![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
189 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
**
Most of the mass of wood came from... |
Carbon dioxide in air
|
|
|
**
(T/F) Plants need Oxygen to survive |
True
|
|
|
*
What are Vegetative Advances? |
Part of plants that are non-reproductive
|
|
|
*
Different modes of cytokinesis amongst Plantae |
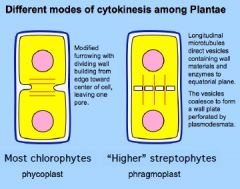
Phycoplast
-cell plate with one pore Phragmoplast -cell plate w/ plasmodesmata |
|
|
*
What is a disadvantage of having a plasmodesmata? |
viruses can move from cell to cell and infect entire plant
|
|
|
*
Apical Growth |
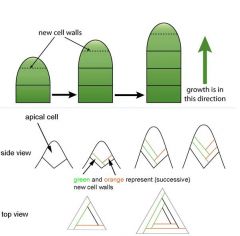
Growth promoted by the apical Meristem region of plants (at the root and shoot tips)
|
|
|
*
Oogamy |
separate egg (large gametes) and sperm (small gametes)
|
|
|
*
Spore |
reproductive cell that is not a gamete
created from zygote going under meiosis undergoes mitosis to make multicellular haploid organism |
|
|
*****
Alternation in Generation |
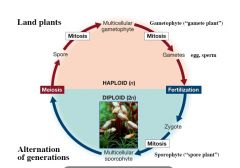
alternates between two multicellular generation (haploid v diploid)
gametophyte is produced by mitosis and cytokinesis of a spore spores are haploid gametophytes produce gametes by mitosis |
|
|
*
3 Possibilities of Eukaryotic Sexual Life Cycle |
Alternation in Generation
Unicellular haploid/Multicellular diploid Multicellular haploid/Unicellular diploid |
|
|
*
Angiosperms |
Flowering Plants
|
|
|
*
Bryophytes are also called... |
non-vascular plants
|
|
|
*
Are Bryophytes a monophyletic group? |
no
Paraphyletic |
|
|
*
Embryophytes are also called... |
Land Plants
|
|
|
*
Cuticle |
waxy layer that covers entire organism
keeps it from drying out |
|
|
*
Rhizoids |
Root-like filament of gametophyte
Anchors self to substrate & absorbs nutrients |
|
|
*
Mycorrhizae |
mutual symbiosis with fungi and rhizoid
mycorr = fungus rhizae = root |
|
|
*
Stomata |
open pores--plant can control
-surrounded by guard cells only in diploid life cycle typically underside of leaves gas exchange--Co2 in, O2 out only happen through diffusion--relatively small |
|
|
**
Which statement about adaptations to plant life on land is true? a. cuticle was one of the last features to appear b. first land plants appeared less than 300MYA c. land plants have thin spore walls d. all plants develop from embryos |
d. all plants develop from embryos
|
|
|
*
Tracheophytes are also called... |
Vascular Plants
|
|
|
*
Xylem |
