![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mammalian Kidney gets how much cardiac output? |
20-25% |
|
|
Nephron (2 main parts) |
Cortical Nephron-- 80% of all nephrons Juxtamedullary nephrons- extend deep helps hyperosmotic urine. |
|
|
Route through Nephron |
1- Bowman's Capsule 2-Proximal Tube 3- Loop of Henle 4- Descending loop (fluid--> medulla) 5-Ascending Loop (fluid----> cortex) 6-Distal Tubule 7-Collecting Duct 8-Renal Pelvis (urine) Big Papa Larry Directs Apartments Down Cobblestone Roads |
|
|
Diuresis |
Removal of excess of water from the BODY in the urine |
|
|
Vasopressin |
1-Inhibits diuresis 2-Stimulates high Osolarity or decrease in blood flow 3-concentrated urine |
|
|
RAAS (renin-angiotensin-aldosterone) |
Stimulus: low blood pressure sensed in the juxtaglomerular apparatus and activates RAAS increases NA+ increases blood pressure |
|
|
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) |
Stimulus: low pressure---> heart stretches more, releases ANAP--->prohibits NA+----> decrease BP |
|
|
3 Types of neurons |
Sensory, Motor, Interneurons |
|
|
Glial Cells are |
Supports cells, 50X more then neurons! |
|
|
Membrane Potential (Vm): |
Potential difference across membrane Resting state is at -70mv |
|
|
Change in Vm when cell depolarizes: |
-70vm----->40vm |
|
|
Change in Vm when cell hyperpolarizes |
-70vm--------> -110vm |
|
|
Where does "Vm" come from? |
1): trapped negative proteins 2): This negative interior attracts cations (K+) 3): unequal distribution of ions (via NA/k pump) |
|
|
How to change Vm: |
Opening and Closing of ion channles |
|
|
How do ion channels open? |
A- changes in membrane *Change in Vm (voltage-gated channels) *Change in membrane tenson
B-channels activated by chemicals(Ligand-gated)
C-Non-gated channels(leak channels) |
|
|
Graded Potentials are defined as: |
Magnitude of the change in Vm |
|
|
Action Potentials (AP's) are: |
ALL or none system, created by threshold (minimum depolarization needed to create AP)
Are produced by graded potentials |
|
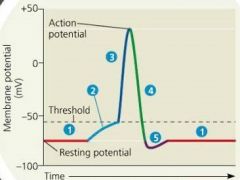
Wave of AP |
1: Resting State 2: Depolarization 3:Rising phase of Action Potential 4: Falling Phase of the action potential 5: Undershoot
|
|
|
Synaptic Transmission: |
*Electrical Synapses (gap junction)--->fast, reliable, limited flexibility
*Chemical Synapses (more common)---> uses chemical messenger ,neurotransmitter,
|
|
|
6 steps in processing AP |
1: Depolarization----> opens ca2+ 2: ca2+ enters cell (~180 mV) 3:Fusion of vesicles containing neurotransmitter 4:Vesicles release neurotransmitter into Synaptic cleff 5:Neurotransmitter binds to Ligand-gated ion channels allows NA+ and K+ Depolarizing cell 6:Neurotranmiter diffuses away |

