![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
216 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
_____ were the first organisms |
microbes |
|
|
life arose on earth about _ billion years ago |
4 |
|
|
scientists know |
little about lifes origin |
|
|
earths crust formed about |
4.2 bya |
|
|
origin of prokaryotic life began around |
4.2-3.8 bya |
|
|
origin of photosynthesis began around |
3.7 bya |
|
|
estimated origin of eukaryote began round |
2.7 bya |
|
|
oxygen accumulated in atmosphere |
2.4 bya |
|
|
the formation of protocells |
simple precursor chemicals are present in a water environment, then those chemicals react to form small organic molecules, then those organic monomers join to form polymers, those polymers(genetic material) then encodes for proteins, and lipids form spheres, which then leads to the formation of a photocell, a self replicating system enclosed in a membrane |
|
|
the formation of protocells |
simple precursor chemicals are present in a water environment, then those chemicals react to form small organic molecules, then those organic monomers join to form polymers, those polymers(genetic material) then encodes for proteins, and lipids form spheres, which then leads to the formation of a photocell, a self replicating system enclosed in a membrane |
|
|
protocell |
a self replicating system enclosed in a membrane |
|
|
a self replicating system enclosed in a membrane |
protocell |
|
|
the miller experiment |
stimulated early earths atmosphere with a mixture of water, hydrogen, methane, and ammonia cycled through an apparatus that delivered electrical sparks to the mixture |
|
|
this experiment stimulated early earths atmosphere with a mixture of water, hydrogen, methane, and ammonia cycled through an apparatus that delivered electrical sparks to the mixture |
the miller experimetn |
|
|
the result of the miller experiment |
after one week about 10-15% of the carbon in the system was now in the form of simple molecules combined into organic compounds such as amino acids -has been repeated and received similar results |
|
|
this demonstrated earths early atmosphere could have given rise to organic molecules
|
the miller experiment |
|
|
____ and _______ might have catalyzed the first synthesis reactions |
clay and iron pyrite |
|
|
clay and iron pyrites role in catalyzing the first synthesis reactions |
iron pyrite in the clay binds to adenines which link through sugar phosphate bonds, the adenines then attract uracils. Uracil link through sugar phosphate bonds and form hydrogen bonds with adenines, clay template would then release the double strand. once a self prelicating molecule, like rna, formed and replicated, natural selection took over -stable molecules that could self replicate became more common |
|
|
once a self prelicating molecule, like rna, formed and replicated, natural selection took over-stable molecules that could self replicate became more common |
-stable molecules that could self replicate became more common |
|
|
_____ miht have enclosed some self replicating systems, forming the first protocells |
lipid membranes |
|
|
lipid membranes might have enclosed some self replicating systems, forming the first |
protocells |
|
|
protocells eventually gave rise to the first lfie |
the prokaryotes |
|
|
prokaryotes predecessor is the |
protocell |
|
|
miller experiment was important because |
it demonstrated that earths early atmosphere could have given rise to organic molecules |
|
|
why is RNA likely to have been pivotal in lifes beginnings |
because it is a stable self replicating molecule that allowed natural selection to take over |
|
|
a single celled organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bounded organelles |
prokaryote |
|
|
prokaryotes two domains |
domain bacteria and domain archaea |
|
|
bacteria and archaea are |
prokaryotes belonging to distinct domains |
|
|
what distinguishes domain bacteria from domain archaea |
dna sequences and chemical composition |
|
|
plasmids |
circles of dna apart from the chromosome |
|
|
circles of dna apart from the chromosome |
plasmids |
|
|
nucloid |
the region where the DNA resides in a prokaryote |
|
|
the region where the DNA resides in a prokaryote |
nucleoid |
|
|
most prokaryotes have |
plasmids and nucleoids |
|
|
prokaryotes shared similar parts |
-plasmids -cytoplasm -ribosomes -nucleoid -cell membrane -cell wall -slime layer -pilus -flagellum |
|
|
riosomes |