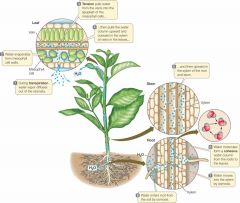
Material: water & minerals
Direction: Roots to Leaves -1 direction Pressure: Negative -as water evaporates out, causes negative pressure -water: H-bonding makes it cohesive *doesn't use metabolic energy--mainly sunlight *xylem cells are dead, otherwise negative pressure would cause the cell membranes to collapse |
|
|
*
Phloem |
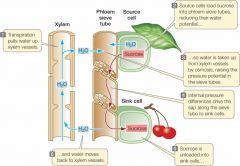
Material: Assimilates
Direction: Source to Sink -Can change Pressure: Positive *uses metabolic energy--actively put sugars into phloem, water goes in |
|
|
*
Xylem: Tracheids |
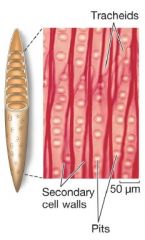
last step of development: death
-cell walls remain pits let water move freely from cell to cell |
|
|
*
Xylem: Vessel Elements |
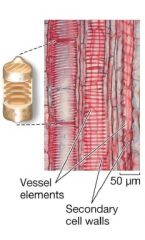
|
|
|
*
Phloem: Sieve Tube Elements |
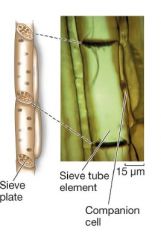
Companion cell
-occurs at its last division -has nucleus, unlike the sieve tube |
|
|
**
Developing wine grapes would be an example of a: (Source/Sink) |
Sink
Source: leaves |
|
|
**
(T/F) Vascular Plants have branching, independent sporophytes |
True
|
|
|
*
Homospory |
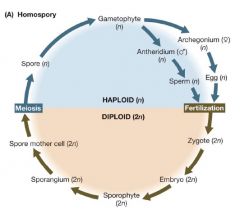
|
|
|
*
Heterospory |
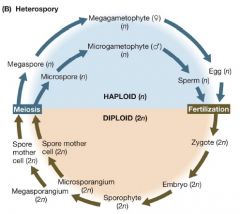
|
|
|
**
Evidence for ferns, whisk ferns and horsetails all belonging to the clade that includes seed plants include |
Presence of chloroplast DNA inversion
|
|
|
*
(T/F) Seed Plants are Monophyletic |
True
|
|
|
*
gymnosperm means... |
Naked Seed
|
|
|
*
Explain how secondary xylem & phloem works. |
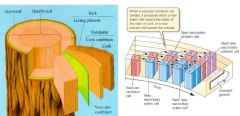
Primary growth
-grows taller Secondary Growth -grows wider in, out, in, out Xylem inside Phloem outside stem has to get thicker |
|
|
*
(T/F) Secondary Xylem is wood |
True
|
|
|
*
What consists of the bark? |
Vascular cambium and on outwards (eg. contains phloem)
does not include xylem |
|
|
*
What is Seed Dormancy? |
period of suspended developmental activity
Maintained by: •exclusion of water or oxygen •mechanical restraint •chemical/hormonal factors |
|
|
**
A major advance/feature that evolved in the seed plants is... |
water is no longer directly required for fertilization
-sperm can be delivered directly to egg |
|
|
**
The innermost structure in a seed is... |
sporophyte
|
|
|
*
(T/F) Vessels only occur in gnetophytes and angiosperms |
true
|
|
|
**
The presence of vessel elements in both Gnetophytes and flowering is an example of... |
convergent evolution
|
|
