![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
99 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Selective Permeability
|
Some things cross membrane easier than others
|
|
|
Amphipathic
|
Both hydrophilic and hydrophobic
|
|
|
Fluid Mosaic Model
|
Membrane is fluid with proteins throughout
|
|
|
Phospholipids movement
|
Move laterally
Rarely flip-flop |
|
|
Cool temperature membranes
|
Turn solid
|
|
|
Membranes need to work properly
|
Need to be fluid
|
|
|
Unsaturated fatty acids
|
More fluid
|
|
|
Saturated fatty acids
|
Less fluid
|
|
|
Cholesterol
|
Steroid that helps regulate fluidity
|
|
|
Peripheral proteins
|
Bound to membrane
|
|
|
Integral Proteins
|
Penetrate the membrane
|
|
|
Transmembrane proteins
|
Span across the membrane
|
|
|
Permeability of lipids and sugars
|
Lipids are hydrophobic and cross easily
Sugars are hydrophilic and don't cross easily |
|
|
Channel Proteins
|
Transport proteins with hydrophilic channel
|
|
|
Aquaporins
|
Channel proteins for water
|
|
|
Carrier protein
|
Transport proteins bind to molecules, change shape, and ship across the membrane
|
|
|
Diffusion
|
Wants to move to available space
|
|
|
Concentration Gradient
|
Move from higher to lower concentration
No energy needed |
|
|
Osmosis
|
Diffusion of water
Lower to higher concentration |
|
|
Tonicity
|
Ability to lose or gain water
|
|
|
Isotonic
|
Even solute concentration
|
|
|
Hypertonic
|
Cell loses water
Higher concentration than inside cell |
|
|
Hypotonic
|
Lower concentration inside the cell
Cell gains water |
|
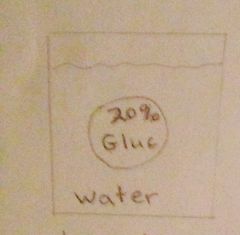
1. Tonicity?
2. Out of cell? 3. Into cell? 4. Water movement? |
Hypotonic
Glucose out of cell Water moves into cell |
|

1. Tonicity?
2. Out of cell? 3. Into cell? 4. Water movement? |
Hypertonic
Water moves out of the cell |
|
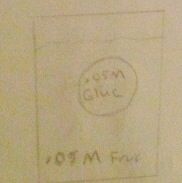
1. Tonicity?
2. Out of cell? 3. Into cell? 4. Water movement? |
Isotonic
Glucose moves out Fructose moves in |
|
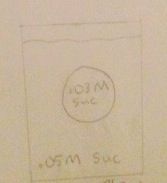
1. Tonicity?
2. Out of cell? 3. Into cell? 4. Water movement? |
Hypertonic
Water moves out of cell |
|
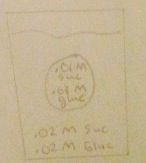
1. Tonicity?
2. Out of cell? 3. Into cell? 4. Water movement? |
Isotonic
Glucose moves out of cell |
|
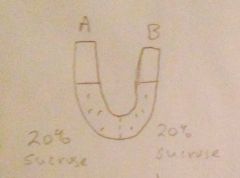
Tonicity of side A?
Water movement? |
Isotonic water doesnt move
|
|
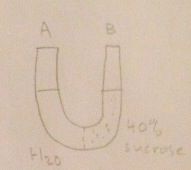
Tonicity of side A?
Water Movement? |
Hypotonic
A-B |
|
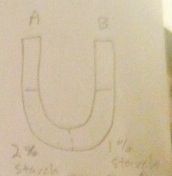
Tonicity of side A?
Water Movement? |
Hypertonic
B-A |
|
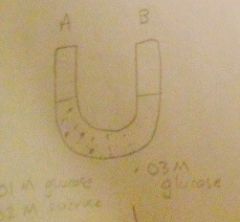
Tonicity of side A?
Water Movement? |
Isotonic
Equal |
|
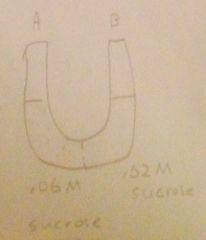
Tonicity of side A?
Water Movement? |
Hypertonic
B-A |
|
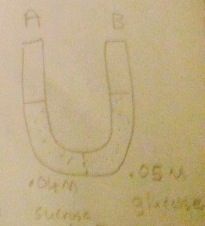
Tonicity of side A?