use mRNA to synthesize proteins |
|
|
this use mRNA to synthesize proteins |
ribosomes |
|
|
a pilus |
is a hairlike projection made of protein. Pili enable cells to adhere to objects |
|
|
a hairlike projection made of protein. which enable cells to adhere to objects |
Pilus |
|
|
flagellum |
give the cell locomotion |
|
|
this gives the cell locomotion |
flagellum |
|
|
cell wall |
gives the cell its shape |
|
|
this gives the cell its shape |
cell wall |
|
|
the 3 most common bacteria shapes are |
coccus= spherical bacillus= rod shaped spirillum= spiral |
|
|
coccus |
spherical bacteria shape |
|
|
spherical bacteria shape |
coccus |
|
|
bacillus |
rod shaped bacteria shape |
|
|
rod shaped bacteria shape |
bacillus |
|
|
spirillum |
sprial shaped bacteria shape |
|
|
sprial shaped bacteria shape |
spirillum |
|
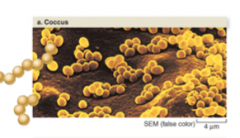
|
coccus |
|
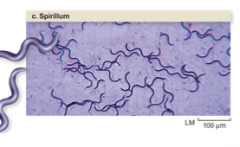
|
spirillum |
|
|
some bacteria form thick walled |
endospores that survive harsh conditions |
|
|
endospores |
dot in bacteria -when thick walled they survive harsh conditions |
|
|
preoteobacteria form |
one phylum of bacteria -their metabolic pathways and habitats are diverse -ecoli and salmonella are types of proteobacteria |
|
|
eloli and salmonella are types of |
proteobacteria |
|
|
cyanobacteria |
form another phylum of bacteria -autotrophs that were the first to release oxygen gas as a byproduct of photosyntheiss |
|
|
these autotrophs were the first to release oxygen gas as a byproduct of photosynthesis |
cyanobacteria |
|
|
domain archaea |
collectively called extremophiles because this domain was first discovered in extreme habitats, and live in place that lack oxygen or that are extremely hot, salty, or acidic, but some live in moderate environments |
|
|
collectively called extremophiles |
domain archaea |
|
|
this lives in places that lack oxygen, or are extremely hot, salty, or acidic, yet some live in moderate environments
|
archaea |
|
|
___ are essential in geochemical cycles on land and in water |
archaea |
|
|
scientists are only beginning to organize |
domain archaea into phyla |
|
|
ecosystems would shut down without |
prokaryotes |
|
|
_____ are essential to life |
prokaryotes |
|
|
prokaryotes in root nodules of some plants carry out |
nitrogen fixation, an esential process in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted ot ammonia |
|
|
nitrogen fixation |
process where atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted to ammonia |
|
|
process where atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted to ammonia |
nitrogen fixation - is done by prokaryotes in root nodules of some plants |
|
|
without nitrogen fixation |
most nitrogen would be locked in the atmosphere |
|
|
only a few species of bacteria and archaea can use |
n2 |
|
|
harmless bacteria in out bodies help |
crowd out pathogenic bacteria |
|
|
the places prokaryotes live on a human |
-scalp -nose and throat -eyes -mouth -skin -large intestine -urinary and genital systems |
|
|
harmful bacterias way of entering the body |
ingest, inhale, or through wounds or orifices |
|
|
when we take antibiotics |
some of our resistant microbes die, sometimes leading to secondary infections |
|
|
resistant microbes die when |
we take antibiotices |
|
|
ways humans exploit the metabolic talents of microbes |
yeast and molds used to make alcohol, cheese, and bread |
|
|
microbes help make |
food and drugs, ex. cheese and synthetic insulin |
|
|
microbes role in wastewater treatment plants |
they help break down organic matter
|
|
|
changes between groups arise from |
common ancestor of the groups had same thing, slight changes have accumulated since the lineages split |
|
|
in what ways are bacteria and archaea important to eukaryotic life in general and to human life in particular? |
bacteria were the first to release oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis -archaea are essential to geochemical cycles on land and in water -a few species of bacteria and archae in root nodules of some plants carry out nitrogen fixation, and conert atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia, which allows nitrogen t not be locked in the atmosphere -harmless bacteria help crowd out pathogenic bacteria -bacteria produce antibiotics which help with battling infections -we produce alcohol, cheese, and bread from yeast and molds -microbes help make food ad drugs - microbes help break down organic matter |