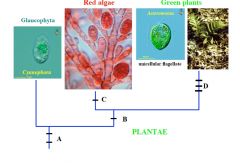
A
|
Two Flagella
Endosymbiosis with Cyanobacterium (Chlorophyll A, Phycobilins, Peptidoglycan in Cyanophora Wall) Cellulose Cell Wall |
|
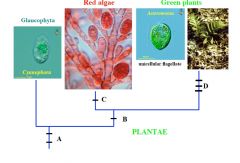
B
|
Loss of peptidoglycan
|
|
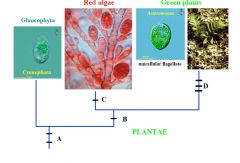
C
|
Loss of Flagella
|
|
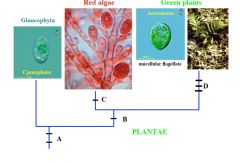
D
|
Chlorophyll B
Loss of Phycobilins Starch stored in Chloroplast |
|
A
|
Filaments
|
|
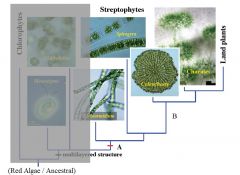
B
|
Oogamy
Branched Filaments Apical Growth Phragmoplast, Plasmodesmata |
|
|
*
(T/F) Even if fossils don't affect inferred molecular relationships among living groups, they can show intermediate morphologies and the order of origin of synapomorphies |
True
|
|
|
*
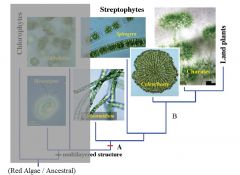
What groups does Streptophytes include? |
Non-Chlorophyte Green Algae
Coleochaetales Charales Land Plants |
|
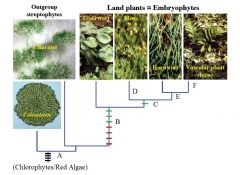
A
|
Phragmoplast
Branched Filaments Apical Growth Oogamy |
|
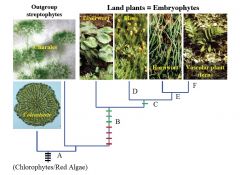
B
|
VEGETATIVE
-Cuticle -Rhizoids -Mycorrhizae REPRODUCTIVE -Alternation of Generation: Origin of Sporophyte -Antheridia & Archegonia -Sporangia -Air-Dispersed Spores |
|
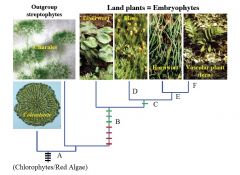
C
|
Stomata
|
|
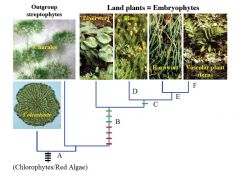
D
|
Leaves on Gametophyte
|
|
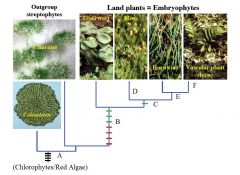
E
|
Green Sporophyte
|
|
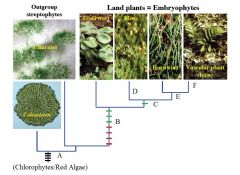
F
|
Branched Sporophyte
Vascular Tissue |
|
|
*
Antheridia |
A sperm-producing organ occurring in seedless plants, fungi, and algae.
|
|
|
*
Archegonia |
A multicellular, often flask-shaped, egg-producing organ occurring in mosses, ferns, and most gymnosperms.
|
|
|
*
What are Jacket Cells? |
vegetative
protects the gametes against desiccation in the terrestrial environment. |
|
|
*
How do air-dispersed spores survive? |
Spore Tetrad
-4 spores stuck together Surrounded by Sporopollenin -protects from dry air |
|
|
*
Compare Rhyniophyte & Typical Angiosperm |
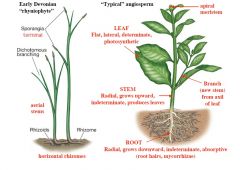
|
|
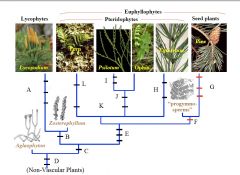
A
|
Roots
Axillary Sporangia Microphylls |
|
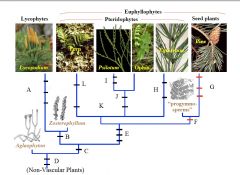
B
|
Lateral Sporangia
|
|
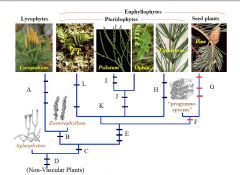
C
|
Typical Tracheids
|
|
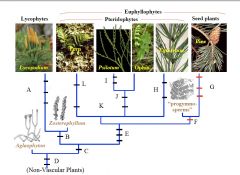
D
|
Branched Sporophyte
Vascular Tissue |
|
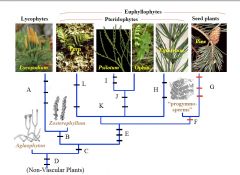
E
|
Multiflagellate Sperm
Chlorplast DNA Inversion Overtopping (Leaves derived from branches) Roots |
