![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
96 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What elements are found in carbohydrates |
Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen |
|
|
What monomers are lactose, maltose and sucrose made of? |
Monosaccharides (They are disaccharides) |
|
|
What monomers are lactose, maltose and sucrose? |
Disaccharides |
|
|
What is a single carbohydrate molecule known as? |
Monosaccharides |
|
|
There are two forms of glucose. What are they and how are they different? |
Alpha glucose and Beta glucose • Differ in position of the H and OH groups on carbon-1 |
|
|
There are two forms of glucose. What are they and how are they different? |
Alpha glucose and Beta glucose • Differ in position of the H and OH groups on carbon-1 |
|
|
Name 3 polysaccharides |
Cellulose, starch and glycogen |
|
|
There are two forms of glucose. What are they and how are they different? |
Alpha glucose and Beta glucose • Differ in position of the H and OH groups on carbon-1 |
|
|
Name 3 polysaccharides |
Cellulose, starch and glycogen |
|
|
What type of glucose is cellulose made from? |
Beta glucose |
|
|
There are two forms of glucose. What are they and how are they different? |
Alpha glucose and Beta glucose • Differ in position of the H and OH groups on carbon-1 |
|
|
Name 3 polysaccharides |
Cellulose, starch and glycogen |
|
|
What type of glucose is cellulose made from? |
Beta glucose |
|
|
What type of glucose is starch made from? |
Alpha glucose |
|
|
There are two forms of glucose. What are they and how are they different? |
Alpha glucose and Beta glucose • Differ in position of the H and OH groups on carbon-1 |
|
|
Name 3 polysaccharides |
Cellulose, starch and glycogen |
|
|
What type of glucose is cellulose made from? |
Beta glucose |
|
|
What type of glucose is starch made from? |
Alpha glucose |
|
|
What type of glucose is glycogen made from? |
Alpha glucose |
|
|
There are two forms of glucose. What are they and how are they different? |
Alpha glucose and Beta glucose • Differ in position of the H and OH groups on carbon-1 |
|
|
Name 3 polysaccharides |
Cellulose, starch and glycogen |
|
|
What type of glucose is cellulose made from? |
Beta glucose |
|
|
What type of glucose is starch made from? |
Alpha glucose |
|
|
What type of glucose is glycogen made from? |
Alpha glucose |
|
|
What is the generic formula for a monosaccharide? |
C6 H12 O6 |
|
|
There are two forms of glucose. What are they and how are they different? |
Alpha glucose and Beta glucose • Differ in position of the H and OH groups on carbon-1 |
|
|
Name 3 polysaccharides |
Cellulose, starch and glycogen |
|
|
What type of glucose is cellulose made from? |
Beta glucose |
|
|
What type of glucose is starch made from? |
Alpha glucose |
|
|
What type of glucose is glycogen made from? |
Alpha glucose |
|
|
What is the generic formula for a monosaccharide? |
C6 H12 O6 |
|
|
Name 3 monosaccharides |
Glucose, fructose and galactose |
|
|
There are two forms of glucose. What are they and how are they different? |
Alpha glucose and Beta glucose • Differ in position of the H and OH groups on carbon-1 |
|
|
Name 3 polysaccharides |
Cellulose, starch and glycogen |
|
|
What type of glucose is cellulose made from? |
Beta glucose |
|
|
What type of glucose is starch made from? |
Alpha glucose |
|
|
What type of glucose is glycogen made from? |
Alpha glucose |
|
|
What is the generic formula for a monosaccharide? |
C6 H12 O6 |
|
|
Name 3 monosaccharides |
Glucose, fructose and galactose |
|
|
Cellulose Where is it found? What is its function? |
Plant cells What cell walls are made from |
|
|
There are two forms of glucose. What are they and how are they different? |
Alpha glucose and Beta glucose • Differ in position of the H and OH groups on carbon-1 |
|
|
Name 3 polysaccharides |
Cellulose, starch and glycogen |
|
|
What type of glucose is cellulose made from? |
Beta glucose |
|
|
What type of glucose is starch made from? |
Alpha glucose |
|
|
What type of glucose is glycogen made from? |
Alpha glucose |
|
|
What is the generic formula for a monosaccharide? |
C6 H12 O6 |
|
|
Name 3 monosaccharides |
Glucose, fructose and galactose |
|
|
Cellulose Where is it found? What is its function? |
Plant cells What cell walls are made from |
|
|
Starch Where is it found? What is its function? |
Plants Storage molecule |
|
|
There are two forms of glucose. What are they and how are they different? |
Alpha glucose and Beta glucose • Differ in position of the H and OH groups on carbon-1 |
|
|
Name 3 polysaccharides |
Cellulose, starch and glycogen |
|
|
What type of glucose is cellulose made from? |
Beta glucose |
|
|
What type of glucose is starch made from? |
Alpha glucose |
|
|
What type of glucose is glycogen made from? |
Alpha glucose |
|
|
What is the generic formula for a monosaccharide? |
C6 H12 O6 |
|
|
Name 3 monosaccharides |
Glucose, fructose and galactose |
|
|
