the apertures, where does it go?
|
circulates through central canal and subarachnoid space of the spinal cord
|
|
|
What does the internal jugular veins do?
|
removes blood from brain
|
|
|
What brings blood to the brain?
|
internal carotid arteries
|
|
|
How much of the body's oxygen and glucose does the brain use?
|
20%
|
|
|
Name the three components of the brain stem going from most inferior to superior.
|
madulla oblongata, pons, midbrain
|
|
|
What is a continuation of the spinal cord and contains both sensory and motor tracts?
|
madulla oblongata
|
|
|
What part of the brain stem contains descending motor tracts?
|
pyramids
|
|
|
What is a decussaton of pyramids?
|
Where the pyramids cross over to the other side
|
|
|
What do the olives of the brain stem do?
|
send input to the cerebellum and relay sensory information on stretching of muscles and joints
|
|
|
What is the most inferior part of the brain?
|
olives
|
|
|
What do the gray matter masses in the CNS control?
|
vital functions
|
|
|
Olives are composed of patches of _____ mater in _____ mater.
|
gray in white
|
|
|
What is the septum policium?
|
separation of the left and right lateral ventricles
|
|
|
What cranial nerves originate on the medulla oblongata?
|
Vestibulocochlear VIII, Glossopharyngeal IX, Vagus X, Accessory XI, Hypoglossal XII
|
|
|
What kind of neurons are ascending tracts made of?
|
Sensory
|
|
|
What kind of neurons are descending tracts made of?
|
Motor
|
|
|
What is a grouping of tracts called?
|
Fasciculus
|
|
|
What are the three vital centers?
|
cardiac, respiratory, vasomotor
|
|
|
What area of the midbrain controls respiratory functions?
|
Pons
|
|
|
What are the centers in the pons that are in control of breathing?
|
Pneumotaxis and apneusitic center
|
|
|
What is the name of the tracts that go from the pons to the cerebellum?
|
Cerebellar peduncles
|
|
|
What are the cranial nerves that originate in the pons?
|
Trigeminal V, Abducens VI, Facial VII, Vestibulocochlear VIII (coclear branch)
|
|
|
What are the tracts that go from the midbrain to cerebrum?
|
Cerebral peduncles
|
|
|
Where is the cerebral aqueduct located?
|
Midbrain
|
|
|
What does the red nucleus do?
|
relays information for motor tracts
|
|
|
What are the cranial nerves that originate in the midbrain?
|
Occulomotor III, Trochlear IV
|
|
|
Where is the corpora quadrigemina?
|
the dorsal/posterior side of the midbrain
|
|
|
What does the superior colliculi in the corpora quadrigemina do?
|
contains visual relfex centers that coordinate head and eye movemnt
|
|
|
What does the inferior colliculi of the corpora quadrigemina do?
|
contains auditory reflex centers
|
|
|
What is the function of the midbrain?
|
integrates visual and auditory reflexes
|
|
|
What is found in the brain stem that keeps you conscious and wakes you up?
|
reticular formation
|
|
|
What does the reticular formation do and where is it found?
|
keeps you conscious and wakes you up, found in brain stem
|
|
|
What is in the central part of the cerebellum?
|
vermis
|
|
|
What is the function of the cerebellum?
|
voluntary muscle contraction and posture based on sensory data from body, gives you a sense of equilibrium
|
|
|
What is the folia?
|
grey matter which surrounds the arbor vitae in the cerebellum
|
|
|
What structure relays information to the cerebellum?
|
olives on medulla oblongata
|
|
|
What do the inferior cerebellar peduncles do?
|
transmit sensory information from vestibule of inner ear and proprioceptors to cerebellum (balance information)
|
|
|
What do the middle cerebellar peduncles do?
|
axons carry commands for voluntary movements
|
|
|
What do the superior cerebellar peduncles do?
|
axons connect cerebellum to red nucleus in mid brain and to several thalamic nuclei
|
|
|
What part of the brain surrounds the 3rd ventricle?
|
Diencephalon
|
|
|
What secretes melatonin?
|
Pineal gland
|
|
|
Where is the pineal gland?
|
diencephalon
|
|
|
What is the relay center for sensory information on it's way to the cortex?
|
Thalamus
|
|
|
What allows you to discriminate from pleasant and unpleasant sensations?
|
Thalamus
|
|
|
What uses both and endocrine mode and a neurotransmitter mode to send information?
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
What are the four major regions of the hypothalamus?
|
Mammillary, Tuberal, Supraoptic, Pre-optic region
|
|
|
Approximately how many nuclei are in the hypothalamus?
|
12
|
|
|
Where is the mammillary region and what does it do?
|
next to the midbrain in the hypothalamus - relay station for smell
|
|
|
What region in the hypothalamus produces hormones?
|
Tuberal
|
|
|
What does the pre-optic do?
|
functions in regulating a number of autonomic activites
|
|
|
What are the elevated ridges of the cerebrum called?
|
gyri
|
|
|
What are the grooves of the cerebrum called?
|
Sulci
|
|
|
What does the ANS depend on to keep working?
|
sensory afferent input from receptors and efferent motor output to effectors
|
|
|
What regulates the autonomic nervous system?
|
Hypothalamus and the brain stem
|
|
|
What are the 12 cranial nerves in order?
|
Olfactory I, Optic II, Oculomotor III, Trochlear IV, Trigeminal V, Abducens VI, Facial VII, Vestibulocohlea VIII, Glossopharyngeal IX, Vagus X, Accessory XI, Hypoglossal XII
|
|
|
What controls the learned motor skills?
