![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Similar anatomy (function) suggests similar ___. |
function (physiology) |
|
|
What is an important example of the relationship between form and function. |
Surface area to volume ratio (SA/V ratio) |
|
|
SA/V ratio helps explain why nearly all cells are small but it also helps explain what two key things? |
Why complex organisms need organ systems & why small-bodied animals have more difficulty maintaining TB than those with large bodies |
|
|
Homeostasis (maintain stable internal environment) can be regulated by animals in 2 ways: |
Conformers and regulators |
|
|
Describe Conformers (using TB as an example): |
TB mirrors that of the external environment and need little or no energy to do so. |
|
|
Describe regulators (using TB): |
Regulators works to maintain TB different than that of the environment and need more energy to do so |
|
|
Can an individual be both conformer and regulator? |
Yes, and individual might be both a conformer and a regulator with respect to different variables Ex. maintaining TB vs regulating internal osmolarity |
|
|
No physiological function is constant for very long, which is we we call them what? What do we call physiological function? Give an example |
variables Ex. blood sugar (glucose) remains fairly steady and predictable in healthy individuals. But after a meal (increase quickly) and if you skip (decrease slightly) |
|
|
What restores glucose to its normal concentration in the blood? |
homeostatic mechanisms |
|
|
homeostatic control system include 4 major components. What are they (in order)? |
set point sensor integrator effector |
|
|
(homeostatic control) describe set point: |
normal value for controlled variable |
|
|
describe sensor (sometimes called receptor): |
monitors particular variable |
|
|
describe integrator |
compares signals from the sensor to set point |
|
|
describe effector: |
compensates for deviations between actual value and set point |
|
|
What is feedback? |
A fundamental feature of maintaining homeostasis |
|
|
How does feedback affect disturbances? |
Feedback is a major way that disturbances can be minimized (prevents overcompensation) |
|
|
Feedback can either ___ or ____ |
negative or positive |
|
|
Mechanisms to regulate homeostasis are based on what type of feedback? |
negative feedback |
|
|
Describe negative feedback and how it differs from positive feedback |
1. moves variables in the opposite direction 2. relatively common (b/c they control homeostasis) |
|
|
How does positive feedback differ from negative feedback? |
1. Moves variable in the same direction - accelerates a process (creates an explosive system) 2. Less common than negative feedback |
|
|
What is a similarity between negative and positive feedback |
They both can occur at several levels: organ, cellular, and molecular level. |
|
|
Briefly explain the negative feedback regulation of TB graph (look at page 2 of notes) |
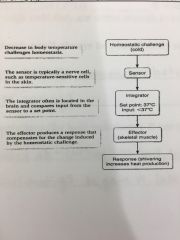
|
|
|
Briefly explain positive feedback labor graph |
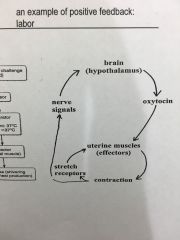
|
|
|
What is feedforward regulation? |
prepares for an upcoming challenge to homeostasis (it is anticipatory-happen in anticipation of something) |
|
|
Does feedforward regulation speed up or down homeostatis responses? Does it minimize or maximize deviations from set point? |
speeds up the homeostatic responses and minimizes deviations from set point |
|
|
Feedforward regulation can result from or be modified by what? |
learning |
|
|
Why was Ivan Pavlov's research important for feedforward regulation? |
Pavlov demonstrated the relationship between learning and feedforward processes. These processes can be conditioned to an irrelevant stimulus. |
|
|
(Regulation of body temperature) Thermoregulation is a critical part of maintaining what? |
homeostasis. |
|
|
Animals are classified according to what? (two parts) |
1. source of heat: internal or environmental? 2. Extent to which the regulate TB: fluctuating or stable? |
|
|
What is endothermic/ endothermic animal? |
regulate internal TB and use heat generated by metabolic processes |
|
|
What is ectothermic/ ectothermic animals? |
Use environment to regulate TB |
|
|
Describe heterothermy: |
Animal that lets TB fluctuate |
|
|
Describe homeothermy: |
Don't let TB to fluctuate |
|
|
What are bird's and mammal's source of heat and to what extent do they regulate TB? Which type quickly adjust mechanisms to keep a stable TB |
Birds and mammals are endothermic and mostly homeothermic |
|
|
Reptiles must bask in the mornings until they are warm enough to become active. What is their source of heat and to what extent do they regulat TB? |
ectothermic and usually heterothermic |
|
|
Can all animals be tidily placed within thermoregulation groups? |
No, examples include hibernating mammals (heterothermic in fall to winter & winter to spring) |
|
|
Behavioral adaptations (for both endotherms and ectotherms) include what? (two parts) |
1. Changing exposed S.A. - curling into ball, huddling, hunching 2. Changing surroundings to gain or lose heat |
|
|
What are the three disadvantages of endothermy: |
1. Large amount of foods (throughout the day or night, whenever the endotherm is active) are required to produce sufficient heat by metabolic proccesses 2. risk of overheating (hyperthermia)during intense activity (especially for large-bodied animals) 3. environments are a little restricted because H2O is needed to release body heat via evaporation (panting or sweating) |
|
|
What are the advantages of endothermy? |
1. the ability to maintain high levels of activity for a relatively long time 2. relatively broad geographic distribution |
|
|
What are 2 disadvantages of ectothermy? |
1. Limited geographic region 2. Can only maintain high level activity for short period of time |
|
|
What are 3 advantages of ectothermy? |
1. Can go long period of time without eating 2. Take calories to reproduce, grow, and develop instead of using it for TB 3. Do not rely on water to maintain TB through evaporation |
|
|
In addition to the mechanisms mentioned (endo vs ectothermic) some animals can regulate heat gain or loss by using what? |
vasoconstriction, vasodilation, and countercurrent heat exchangers |
|
|
Rates of heat gain or loss can be affect by the flow of blood to skin. How does vasodilation and vasoconstriction affect it? |
Vasodilation increase flow of blood to skin meaning more heat is lost Vasocontriction decrease the flow of blood to skin meaning less heat is lost |
|
|
Rates of gain or lass can be affected by using countercurrent heat exchange. What type of animals are they found in? |
bird legs (not all birds) and dolphin fillers |
|
|
How does countercurrent heat exchange work? |
heat moves from warm arteries to adjacent veins with cooler blood |
|
|
Countercurrent heat exchangers help these animals maintain TB and save energy because... |
the body core doesn't have to be warmed up the flippers and feet don't have to be warmed up (not frostbite because their internal temperature approximate those of temperature of the environment |