Cellulose Where is it found? What is its function? |
Plant cells What cell walls are made from |
|
|
Starch Where is it found? What is its function? |
Plants Storage molecule |
|
|
Glycogen Where is it found? What is its function? |
Animals Storage molecule |
|
|
Draw a detailed diagram to show the gross structure of the human digestive system |
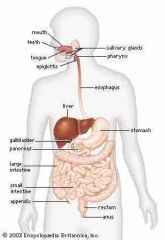
|
|
|
Three types of carbohydrates |
Glucose, fructose and galactose |
|
|
Three types of carbohydrates |
Glucose, fructose and galactose |
|
|
Monomer units which carbohydrates are composed? |
Monosaccharides |
|
|
Three types of carbohydrates |
Glucose, fructose and galactose |
|
|
Monomer units which carbohydrates are composed? |
Monosaccharides |
|
|
Draw the structure of alpha glucose |
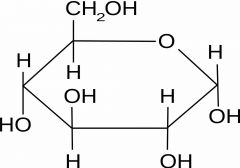
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Three types of carbohydrates |
Glucose, fructose and galactose |
|
|
Monomer units which carbohydrates are composed? |
Monosaccharides |
|
|
Draw the structure of alpha glucose |
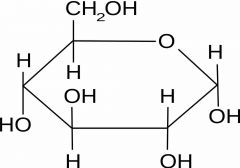
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Draw a basic structure of beta glucose |
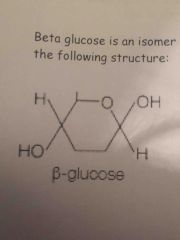
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Three types of carbohydrates |
Glucose, fructose and galactose |
|
|
Give the chemical equation for a hydrolysis reaction |
C12H22011 + H2O ---> C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 |
|
|
Draw the structure of alpha glucose |
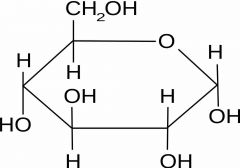
|
|
|
Draw a basic structure of beta glucose |
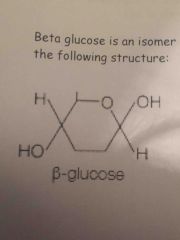
|
|
|
Draw the basic structure of alpha glucose |
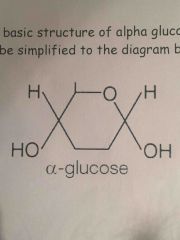
|
|
|
Draw the structure of beta glucose |

|
|
|
Draw a diagram to show how two alpha glucose are joined by a condensation reaction |
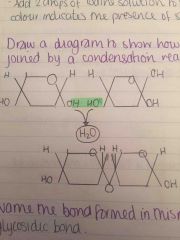
|
|
|
Draw the structure of fructose |
|
|
|
Structure of cellulose |
•Beta glucose molecules join together through condensation reactions to form long straight chains • every other beta glucose molecules rotates 180 degrees to allow OH groups on carbon 1 and 4 to be adjacent to each other to form a glycosidic bond •several chains of cellulose are joined together in layers; these chains are held together by the formation of hydrogen bonds formed between OH groups •Hundreds of these chains are then held together by hydrogen bonds to form microfibrils •microfibrils form hydrogen bonds between other microfibrils and together form a cellulose fibre •cellulose fibres are woven to form cellulose cell wall •the large numbers of hydrogen bonds in the structure makes it extremely strong |
|
|
Structure of starch |
•Important characteristic of starch = insoluble -does it affect osmosis (presence of starch on solution will not lower water potential causing unwanted movement of water) -does not diffuse
Starch comes in two forms Amylase and Amylopectin |
|
|
Amylose |
•Long and straight chains of alpha glucose which coil into a helix •Carbon 1:4 •this structure is compact so is good for storage |
|
|
Monomer units which carbohydrates are composed? |
Monosaccharides |
|
|
Amylopectin |
•Branched chain of alpha glucose molecules •Carbon 1:4 and carbon 1:6 links •This provides a large surface area for rapid hydrolysis of enzymes |
|
|
Structure of glycogen |
Similar to starch however: -storter chains -more highly branched -larger surface area
•stored in muscles and liver •more short chains lead to glycogen being more readily hydrolysed into glucose •Like starch, glycogen is insoluble so does so does not affect water potential or diffuse out of cells |
|
|
Test for carbohydrates Reducing sugar |
1. Add Benedicts solution to sample 2. Heat to 95 degrees (C) 3. Colour change: blue--> green/yellow/orange/red (presence of reducing sugar) 4.No change = there could be a non-reducing sugar present |
|
|
Draw the structure of galactose |
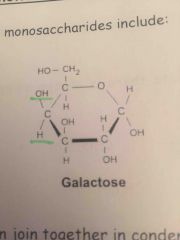
|
|
|
Draw the structure of fructose |
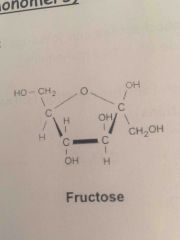
|
|
|
Give the name of a non-reducing sugat |
Sucrose |
|
|
Draw the structure of alpha glucose |
|
|
|
Draw a basic structure of beta glucose |
|
|
|
Draw the basic structure of alpha glucose |
|
|
|
Draw the structure of beta glucose |
|
|
|
Draw a diagram to show how two alpha glucose are joined by a condensation reaction |
|
|
|
What happens during a condensation reaction? |
•two monosaccharides join together. This forms a disaccharide •the reaction occurs between the OH groups on carbon 4 of one of the monosaccharide and carbon 1 on the other monosaccharides •the reaction produces one molecule of H2O •the bond which forms between the two monosaccharides is called a glycosidic bond |
|
|
What is molecule is produced in a condensation reaction? |
H2O |
|
|
Chemical equation for a condensation reaction |
C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 ----> C12H22O11 + H2O |