|
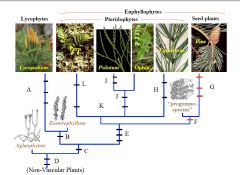
F
|
Secondary Growth
-Secondary Xylem, Phloem, periderm |
|
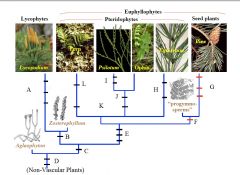
G
|
Axillary Branching
Seeds Compound Leaves |
|
|
*
Genes in the DNA are ___ into mRNA and ___ into proteins |
transcribed
translated |
|
|
*
(T/F) Genes are expressed in specific places where required |
True
|
|
|
*
Genes for Leaf Development |
KNOX genes
-expressed at the tips of stems -promote indeterminate growth ARP genes -expressed in leaves -turn off KNOX -promote determinate leaf growth Same genes used in independently evolved leaves |
|
|
*
(T/F) "Advanced streptophytes" evolved fundamental cellular functions common to all plants |
True
EX: Chlorophyll A, Phagmoplast |
|
|
*
(T/F) “Advanced streptophytes” had a haploid life cycle that was modified in land plants to include both diploid and haploid multicellular stages. |
True
ALTERATION OF GENERATION |
|
|
*
(T/F) Land plants evolved features associated with survival and reproduction in the aerial environment |
True
EX: Cuticle, Stomata |
|
|
*
(T/F) Evolution of land plants saw progressive reduction of the gametophyte generation and increasing dominence of the sporophyte generation. |
True
|
|
|
*
(T/F) Charles Darwin found Apical Perception. Frits Went found Sub-Apical Response |
True
|
|
|
*
Explain Axillary branching in seed plants |
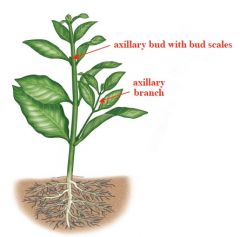
hormone comes from tip that prevents axillary branches
in axials of leaves are dormant meristems -branching occurs here |
|
|
*
(T/F) Cycad seeds have multiflagellated sperm |
True
|
|
|
*
(T/F) Ginkgo have dichotomous veins |
True
|
|
|
*
What is a Bracht? |
Modified Leaf
|
|
|
*
What is a Male Cone? |
Simple strobilus
Stem with sporophylls |
|
|
*
What is a Female Cone? |
Compound strobilus
Stem with leaves, fertile branches |
|
|
*
(T/F) Largest and most diverse clade within the Plantae clade is Angiosperms |
True
|
|
|
*
Angiosperm Life Cycle |
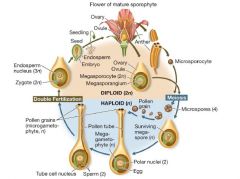
|
|
|
**
In seed plants, the ovule... |
contains female gametophyte
contains female sporoganium when mature is called a seed -- structures that will become seeds contain outer protective coverings called integuments & a megasporangium within the integuments Within the megasporangium, megaspores are produced by meiosis. The megaspores produce megagametophytes, which, in turn, produce eggs. |
|
|
*
(T/F) Angiosperms also mean Vessel Seeds |
True
|
|
|
*