Water Movement? |
Hypotonic
A-B |
|
|
Osmoregulation
|
Control of water balance
|
|
|
If animal cell gains too much water
|
It bursts
|
|
|
If animal cell loses too much water
|
Shrivels up
|
|
|
If plant cell gains too much water
|
Normal, turgid
|
|
|
If plant cell is isotonic
|
It is flaccid
|
|
|
If plant cell loses too much water
|
Plasmolysis
|
|
|
Plasmolysis
|
Membrane go's away from cell wall
Results in death of plant |
|
|
Facilitated diffusion
|
Speeds the movement of molecules across membrane
|
|
|
Active transport
|
Moves against concentration gradient
Needs energy |
|
|
Bulk transport
|
Uses vesicles to go through membrane
Needs energy |
|
|
Exocytosis
|
Vesicles bind to membrane and release contents inside
|
|
|
Types of endocytosis
|
Phagocytosis
Pinocytosis Receptor mediated |
|
|
Endocytosis function
|
Forms vesicles from the membrane
|
|
|
Phagocytosis
|
Engulfs particles in a vacuole
Vacuole goes to lysosome to digest |
|
|
Pinocytosis
|
Extracellular fluid is taken in to create vesicles
|
|
|
How to set up Net Reaction
A ➡️ B ➡️ C ➡️ D |
Line them up and cancel out duplicates
A ➡️ B Cancel out B and C B ➡️ C Left with A ➡️ D C ➡️ D |
|
|
Catabolism
|
Metabolic pathway that releases energy
|
|
|
Anabolic
|
Metabolic pathway that absorbs energy
|
|
|
Kinetic Energy
|
Energy with movement
|
|
|
Potential energy
|
Energy based on structure or location
|
|
|
Regeneration of ATP
|
ATP + Water = ADP
ADP + Phosphate =ATP |
|
|
Enzymes end in
|
-ase
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Speed up reaction
|
|
|
Denaturation
|
Protein unfolds
|
|
|
Denaturation needs
|
Heat, acid, or salt
|
|
|
Cycle of Enzyme
|
1. Enzyme takes in substrate
2. Add water to break bond 3. Release products |
|
|
Active site
|
Where substrates enter enzyme
|
|
|
Enzyme substrate complex
|
Before water is added
|
|
|
Eā
|
Energy needed for reaction
|
|
|
Enzymes and Eā
|
Enzymes lower the Eā, which speeds reaction
|
|
|
Relocating electrons
|
Energy is released
That energy is used to make ATP |
|
|
Oxidation and Reduction
|
LEO the lion says GER
Lose electron oxidation Gain electron reduction |
|
|
How does NAD+ turn to NAPH
|
Reduction
|
|
|
How does NADH turn to NAP+
|
Oxidation
|
|
|
Cofactors
|
Nonprotein that binds to enzyme
Necessary for activity |
|
|
Coenzymes
|
Organic cofactors
|
|
|
H+
|
Hydronium ion
Proton |
|
|
Acid
|
Below 7 pH
Increases H+ |
|
|
Base
|
Decreases H+
Higher than 7 pH |
|
|
pH
|
Each number category is 10x the next
|
|
|
Net Balanced Equation
|
Glucose + 6 Oxygen = Carbon Dioxide oxygen and energy evened up
C6 H12 O6 + 6(O2) = 6(CO2) + 6(H2O) + energy |
|
|
Six major functions of a protein
|
1. Transport
2. Enzymatic 3. Cell - Cell Recognition 4. Signal Transduction 5. Intercellular joining 6. Attachment |
|
|
Transport
|
Transports molecules across the membrane
|
|
|
Enzymatic
|
Enzymes are located in the membrane
|
|
|
Signal transduction
|
Signaling molecule bonds to outside
Protein changes shape and releases something |
|
|
Intercellular joining
|
Forms cytoplasmic connection between cells
|
|
|
Cell - Cell Recognition
|
Glycoproteins determine wether or not it is self or foreign
|
|
|
Attachment
|
Attaches to cytoskeleton (outside) and ECM (inside)
To maintain shape or transmit pressure signals |
|
|
Cell Cycle
|
Interphase
Mitosis Cytokinesis |
|
|
PMAT
|
Prophase
Metaphase Anaphase Telophase |
|
|
Interphase
|
90% of cell cycle
G1 S G2 |
|
|
G1
|
Cytoplasm grows and new organelles are made
|
|
|
S
|
DNA Replicates
|
|
|
G2
|
Prepares for nuclear division and cytoplasm grows more
|
|
|
Chromatin
|
Thin and stringy
In this form during interphase |
|
|
Centromere
|
Where sister chromatids are attached
|
|
|
Kinetochore
|
Where microtubules attach to centromere
|
|
|
Prophase
|
Sister chromatids condense
Nucleoli and membrane disappear Spindle forms Centrioles move to opposite poles in animal cells |
|
|
Metaphase
|
Sister chromatids line up in middle
Spindle fibers attach |
|
|
Anaphase
|
Seperate into daughter cells
Move toward opposite poles |
|
|
Telophase
|
Chromosomes relax and go back to chromatin
Nucleus and Nucleoli reform Spindle disappears |
|
|
Cytokinesis
|
Division of Cytoplasm
|
|
|
Cytokinesis in plants
|
Cell plate forms
|
|
|
Cytokinesis in animals
|
Cleavage
|
|
|
Functions of cell cycle
|
Growth
Tissue Renewal Asexual Reproduction |

