![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is another name for the kingdom Animalia? |
Metazoa |
|
|
When did animals first evolve? Give the time frame, name of the eon, and name of the period: |
|
|
|
What animal group do Choanoflagellates belong to? |
The Protozoans |
|
|
Name 5 characteristics of Choanoflagellates: |
|
|
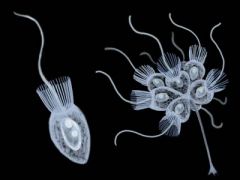
What organism is this? |
A Choanoflagellate |
|
|
What does Darwin's theory of Perpetual Change encompass? |
The world is always changing and organisms undergo perpetual changes over the course of many generations |
|
|
What does Darwin's theory of Common descent encompass? |
All forms of life have branched from one common ancestor |
|
|
What is the branching tree of life called? |
A phylogeny |
|
|
What is Homology? |
The same organ found in many different organisms in a variety of forms and functions. Means that two organisms derived from one common ancestor |
|
|
What is Darwin's theory of Multiplication of Species? |
Genetic variation will split older ancestors into two or more different unique species.
To be a species, you have to be able to interbreed |
|
|
What is Speciation? |
The formation of a new species |
|
|
What is alleopatric speciation? |
When a species becomes vicariant because of geological separation and makes it impossible for the two species to breed after a while |
|
|
What is the Founder Event? |
When a small group of the population leaves a larger group of the population and evolves to a point where they become a different species |
|
|
If an animal is viviparous what does that mean? |
it means it gives live birth |
|
|
What does it mean for an animal to be oviparous? |
it lays eggs |
|
|
What does it mean for an animal to be ovoviparious? |
it has an egg inside itself but gives live birth |
|
|
What dos it mean to be hermaphroditic? |
the animal has both sexes |
|
|
What does it mean to be dioecious? |
different sexes |
|
|
What is Sympatric speciation? |
when different individuals within a species become specialized for different areas of the environment, most of the time for food
(exp: fish --> filter feeders) |
|
|
What is Parapatric speciation? |
an environment is subdivided in two (as a result of the environment) and is still in contact along a border but can never cross that border |
|
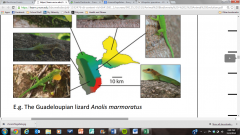
The Guadeloupian lizards are an example of what kind of speiciation?
|
Parapatric |
|
|
What is Gradualism? |
Different anatomical traits happened gradual by incremental changes over a long period of time |
|
|
Is Gradualism always true? Why not?
|
No because anatomical change happens in relatively short bursts and then goes through long periods of no change |
|
|
Can Choanoflagellates be apart of the Metazoans? Why? |
No because choanoflagellates are unicellular and metazoans are multicellular |
|
|
What are the 3 propositions of Natural Selection? |
|
|
|
What is the study of microevolution? |
The study of genetic change occuring within natural populations |
|
|
What are the 4 triphosphates in DNA? |
A,T,C, and G |
|
|
What is a change or alteration in one of the DNA bases called? |
a mutation |
|
|
What is having 2 pairs of each chromosome called? |
diploid |
|
|
What is one gene called? |
an allele |
|
|
What is the difference between homozygosis and heterozygosis? |
homozygosis: the alleles are identical heterozygosis: the alleles are different (mutation) |
|
|
What is the difference between monomorphism and polymorphism? |
Monomorphism: all individuals have identical alleles for a given gene Polymorphism: different allele combinations for individuals with a given gene |
|
|
What is allelic frequency? |
The number of times a specific allele shows up over the total number of alleles in the group |
|
|
According to the Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium, alleles will never change unless what 5 things occur? |
|
|
|
Genetic drift is a change in allelic frequencies due to chance, and especially effects _________ populations. |
small |
|
|
What does nonrandom mating of animals cause? (2) |
|
|
|
Migratory animals entering a new environment can affect __________ ___________. |
Allelic frequencies |

