![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 6 stages of Animal development? |
|
|
|
What happens during Gamete formation? |
Sperm and egg forms, and matures |
|
|
What happens during the cleavage stage of development? |
The zygote subdivides
Cytoplasm is partitioned in blastomeres |
|
|
What happens during the gastrulation stage? |
the germ layer forms |
|
|
What happens during Organogenesis? |
The body organs form and cells interact and differentiate |
|
|
What happens during the final stage of development, growth? |
The organs increase in size and the adult body form is created |
|
|
What is Gametogenesis called for male and female animals? |
in testes: spermatogenesis in ovaries: oogeneis |
|
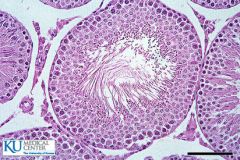
is this male or female gametogenesis and what is it called? |
MALE : spermatogeneis |
|
|
What is Oligolecithal? |
Little Yolk |
|
|
What is Mesolecithal? |
Moderate Yolk |
|
|
What is Polylecithal? |
Lots of Yolk |
|
|
Polylecithal eggs exhibit _________ ___________. |
Direct development |
|
|
Isolecithal and heterolecithal eggs exhibit __________ ___________. |
Indirect development, meaning they have a larval stage |
|
|
What is a mass of blastomeres called? |
a Morula |
|
|
What is mosaic development of yolks? |
Blastomeres lack the capacity |
|
|
What is regulative development of yolks? |
Blastomeres have the capacity to develop into entire embryos when isolated |
|
|
After all the divided cells move to the periphery of the egg, the inside fluid filled region is called the ____________. |
Blastula |
|
|
When the blastula bends inward to create a cavity, what is that called? |
Invagination |
|
|
After invagination, there are two new cavities inside the blastula. What are they called? |
Archenteron and the Blastopore |
|
|
In Gastrulation, for protosomes the blastopore becomes the _________. It originates from __________ ____________. |
mouth spiral cleavage |
|
|
During Gastrulation in Deuterostomes, a new _______ is formed, and an _________ may be formed (or not!) from the blastopore. |
mouth anus |
|
|
What is the 3rd layer of the blastula called? |
The Mesoderm |
|
|
What are the 2 ways that the mesoderm can be formed? |
|
|
|
A coelem is a cavity surrounded by the mesoderm and is formed two ways. What are those 2 ways? |
|
|
|
The coelem is in most protosomes except which two? |
Acoelomates |
|
|
Diploblastic animals do not have organs. They just have two tissues what are they? |
The epidermis and the gastrodermis |
|
|
What is Organogenesis? |
The differentiation of 3 embryonic layers |
|
|
What is the ectoderm? |
the nervous system and other epithelium |
|
|
What is in the endoderm? |
the digestive tube and gill arches |
|
|
What does the mesoderm do? |
it supports movement, circulatory system, urine, and reproductive organs |

