![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
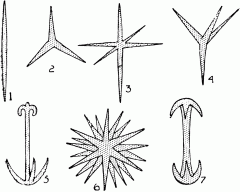
What are these and how are they formed? |
Spicules, and they are formed by calcareous or sileceous structures for support formed by sclerocytes |
|
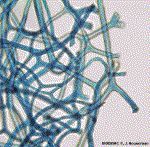
What is this called in a sponge and how is it formed? |
Spongin are collagenous protein arranged in fibers and formed by spongocytes. |
|
|
What is the most common structure for a sponge? |
the Leuconoid structure |
|
|
What do Archeocytes do in sponges? |
They catch food and obstructions when entering the sponge and absorb them into the sponge for digestion |
|
|
In asexual reproduction for sponges, what is fragmentation? |
A part of the sponge breaks off to become a new sponge |
|
|
In asexual reproduction in sponges, what is budding? |
Budding is an unequal division of an organism, it is caused by an outgrowth on the parent cell and eventually breaks off to become it's own organism. |
|
|
What is the cyst-like reproductive unit that takes place in fresh water sponges and is capable of surviving over the winter? |
Gemmule formation |
|
|
Oocytes develop from either __________ or __________. |
archeocytes or choanocytes |
|
|
Sperm in sponges develops from ____________. |
choanocytes |
|
|
What type of birth do sponges give when they do internal fertilization?(sperm is released but oocytes stay) |
viviparous |
|
|
What is the name of the free-swimming larva of most sponges? |
Parenchymula |
|
|
What are the 4 classes of sponges? |
|
|
|
What are 3 characteristics of the Class Calcarea? |
|
|
|
What are 3 characteristics of the Class Homoslcera? |
|
|

What sponge class does this image belong to? |
Hexactin |
|
|
What are 3 characteristics of the Hexactin Class? |
|
|

What sponge class is this and give 3 characteristics: |
Demospongia
|
|
|
What phylum is the most used for Marine Natural Products as of 2009? |
Porifera |