Angiosperms are essential to humans for... |
Food
Clothing and Shelter Medicine |
|
|
*
Carpals and Double Fertilization are one of the key features of... |
Angiosperms
|
|
|
*
Carpals |
female part of the plant which produce fruit once pollination has taken place. The fruit contains seeds
stigma -> top where it gets pollen, style -> pollen travels down, ovary -> where fruit is formed |
|
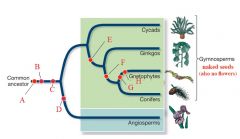
D
|
Flowers
|
|
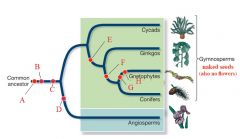
E
|
Simple Leaves
|
|
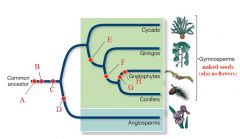
F
|
Nonmotile Sperm
|
|
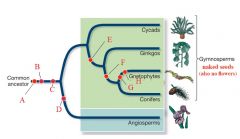
G & H
|
Vessels & Opposite Leaves
|
|
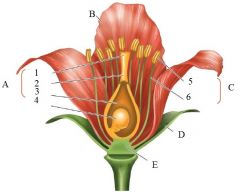
**
A |
Carpals
1. Stigma 2. Style 3. Ovary 4. Ovule |
|
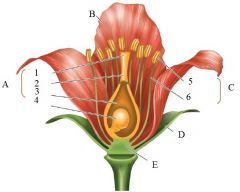
B
|
petal
|
|
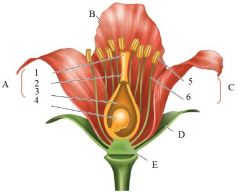
C
|
Stamen
5. Anther 6. Filament |
|
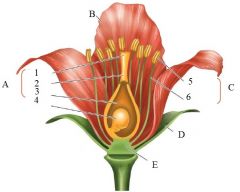
D
|
Sepal
|
|
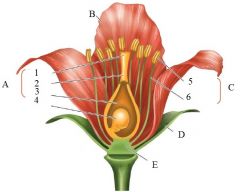
E
|
Receptacle = Floral Axis
|
|
|
*
Sepals + Petals = |
Perianth
|
|
|
*
Carpal and Stamen Evolution |
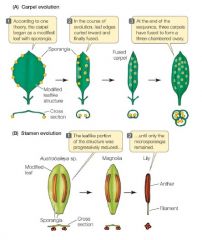
|
|
A
|
Carpels
Endosperm Seeds in Fruit Reduced Gametophytes Double Fertilization Flowers Phloem with Companion Cells |
|
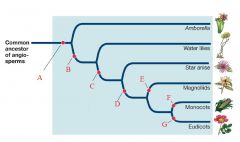
B
|
Transitional Tracheid Vessel Elements
|
|
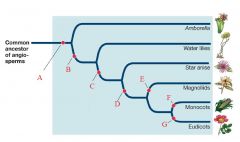
C
|
Vessel Elements
|
|
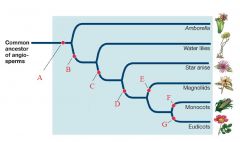
D
|
Carpels fused by tissue connection
|
|
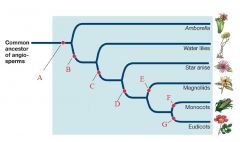
E
|
Perianth of 2 Whorls
|
|
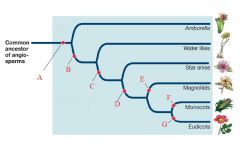
F
|
Single Cotyledon
Loss Secondary Growth Parallel Veins |
|
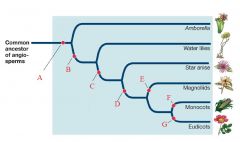
G
|
Pollen with 3 grooves
|
|
|
*
Conifer Tracheids v. Angiosperm Vessels and Fibers |
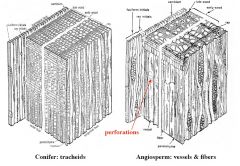
|
|
|
*
Angiosperm Gametophytes |
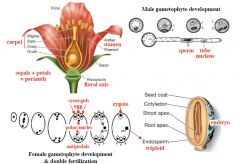
|
|
|
*
(T/F) In angiosperms, the seed comes from the ovule and fruit from the ovary |
True
Ovary is lower portion of the carpal or pistil After fertilization, the ovary enlarges and becomes the fruit |
|
|
*
Angiosperms: Multiple seeds mean that the flower had... |
Multiple ovules
|
|
|
*
Accessory Fruits |
Organs other than ovary contributes to fruit
EX: Strawberry -Ea "seed" is a fruitlet, complete with mature ovary wall |
|
|
**
Double fertilization refers to the process in angiosperms whereby... |
1st sperm nucleus unites with the egg to form the 2N zygote to make EMBRYO.
