![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

Hypertonic
|
high solute, low water. Water leaves cell. cell shrivels
|
|
|
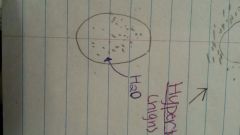
Hypotonic
|
low solute, high water. Water enters. cell swells/burst.
|
|
|

Isotonic
|
Equal solutes in and out. Water moves in and out. cell stays the same. is at equilibrium
|
|
|
|
Passive transport
|
does not require energy
|
|
|
|
Diffusion
|
Movement of molecules from high to low concentration
|
|
|
|
Osmosis
|
Movement of water from low solute concentration to high solute concentration
|
|
|
|
Equilibrium
|
balanced by opposing forces
|
|
|
|
homeostasis
|
Stable internal conditions
|
body temperature, heart rate, blood pressure / sugar
|
|
|
Facilitated diffusion
|
Movement from high to low through protein channel
|
|
|
|
Active transport
|
Requires energy moves from low to high
|
|
|

Endocytosis
|
Cell engulfs large particles by folding its membranes
|
For things too big to fit through membrane
|
|
|
Exocytosis
|
cell gets rid of waste
|
|
|
|
Prokaryote
|
contains no nucleus. Does not have structure surrounded by membranes. few internal structures. One celled organisms
|
Bacteria
|
|
|
Eukaryotic
|
Have a true nucleus surrounded by a membrane. Contains organelles surrounded by membranes. Most living organisms.
|
|
|
|
Levels of organization multicellular organisms
|
Cells. Tissue. Organs. Organ system. Organism.
|
|
|
|
Cancer
|
Uncontrolled division of cells.
|
|
|
|
Semi permeable
|
Only allows certain things inside
|
|
|
|
Anaerobic
|
doesn't require oxygen
|
|
|
|
Aerobic
|
Requires oxygen
|
|
|
|
Semi conservative model of DNA replication
|
half old, half new
|
|
|
|
interphase
|
Division and replication of cells
|
|
|
|
mitosis
|
Four phases prophase metaphase anaphase telophase and cytokinesis
|
|
|
|
G2
|
Step before cell division: preparation
|
|
|
|
Prophase
|
First stage of mitosis. Nucleus disappears, chromosomes appear spindle and centrioles
|
|
|
|
Metaphase
|
Second stage of mitosis
|
|
|
|
Anaphase
|
two separate chromatids
|
|
|
|
Telophase
|
Nuclei reappear. Cells begin to separate.
|
|
|
|
Cytokinesis
|
Two separate daughter cells.
|
|

