![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
137 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Two types of reproduction. |
Asexual and Sexual. |
|
|
Asexual reproduction needs only... |
A female. |
|
|
The offspring of asexual reproduction are... |
Identical to the parent and eachother. |
|
|
Asexual reproduction is common in... |
Plants and animals, more common in plants. |
|
|
Sexual reproduction needs... |
Both sexes (two parents) |
|
|
The offspring of sexual reproduction are... |
Similar, not identical to parents. (Combination of characteristics) |
|
|
Sexual reproduction is common in... |
Plants and animals (most organisms). |
|
|
The two types of variation are... |
Continuous and discontinuous. |
|
|
In continuous variation there is a... |
Complete range of measurements from one extreme to the other. (All have many outcomes). |
|
|
Examples of continuous variation include: |
Hair colour, height, weight, heart rate, finger length, leaf length. |
|
|
Examples of discontinuous variation include: |
Tongue rolling, finger prints, eye colour, blood groups, Hitchhiker's thumb, attached/detached ears. |
|
|
All organisms are made of... |
Cells. |
|
|
The human body contains (how many cells) |
50 trillion-100 trillion. |
|
|
Human cell which doesn't contain a nucleus. |
Red blood cells. |
|
|
The purpose of chromosomes is to... |
Give instructions to tell the cell how to function. |
|
|
There are ..... chromosomes in each cell. |
46. (Half from your father, half from your mother) |
|
|
Chromosomes are made of... |
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) |
|
|
Each chromosome has sections called ..... which are responsible for coding our ......... and ......... |
Genes, features, traits. |
|
|
The structure of DNA is .............. in all living things. |
Identical. |
|
|
DNA consists of a .................... and is made of up simple repeating units called ................... |
Double helix, nucleotides. |
|
|
A nucleotide is comprised of a: |
Sugar, a phosphate and base. |
|
|
The four different nucleotide bases are: |
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine and Guanine. |
|
|
Adenine always bonds with... |
Thymine. |
|
|
Cytosine always bonds with... |
Guanine. |
|
|
Evolution is the... |
Change of species over time, through a process called "natural selection". |
|
|
Vestigial structures are... |
Parts of an organism which have reduced in size over time and are no longer functional, however they are thought to have a use in the ancestors of the organism. |
|
|
Mitosis is the process of... |
Cell division. |
|
|
For an embryo to grow... |
More cells are required. |
|
|
Sex cells divide to produce... |
Gametes (sperm, ovum). |
|
|
The skeletal system is made up of... |
Bones and cartilage. |
|
|
A bone is made up of... |
Salts, water and tissue. |
|
|
Bone marrow produces... |
Red blood cells. |
|
|
The human body has about ..... muscles. |
650. |
|
|
Muscles make up ....... your body weight. |
Half. |
|
|
Muscles need ............ to function. |
Oxygen. |
|
|
A heart attack is caused by... |
Fatigued cardiac muscles which aren't getting enough oxygen. |
|
|
Muscles work in .......... . One ................ , one ................ |
Pairs, contracting, relaxing. |
|
|
Tendons attach... |
Muscles to bones. |
|
|
Ligaments attach... |
Bones to bones. |
|
|
The three types of muscles are: |
Skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles. |
|
|
Skeletal muscles are the... |
Voluntary muscles on our bones. |
|
|
Smooth muscles are the... |
Involuntary muscles found in blood vessels, digestive organs etc. |
|
|
Cardiac muscles are the... |
Involuntary muscles that make up the heart. |
|
|
The ends of bones in a joint are covered with... |
Cartilage. |
|
|
Cartilage reduces ................. and acts as a ......... ............ |
Friction, shock absorber. |
|
|
Cartilage is made up of .................. fluid produced in the ................. ...................... . |
Synovial, synovial membrane. |
|
|
The circulatory carries ............ and ............... around the body and .................. substances. |
Blood, oxygen, dissolves. |
|
|
Blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood away from the heart under high pressure. |
Arteries. |
|
|
Arteries have.... |
Thick walls and thick layers of muscle and elastic fibres. They also have a narrow bore hole and no valves. |
|
|