2nd sperm unites with the two nuclei in embryo sac to make 3N nucleus of the cell from which the ENDOSPERM develops |
|
|
*
Multiple Fruit |
Many Flowers, One Fruit
|
|
|
*
Ethylene |
Promotes fruit ripening
|
|
|
***
Fruits provide important mechanisms of ... |
seed dispersal
|
|
|
*
Monocots v. Eudicots |
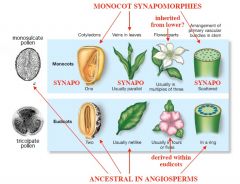
|
|
|
*
Eudicots |
Many have compound leaves
Most have fused petals EX: Rosidae, Asteridae |
|
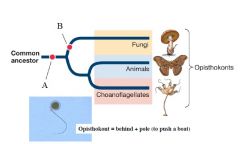
A
|
Flagellum, if present, is single and posterior
|
|
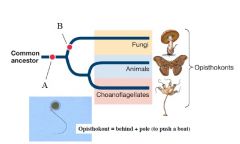
B
|
Absorptive heterotrophy
Chitin in cell walls |
|
|
*
Opposed to plants (producers), fungi--along with animals and bacteria--are... |
consumers and decomposers
(CH2O) + O2 --> CO2 + H2O |
|
|
*
Saprobes |
Live on dead organic matter
|
|
|
**
Fungi have ____ in their cell wall |
chitin
|
|
|
**
Fungi grow by... |
Tip growth of hyphae, which is made up of mycelium
|
|
|
**
Fungi live by... |
Absorptive Heterotrophy
-smaller diameter = higher SA:V to absorb nutrients from the environment |
|
|
**
Dikarya hyphae fungi have... |
septum
-has 2 nuclei -does not have complete cell wall -large pores OPPOSED to Coenocytic hyphae -if chopped, it can close itself off better |
|
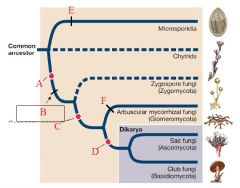
A
|
Plasmogamy precedes karyogamy
|
|
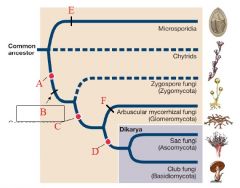
B
|
Loss of motile cells
Terrestrial |
|
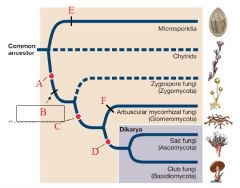
C
|
gene sequences support monophyly
|
|
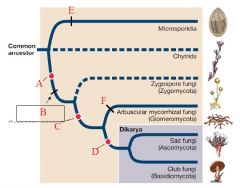
D
|
Dikaryon stage
Septate hyphae |
|
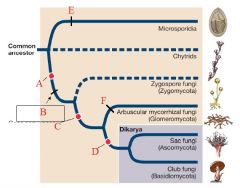
E
|
Loss of motile cells
|
|
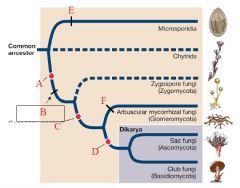
F
|
Form mycorrhizae
|
|
|
*
(T/F) In Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, no sexual life cycle is ever observed |
True
|
|
|
*
Microsporidia |
Intracellular parasites of animals
Greatly reduced, among smallest eukaryotes known Polar tube used to infect hosts |
|
|
*
Chytrids |
PARAPHYLETIC
Mostly aquatic & microscopic Zoospores have flagella Alternation in Generation |
|
|
*
Zygomycota |
Reproductive structure is a unicellular zygospore with many diploid nuclei in a zygosporangium
No regularly occuring septa Usually no fleshy fruiting body |
|
|
*
Glomeromycota |
Form arbuscular mycorrhizae on plant roots
Only asexual reproduction is known |
|
|
*
Ascomycota (Sac Fungi) |
Sexual reproductive saclike structure known as an ascus, which contains haploid ascospores
Perforated septa Dikaryon |
|
|
*
Basidiomycota (Club Fungi) |
Sexual reproductive structure is a basidium, a swollen cell at the tip of a specialized hypha that supports haploid basidiospores
Perforated septa Dikaryon |
|
|
*
Generalized Life Cycle of Dikarya |
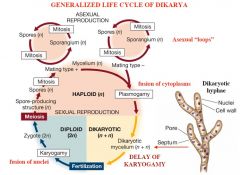
(just notice that there is a dikaryotic cycle)