|
Pre-motor area
|
|
|
What does the primary motor area do?
|
permits conscious control of skeletal muscle
|
|
|
Where is the primary motor area located?
|
in pre-central gyrus of frontal lobe
|
|
|
Where is the pre-motor area located?
|
Anterior to the precentral gyrus of frontal lobe
|
|
|
What is another name for Broca's speech area?
|
Motor speech area
|
|
|
Where is the motor speech area located?
|
at the base of pre-motor area
|
|
|
What does Broca's speech area do?
|
produces impulses for muscle contraction necessary for speech
|
|
|
What is another name for the primary sensory area?
|
Somatosensory
|
|
|
Where is the primary sensory area?
|
post central gyrus of parietal lobe
|
|
|
What does the primary sensory area do?
|
receives info from skin and proprioceptor centers in skeletal muscles
|
|
|
What allows you to ID the body region being stimulated?
|
Primary sensory area
|
|
|
What does the visual cortex of the occipital lobe do?
|
contains primary visual center surrounded by the visual association area
|
|
|
Where is the Wernike's area located?
|
temporal lobe
|
|
|
What hemisphere is the Wernike's area usually located?
|
opposite Broca's
|
|
|
What does the Wernike's area do?
|
allows you to comprehend written language and auditory language, receives sensory info from eyes and ear
|
|
|
Where is the auditory cortex?
|
temporal lobe
|
|
|
Where is the olfactory area?
|
temporal lobe
|
|
|
Where is the gustatory area?
|
In the parietal lobe at base of the postcentral gyrus
|
|
|
What goes on in the left hemisphere?
|
language, analytical thinking, math skills, logic
|
|
|
What goes on in the right hemisphere?
|
motor activity, visual spatial skills, intuition and emotion, appreciation of art and music
|
|
|
What are the 3 groups of cerebral white matter?
|
commissure, corpus callosum, and basal ganglia
|
|
|
What does the association areas of the cerebrum allow you to do?
|
analyze and recognize sensory info then send info to motor area for a proper response
|
|
|
What are the 4 areas of the association areas of the cerebrum?
|
somatosensory, pre-frontal cortex, general interpretaton/gnostic, and affective language area
|
|
|
What area is necessary for abstract thinking?
|
pre-frontal
|
|
|
What does the corpus callosum allow?
|
communication between the two hemispheres
|
|
|
What are the three different fibers of the corpus callosum?
|
association, projection, the basal ganglia
|
|
|
What allows you intense pleasure and intense pain?
|
limbic system
|
|
|
Strong emotions increase ___________
|
memory
|
|
|
Which neuronal system receives input from receptors of the special senses and is consciously perceived?
|
Somatic Sensory Neron
|
|
|
Which neuronal system innervates skeletal muscles to produce conscious voluntary movement?
|
Somatic Motor Neurons
|
|
|
What regulates visceral activities by either increases or decreasing ongoing activities of cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands?
|
Autonomic Motor Neurons
|
|
|
What kind of responses cannot be consciously altered or suppressed?
|
Autonomic
|
|
|
How many neurons are in a motor pathway for somatic and autonomic?
|
1 for somatic
2 for autonomic |
|
|
In an autonomic motor pathway, where is the synapse?
|
in the ganglia
|
|
|
What kind of fiber is the pre and postganglion of the autonomic motor pathway?
|
Pre is B
Post is C |
|
|
Which is longer in the autonomic motor pathway, pre or postganglions?
|
Pre
|
|
|
Which division of the efferent ANS increases heart rate?
|
Sympathetic
|
|
|
Which division of the efferent ANS decreases heart rate?
|
parasympathetic
|
|
|
Where can the parasympatheric ganglia be found?
|
very close or inside the wall of the visceral organ
|
|
|
Where can the preganglionic cell bodies of the parasympathetic NS be found?
|
4 cranial nerve nuclei in brainstem and S2-S4 in spinal cord
|
|
|
What does Cholinergic bind for?
|
muscanin and nicotinic for ACh
|
|
|
What does adrenergic bind for?
|
receptors that bind for adrenalin
|
|
|
Where is nicotinic receptors found?
|
on dendrites and cell bodies of autonomic NS cells
|
|
|
Where is muscarnic receptors found?
|
plasma membranes of all parasympathetic effectors
|
|
|
What enzyme inactivates noepinerphrine?
|
monoamine oxidase (MAO)
|
|
|
What enzyme inactivates norepinerphine?
|
monoamine oxidase (MAO) or catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT)
|
|
|
What does Alpha 1 and Beta 1 do?
|
produce excitation
|
|
|
What do Alpha 2 and Beta 2 do?
|
cause inhibition
|
|
|
What does Beta 3 do?
|
increases thermogenisis (heat generation)
|
|
|
what does an agonist do?
|
binds to a receptor and mimickes the effect of the normal neurotransmitter or hormone
|
|
|
What does an antagonist do?
|
binds to a receptor and blocks the normal neurotransmitter and hormone
|
|
|
Are most organs dual innervations?
|
yes
|
|
|
What does dual innervations mean?
|
innervations by both sympathetic and parasympathetic
|
|
|
What balances the use of the sympathetic and the parasympathetic NS
|
hypothalamus
|
|
|
Which is more dominant symp or para
|
Para
|
|
|
What are some examples of SLUDD type responses?
|
any liquid that comes out of the body such as urination, lactation, salivation, etc
|
|
|
What happens when paradoxical fear takes place?
|
loss of control over urination adn defecation
|
|
|
What enhances "rest-and-digest" activities?
|
Para
|