|
|
_______ after prokaryotes arose, the first eukaryotes evolved |
over a billion years after |
|
|
this has a nucleus and other membrane bounded organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts |
a eukaryotic cell |
|
|
membrane bounded organelles |
mitochondria and chloroplasts |
|
|
many organelles, such as the nucleus, might have resulted from |
membrane infolding |
|
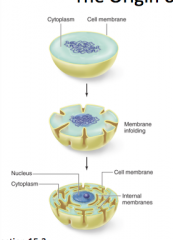
|
how organelles may have resulted from membrane enfolding |
|
|
endosymbiosis |
explains the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts -it proposes that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated as free living bacteria that were engulfed by other microbes |
|
|
explains the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts -it proposes that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated as free living bacteria that were engulfed by other microbes |
endosymbiosis |
|
|
it proposes that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated as free living bacteria that were engulfed by other microbes |
endosymbiosis theory |
|
|
mitochondria originated as |
aerobic bacteria |
|
|
chloroplasts originated as |
photosynthetic bacteria |
|
|
endosymbiosis |
through membrane infolding aerobic and photosynthetic bacterium entered the common ancestor which then split into non photosynthetic eukaryotes and photosynthetic eukaryotes |
|
|
genes moved form the DNA of the new organelles to the nuclei of the host cells, so the captured microorganisms(aerobic and photosynthetic bacterium) |
lost the ability to live on their own |
|
|
why aerobic and photosynthetic bacterium chloroplast and mitochondria lost the ability to live on their own |
genes moved form the DNA of the new organelles to the nuclei of the host cells |
|
|
some eukaryotes have chloroplasts, with three membranes |
resulting from two endosymbiosis events |
|
|
cyanobacterium= |
photosynthetic bacterium |
|
|
cyanobacterium becomes |
chloroplast |
|
|
primary endosymbiosis |
early eukaryote engulfs an aerobic and photosynthetic(cyanobacterium) which creates the early green alga |
|
|
secondary endosymbiosis |
eukaryote engulfs early green alga -this produces a chloroplast with three membranes |
|
|
in alga derived from secondary endosymbiosis |
the chloroplast has three membranes
|
|
|
the chloroplast has three membranes if |
the eukaryote went through two endosymbiosis events |
|
|
multicellularity might also have its origin in |
cooperation |
|
|
cooperation might be where _____ originated |
multicellularity |
|
|
volvox colony is |
between a group of individuals and a multicellular organism |
|
|
multicellularity resulted in an |
explosion in the variety of body sizes and forms -this introduced new evolutionary possibilities and opened new habitats for other organisms |
|
|
the explosion in the variety of body sizes and forms resulted in |
multicelluarity |
|
|
chloroplasts and mitochondria DO NOT have |
their own nuclues |
|
|
mitochondria DO |
have their own ribosomes |
|
|
how might the endoplasmic reticulum, nuclear envelope, and other internal membranes have arisen in eukaryotic cells? |
membrane infolding |
|
|
_____ are the simplest eukaryotes |
protists |
|
|
kingdom protista |
contains eukaryotes that do not fit in any of the other three eukaryotic kingdoms |
|
|
this contains eukaryotes that do not fit in any of the other three eukaryotic kingdoms |
kingdom protista |
|
|
the 3 main groups of protists |
1. algae 2. slime molds/ water molds 3. protozoa |
|
|
1. algae2. slime molds/ water molds3. protozoa |
the three main groups of protists |
|
|
_____ are aquatic, photosynthetic protists |
algae |
|
|
common types of algae |
dinoflaellates, diatoms, brown algae, red algae, and green algae |
|
|
dinoflagellets |
have two flagella and often produce toxins -this causes red tide |
|
|
have two flagella and often produce toxins-this causes red tide |
dinoflagellates |
|
|
diatoms |
have silica cell walls and are abundant in all moist habitats |
|
|
silica |
glass |
|
|
brown algae |
large, multicellular protists -ex. kelp |
|
|
large, multicellular protists-ex. kelp |
brown algae |
|
|
have photosynthitic pigments that absorb re and blue wavelengths of light - allows them to live deep in the ocean |
red algae |
|
|
diverse group with many similarites to land plants - one lineage of green algae is the common ancestor to all plants |
green algae |
|
|