|
|
|
*
What is Plasmogamy? |
stage in the sexual reproduction of fungi
CYTOPLASM of two parent mycelia fuse together without the fusion of nuclei |
|
|
*
What is Karyogamy? |
fusion of NUCLEI of sperm/egg of two cells during fertilization
|
|
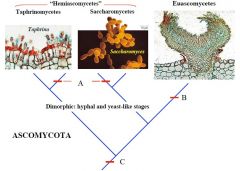
A
|
Yeasts
Secondarily unicellular |
|
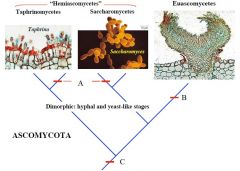
B
|
Ascocarp
|
|
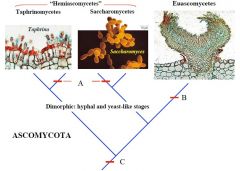
C
|
Ascus
Conidia/Budding? |
|
|
*
Conidia |
asexual spore-producing structures
|
|
|
*
Ergot |
Ascomycete that infects rye
Eating bread made from infected rye causes ergotism (St. Anthony's Fire) -gangrene -hallucinations -miscarriages Source of useful medicines -ergotomine -ergonovine:labor-inducing |
|
|
*
Cordyceps |
Ascomycetes
parasitic on insects |
|
|
*
Arthrobotrys |
euascomycete predator of nematodes
|
|
|
*
Lichens |
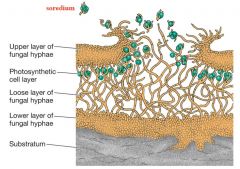
Symbiosis involving a cyanobacterium or alga and a fungus often (not always) an Ascomycete
-crustose -fruiticose -foliose |
|
|
*
Basidiomyocota |
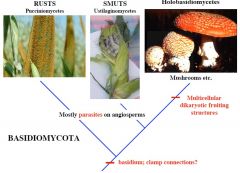
|
|
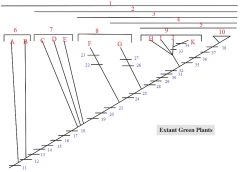
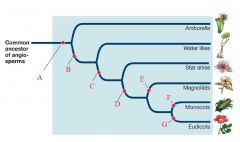
1,2,3,4,5
|
1. Streptophytes
2. Embryophytes 3. Tracheophytes 4. Euphyllophytes 5. Seed Plants |
|
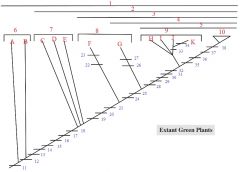
6: A, B
|
6. Charophycean Algae
A: Coleochaete B: Chara |
|
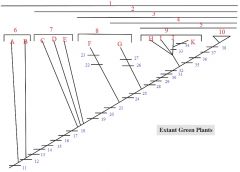
7: C, D, E
|
7. Bryophytes
C: liverworts D: mosses E: hornworts |
|
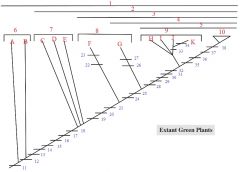
8: F, G
|
8. Seedless Vascular Plants
F: Lycophytes (lycopodium, selaginella) G: monilophytes (ferns, Psilotum, Equisetum) |
|
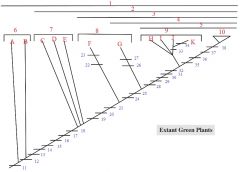
9: H,I,J,K
|
9. Gymnosperms
H: cycads I: Ginkgo J: conifers K: gnetophytes |
|
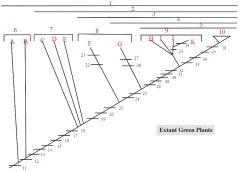
10
|
Angiosperms
|
|
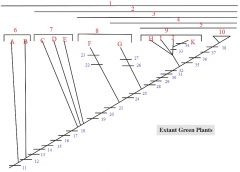
12
|
Apical growth with 1 cutting face
|
|
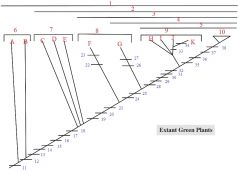
13,14,15,16,17,18
|
13. Apical Cell with 2+ cutting faces
14. Alternation of Heteromorphic Generations 15. Multicellular Embryo 16. Unbranched Sporophyte with Sporangium with Sterile Jacket 17. Multicellular Gametangia with Sterile Jackets 18. Cuticle, Stomates |
|
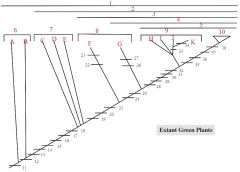
19,20,21
|
19. Tracheids
20. Dominant, branched sporophyte 21. Reduced gametophyte EXTRA: lateral sporangia, vascular tissue |
|
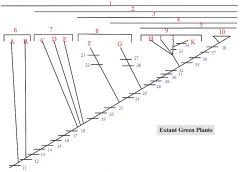
22,23
|
22. Microphylls
23. Heterospory in some |
|
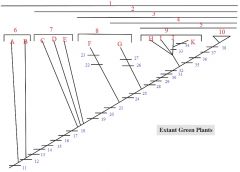
24,25
|
24. Chloroplast DNA inversion
25. Megaphylls (evolved multiple times) EXTRA: Multiflagellate Sperm, Leaves derived from branches, Roots |
|
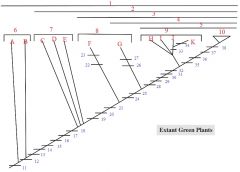
26,27
|
26. Loss of roots in Psilotum
27. Reduced megaphylls in some |
|