Blood vessel that carries deoxygenated blood back to the heart under low pressure. |
Veins. |
|
|
Blood vessels that exchange material between the blood and the other body cells. (Contains both deoxygenated blood and oxygenated blood) |
Capillaries. |
|
|
Veins have... |
Thinner walls and a large bore hole. |
|
|
Capillaries have... |
Walls one cell thick. |
|
|
Capillaries exchange... (with the body cells) |
Hormones, nutrients, carbon dioxide and oxygen. |
|
|
Thigh bone. |
Femur. |
|
|
Largest bone in the body. |
Femur. |
|
|
Knee bone. |
Patella. |
|
|
Bones found in both hands and feet. |
Phalanges. |
|
|
Breast bone. |
Sternum. |
|
|
Ear bones. |
Hammer, anvil and stirrups. |
|
|
Smallest bones in the body are found here. |
The ear (inner ear). |
|
|
Forearm bones. |
Radius and Ulna. |
|
|
The bone which both legs are attached to. |
The pelvis. |
|
|
The skull. |
Cranium. |
|
|
The jaw bone. |
Mandible. |
|
|
Bones which provide as a cage for the lungs and heart. |
Ribs. |
|
|
Your funny bone. |
Humerus. |
|
|
The bones that protect your spinal cord. |
Vertebrae. |
|
|
The right ventricle... |
Pumps blood to the lungs. |
|
|
The left ventricle... |
Pumps blood to the entire body. |
|
|
The left ventricle has a ................... muscle wall. |
Thicker. |
|
|
The right ventricle has a ................... muscle wall. |
Thinner. |
|
|
Deoxygenated blood enters the heart through the... |
Inferior vena cava (on the bottom) and the superior vena cava (on the top). |
|
|
Outline the circulatory process of the heart. |
Vena cava vessels > right atrium > right ventricle > pulmonary artery > lungs > pulmonary veins > left atrium > left ventricle > aorta. |
|
|
The biggest artery in the body. |
The aorta. |
|
|
The atrium which the oxygenated blood is pumped out of. |
The left atrium. |
|
|
Oxygenated blood from the lungs re-enters the heart through these. |
Pulmonary veins leading to the left atrium. |
|
|
Red blood cells contain... |
Hemoglobin. |
|
|
Red blood cells are the only cell in the body which don't contain... |
A nucleus. |
|
|
Red blood cells can .......... .......... to enter through the capillaries. |
Change shape. |
|
|
White blood cells have a... |
Nucleus. |
|
|
The two types of white blood cells are... |
Lymphocytes and macrophage. |
|
|
Outline the process of respiration. |
Mouth/nose > trachea > bronchi > bronchioles > alveoli > bloodstream |
|
|
Respiration word equation. Oxygen + .................. --> |
Oxyegn + glucose --> carbon dioxide + water + energy/heat. |
|
|
The trachea is also known as the... |
Windpipe. |
|
|
The trachea divides into two... |
Bronchi. (One bronchus for each lung) |
|
|
Each bronchus divides further in the lungs into smaller tubes called... |
Bronchioles. |
|
|
At the end of each bronchiole, there is a group of tiny air sacs. These air sacs have bulges called... |
Alveoli. |
|
|
The human body needs many alveoli to... |
Increase their surface area and speed up the absorption of oxygen. |
|
|
The muscles between ribs are called the... |
Intercostal muscles. |
|
|
During inhalation, the muscles between the ribs... |
Lift the ribcage up and out, expanding the chest. |
|
|
During inhalation, the diaphragm... |
Flattens to reduce air pressure in the lungs. |
|
|
During exhalation, the muscles between the ribs and the diaphragm... |
Relax to increase the amount of air pressure in the lungs which forces air (carbon dioxide) out the trachea. |
|
|
(M) Flexible bag for storing urine. |
Bladder. |
|
|
(M) A tube inside the penis through which urine and semen pass out of the penis. |
Urethra. |
|
|
(M) The external sex organ of a male. A hood of skin (foreskin) covers the head (glans). |
Penis. |
|
|
(M) Tubes at the back of the testes that store sperm. |
Epididymis. |
|
|
(M) Tubes that connect the epididymis to the urethra. Often called the 'sperm duct'. |
Vas deferens |
|
|
(M) Glands in the scrotum that produce sperm and the hormone testosterone. |
Testes. |
|
|
(M) A sac that holds the testes. |
Scrotum. |
|
|
(M) Elastic sac that stores solid body waste before being passed as faeces. |
Rectum. |
|
|
(M) Opening through which faeces passes. |
Anus. |
|
|
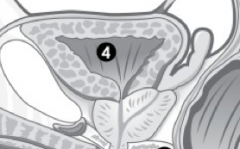
(M) A gland just below the bladder that produces a fluid that provides the sperm cells with nutrients. |
Prostate gland. |
|
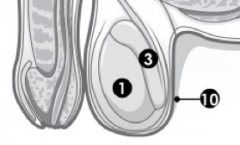
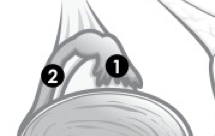
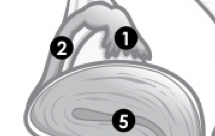
(M) Label 1. |
Testes. |
|
(M) Label 2.
