![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How is DNA stored in eukaryotic cells? |
• It contains linear DNA molecules that exist as chromosomes, each made up of one long molecule of DNA and its associated proteins. • Because it's really long it has to be wrapped around a protein called histones. The DNA is then coiled very tightly to make a compact chromosomes. |
|
|
How is DNA stored in a prokaryotic cell? |
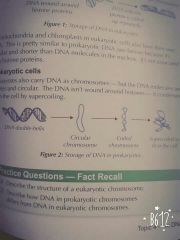
• They carry DNA as chromosomes - but DNA molecules are shorter and circular. •DNA condenses to fit in the cell by supercoiling. |
|
|
What is a gene? |
A gene is a base sequence of DNA that codes for the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide or a functional RNA (including ribosomal RNA and tRNAs). |
|
|
How is each amino acid coded for? |
It is coded for by a sequence of three bases in a gene called a triplet or codon. |
|
|
What is a genome and a proteome? |
• Genome - Complete set of genes in a cell. • Proteome - Full range of proteins that a cell is able to produce. |
|
|
What are introns? What are exons? |
• Introns - It is a section of DNA within a gene that does not code for amino acids. • Exons - It is a section of DNA within a gene that does code for amino acids. |
|
|
Which DNA has introns? |
Eukaryotic only. |
|
|
What are non-coding multiple repeats? |
They are codes that just repeat over and over again and aren't relevant. |
|
|
What is an allele? |
It is a different form of gene. The order of bases are different so they code for different types of the same polypeptide. |
|
|
What are homologous pairs? |

• They are pairs of matching chromosomes. They are the same size and have the same genes but may have different alleles. • Alleles coding for the same characteristic will be found in the same position. |
|
|
What two main stages does polypeptide synthesis involve? |
• Transcription - where the DNA code is coped into a molecule called mRNA. • Translation - where the mRNA joins with an organelle called a ribosome and the code it carries is used to synthesise a protein. |
|
|
How is mRNA involved in protein synthesis? |
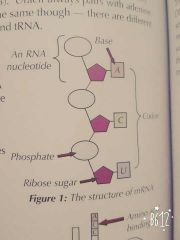
• mRNA is made during transcription. • It carries the genetic code from the DNA to the ribosomes, where it's used to make a protein during translation. • mRNA is a single polynucleotide. • In mRNA, groups of three adjacent bases are usually called codons. |
|
|
How is TRNA involved in protein synthesis? |
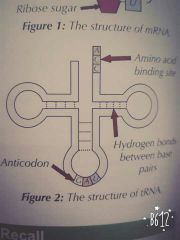
• It is involved in translation. • It carries amino acids that are used to make proteins to the ribosomes. • tRNA is a single polynucleotide strand that's folded in a clover shape. Hydrogen bonds between specific base pairs hold the molecule in shape. • Each tRNA molecule has a specific sequence of three bases at one end called an anticodon. It also has another amino acid binding sites at the other end. |
|
|
What is transcription and how does it work? |
• It is the production of mRNA from DNA. • RNA polymerase attaches to the DNA - the RNA polymerase attaches to the double-helix at the beginning of the gene. The hydrogen bonds between the two DNA strands break, separating the strands, and the DNA molecule uncoils. One of the strands is used as a template to make an RNA copy. • Complementary mRNA is formed - The RNA polymerase lines up free RNA nucleotides alongside the exposed bases on the template strand. The free bases are attracted to the exposed bases. The mRNA strand becomes a complementary copy of the DNA template strand. They are the joined together by RNA polymerase. • RNA polymerase moves down the DNA strands - RNA polymerase moves along the DNA, separating the strands and assembling the RNA strand. The hydrogen bonds between the uncoiled strands of DNA re-form once the RNA polymerase has passed by and the strands coil back into a double-helix. • RNA polymerase reaches stop signal - When RNA polymerase reaches a particular sequence of DNA called a stop signal, it stops making RNA and detaches from the DNA. In eukaryotes, the MRNA goes the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome and translation happens. |
|
|
What is different about eukaryotes in terms of mRNA being produced. |
After transcription happens, the mRNA strands have introns and exons in them so they are pre-mRNA. A process called splicing occurs that changes it into mRNA. |
|
|
What is translation and how does it work? |
• It is the production of polypeptides from the sequence of codons carried by mRNA. • Takes place in the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. • The mRNA attaches itself to a ribosome and tRNA molecules carry amino acids to it. ATP provides the energy needed for the bond between the amino acid and the TRNA to form. • A tRNA molecule, with an anticodon that's complementary to the first codon attaches itself to the mRNA by complementary bases pairing. A second tRNA molecule attaches itself to the next codon. • The amino acids are attached to the tRNA molecule is joined by a peptide bond. The first tRNA molecule moves away, leaving its amino acid behind. • This carries on until there's a stop signal. |
|
|
What is non-overlapping? |
Each base is part of one triplet. Every base triplet is separate from the triplet before it and after it. |
|
|
What is the meaning of degenerate? |
There is more than one base triplet. There are more possible combination of triplets than there are amino acids. |
|
|
What is the meaning of universal? |
The same specific base triplets code for the same amino acids in all living things. |