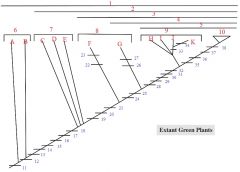
28,29,30,31,32
|
28. Apical meristem
29. Bifacial vascular cambium 30. Heterospory 31. Pollen with pollen tube 32. Integument, ovule, seed |
|
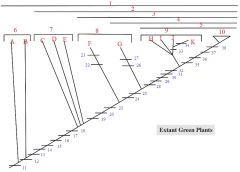
33
|
Loss of Swimming Sperm
|
|
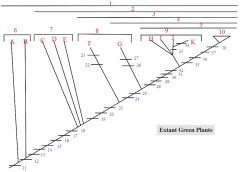
34
|
Double Fertilization
|
|
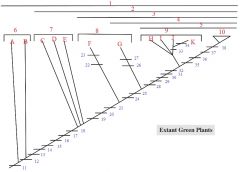
35,36,37,38
|
35. Carpel, fruit
36. Loss of swimming sperm 37. Double fertilization 38. Endosperm EXTRA: Flowers |
|
|
*
Sporophyll |
Sporangia bearing leaf (not vegetative)
|
|
|
*
Strobilus |
collection of sporophylls
|
|
|
*
Angiosperm Sporophylls: Megasporophylls & Microsporophylls |
Megasporophyll = Carpel = Stigma+Style+Ovary
Microsporophyll = Stamen = Anther+Filament |
|
|
*
Seed |
Embryo
Mature Ovule |
|
|
*
Microgametophyte of Angiosperms |
Pollen Grain
|
|
|
*
Megagametophyte contains... |
egg
|
|
|
*
Sepals protect |
developing bud
|
|
|
*
Anther contains |
microsporangia
Microspores and microgametophytes are produced within the anther |
|
|
**
Fungi are opisthokont together with animals. They both have a common ancestor that had... |
mitochondria and single posterior flagellum
|
|
|
**
For the fungal tree of life, what fungal group did not lose their flagellum? |
Chytrids
|
|
|
*
Basidiomycota Clamp Connections |
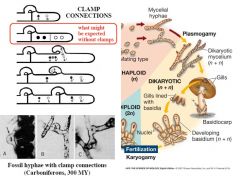
|
|
|
*
Aflatoxin |
mycotoxin made by Aspergillus
toxic and cancerous, particularly in the liver |
|
|
*
mycelium |
vegetative part of a fungus, consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae
absorbs nutrients from its environment |
|
|
*
dimorphic |
one that lives as a yeast or mold, depending on environmental conditions
EX: penicillum |
|
|
*
ascus |
sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi
|
|
|
*
basidium |
small, specialized club-shaped structure typically bearing four basidiospores at the tips of minute projections
|
|
|
*
ascospore |
sexually produced fungal spore formed within an ascus of ascomycetes
|
|
|
*
basidiospore |
sexually produced fungal spore borne on a basidium in the fungi known as basidiomycetes
|
|
|
*
Dikaryon |
The state in certain fungi in which each compartment of a hypha contains two nuclei, each derived from a different parent
|
|
|
*
mitospore |
spores produced by mitosis; they are characteristic of Ascomycetes.
asexual |
|
|
*
meiospore |
spores produced by meiosis
they are thus haploid, and give rise to a haploid daughter cell(s) or a haploid individual sexual |
|
|
*
Fruiting Body (Sporocarp) |
multicellular structure on which spore-producing structures, such as basidia or asci, are borne
basidiomycete = basidiocarp ascomycete = ascocarp |
|
|
*
Mycotoxin |
toxic secondary metabolite produced by organisms of the fungus kingdom
|
|
|
*
coenocytic |
Fungal mycelia in which hyphae lack septa
|

