![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Chapter 27 Bacteria and Archaea |
|
|
|
Concept 27.1 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success |
|
|
|
A key feature of nearly all prokaryotic cells is the |
Cell wall |
|
|
Most bacterial cell walls contain |
Peptidoglycan A polymer composed of modified sugars cross-linked by short polypeptides. This molecular fabric encloses the entire bacterium and anchors the molecules that extend from its surface. |
|
|
Archaeal cell walls contain |
A variety of polysaccharides and proteins but lack peptidoglycan |
|
|
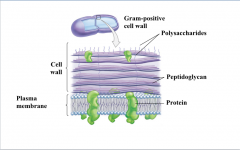
Gram-positive bacteria |
Have a thick wall made of peptidoglycan. The crystal violet enters the cell, where it forms a complex with the iodine in the stain. Too large to pass through the thick cell wall, this complex is not removed by the alcohol rinse. Result: The crystal violet masks the safranin dye. |
|
|
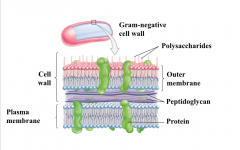
Gram-negative bacteria |
Have a thin layer of peptidoglycan, which is located between the plasma membrane and an outer membrane that contains lipopolysaccharides. The crystal violet-iodine complex can pass through this thin cell wall and hence is removed by the alcohol rinse. Result: The safranin dye stains the cell pick or red. |
|
|
Gram-negative bacteria |
|
|
Gram-positive bacteria |
|
|
The cell wall of many prokaryotes is surrounded by a sticky layer of polysaccharide or protein. This layer is called a |
Capsule, if it is dense and well defined, or a slime layer if it is no as well organized. Both kinds of sticky outer layers enable prokaryotes to adhere to their substrate or to other individuals in a colony. Some capsules and slime layers protect against dehydration, and some shield pathogenic prokaryotes from attacks by their host's immune system. |
|
|
In another way of withstanding harsh conditions, certain bacteria develop resistant cell called ___ when they lack an essential nutrient |
Endospores |
|
|
Some prokaryotes stick to their substrates or to one another by means of |
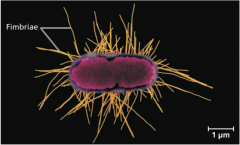
Fimbriae Hairlike appendages |
|
|
Pili or Sex pili |
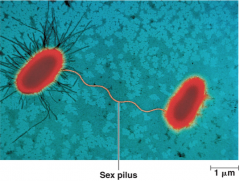
Appendages that pull two cells together prior to DNA transfer from one cell to the other |
|
|
Taxis |
A directed movement toward or away from a stimulus For example, chemotaxis is a directed movement in response to a chemical |
|
|
Of the various structures that enable prokaryotes to move, the most common are |
Flagella |
|
|
Prokaryotic flagella differ greatly from eukaryotic flagella |
Prokaryotic flagella are one-tenth the width and typically are not covered by an extension of the plasma membrane. The flagella or prokaryotes and eukaryotes also differ in their molecular compositions and their mechanism of propulsion. |
|
|
Internal Organization and DNA: Bacteria don’t have mitochondria or chloroplasts, but still need to metabolize |
Some prokaryotic cells have specialized membranes that perform metabolic functions. These membranes are usually infoldings of the plasma membrane. |
|
|
Prokaryotes have ___ chromosomes |
Circular |
|
|
Since prokaryotes lack a nucleus, their chromosome is located in the |
Nucleoid A region of the cytoplasm that is not enclosed by a membrane |
|
|
Plasmids |
Smaller rings of DNA |
|
|
Three factors that contribute to the vast genetic diversity of prokaryotes. |
1. Rapid reproduction 2. Mutation 3. Genetic recombination |
|
|
Prokaryotes can reproduce quickly in favorable conditions by |
Binary fission |
|
|
Mutation |
Due to insertions, deletions and base-pair substitutions in DNA, some offspring may differ genetically. New mutations, though are on a per gene basis, can increase genetic diversity quickly in species with short generation times and large populations. |