|
Urethra. |
|
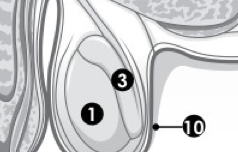
(M) Label 3. |
Epididymis. |
|
(M) Label 4. |
Bladder. |
|
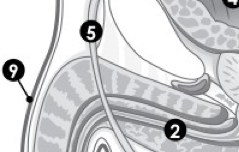
(M) Label 5. |
Vas deferens. |
|
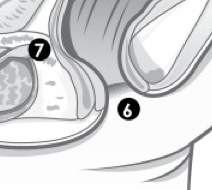
(M) Label 6. |
Anus. |
|
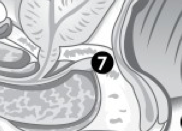
(M) Label 7. |
Prostate. |
|
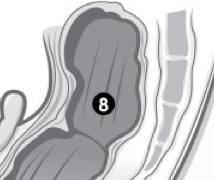
(M) Label 8. |
Rectum. |
|
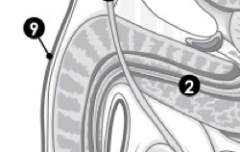
(M) Label 9. |
Penis. |
|
(M) Label 10. |
Scrotum. |
|
|
(F) Urine is stored here before passing out the urethra. |
Bladder. |
|
|
(F) One of the two tubes that connect the ovary to the uterus. |
Fallopian tube. |
|
|
(F) One of the two organs either side of the uterus. They contain the eggs. |
Ovary. |
|
|
(F) Organ in which the baby develops if an egg is fertilised. |
Uterus. |
|
|
(F) A tube that connects the cervix to the external opening called the vulva. |
Vagina. |
|
|
(F) External opening of the vagina. |
Vulva. |
|
|
(F) Junction between the uterus and vaginal tube. |
Cervix. |
|
|
(F) Elastic sac that stores solid body waste before being passed as faeces. |
Rectum. |
|
|
(F) Opening through which faeces passes. |
Anus. |
|
|
(F) Tube through which urine flows through after exiting the bladder. |
Urethra. |
|
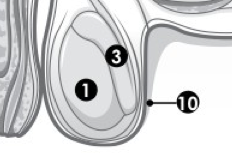
(F) Label 1. |
Ovary. |
|
(F) Label 2. |
Fallopian tube. |
|
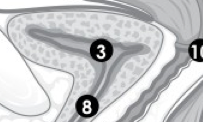
(F) Label 3. |
Bladder. |
|
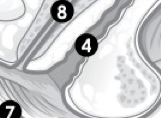
(F) Label 4. |
Vagina. |
|
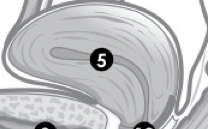
(F) Label 5. |
Uterus. |
|
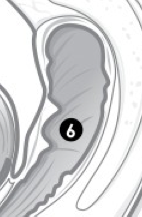
(F) Label 6. |
Rectum. |
|
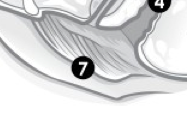
(F) Label 7. |
Vulva. |
|
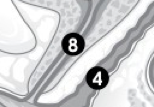
(F) Label 8. |
Urethra. |
|

(F) Label 9. |
Anus. |
|
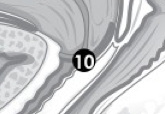
(F) Label 10. |
Cervix. |
|
|
During sexual intercourse the man releases... |
Semen and sperm into the woman's vagina. |
|
|
The ......... cells travel in the semen from the ........ and into the top of the ........... . They enter the ......... through the cervix and travel to the ......... . If a ........ cell meets with an ...... cell there, ................ can happen. Fertilisation happens when an ...... cell meets with a ........ cell and joins with it. |
The sperm cells travel in the semen from the penis and into the top of the vagina. They enter the uterus through the cervix and travel to the uterus. If a sperm cell meets with an egg cell there, fertilisation can happen. Fertilisation happens when an egg cell meets with a sperm cell and joins with it. |
|
|
When an egg is fertilised it will contain... |
Half of the man's genetic material and half of the woman's genetic material. |
|
|
The egg, when fertilised, divides to form a ball of cells called a(n) ......... . This attaches to the lining of the ......... and begins to develop into a ......... . After ....... months, the baby is ready to be born. The ......... relaxes and muscles in the wall of the ......... contract, pushing the ....... out of the mother's body. |
The egg, when fertilised, divides to form a ball of cells called an embryo. This attaches to the lining of the uterus and begins to develop into a foetus. After nine months, the baby is ready to be born. The cervix relaxes and muscles in the wall of the uterus contract, pushing the baby out of the mother's body. |