water molds, slime molds, and protozoa are mostly |
heterotrophic |
|
|
the simplest eukaryotes |
protists |
|
|
_____ are decomposers and parasites of plants and animals |
water molds |
|
|
water mold caused potato blight |
irish potato famine |
|
|
_____ can exist as single cells or as large masses that behave like a multicellular organism |
slime molds |
|
|
slime molds |
can exist as single cells or as large masses that behave like a multicellular organism |
|
|
dog vomit slime mold |
detects airborne chemicals and moves toward the food source |
|
|
slime molds are cool bc |
they take the minimum length solution to a food source |
|
|
most _____ are one celled, heterotrophic, and motile |
protozoa |
|
|
protozoa |
are mostly one celled, heterotrophic, and motile |
|
|
protozoa are surrounded by |
cilia which allows for movement of this single cell |
|
|
cilia |
allows for movement of cells |
|
|
allows for movement of cells |
cilia or cillates |
|
|
dinoflagelletes is an |
algae |
|
|
kelp is an |
algae |
|
|
red algae |
are photosynthetic protists |
|
|
ciliate is on |
protozoa |
|
|
what features define the protists |
usually either algae, slime/water molds, or protozoa -these are eukaryotes that do not fit in any of the other three eukaryotic kingdoms |
|
|
fungi characteristics |
1. eukaryotic 2. hetertrophic via extracellular digestion (absorption) 3. nearly all are multicellular and filmentous, few unicellular 4. cell walls composed of chitin 5. intranuclear mitosis and meiosis 6. store extra carbohydrates as glycogen and lipids 7. reproduce via spores 8. UGA codes for tryptophan instead of termination |
|
|
cell wasll of fungi are composed of |
chitin |
|
|
chitin |
is what cell wasll of fungi are composed of |
|
|
nearly all fungi are |
multicellular and filmentous, few are unicellular |
|
|
hyphae |
single filament of fungal material |
|
|
single filament of fungal material |
hyphae |
|
|
mycelium |
the plural of hyphae, several fungal filament strands together |
|
|
the plural of hyphae, several fungal filament strands together |
mycelium |
|
|
reproductive structure of fungi |
is what we see |
|
|
mycellium is |
the collective hyphae what holds together soil |
|
|
hyphae can be specialized |
hunting fungi |
|
|
fungi reproduce |
via spores |
|
|
output of spores |
reaches the trillions -dispersed by wind, water, or animal, sometimes via elaborate coevolution -spore shape and ornamentation are taxonomically important |
|
|
these are taxonomically important |
spore shape and ornamentation |
|
|
fungi reproduce |
sexually or asexually |
|
|
in asexual reproduction of fungi |
mycelium makes spore producing structures which releases spores then goes through germination and repeats this cycle |
|
|
in sexual reproduction of fungi |
mycelium goes into plasmogamy(fusion of cytoplasm) and enters the heterokaryotic stage, then goes through karyogamy(fusion of nuclei) where it produces a diploid zygote and then goes through meiosis and spore producing structures release spores for germination and repeats cycle |
|
|
mushroom is ____ the entire body of the fungus |
not |
|
|
saprotrophic fungi |
obtains nutrients from dead organic material or inorganic material, primary decomposers |
|
|
obtains nutrients from dead organic material or inorganic material, primary decomposers |
saprotrophic fungi |
|
|
biotrophic fungi |
obtain nutrients from living organism, also called symbiotic; a close long term relationship between two or more organisms |
|
|
types of biotrophic fungi |
-pathogenic -commensal -mutualistic |
|
|
pathogenic biotrophic fungi |
are harmful to one partner, beneficial to the other |
|
|
are harmful to one partner, beneficial to the other |
pathogenic biotrophic fungi |
|
|
commensal biotrophic fungi |
not harmful nor beneficial |
|
|
not harmful nor beneficial to either organism |
commensal biotrophic fungi |
|
|
mutualistic biotrophic fungi |
beneficial to both partners |
|
|
biotrophic fungi nutrient exchange that is beneficial to both partners |
mutualistic |
|
|
pathogenic fungi |
30% of fungi -rusts, smuts, molds, pathogens, and parasites |
|
|
commensal fungi |
are endophytes- living inside another organism -in nearly every plant species examined - in at least 5% of all antropods |
|
|
endophytes |
living inside another organism |
|
|
commensal fungi are |
endophytes |
|
|
mutualistic symbiosis fungi |
lichen, leafcutter ants, termite mounds |
|
|
mycorrhizae |
fungal association with plants roots or rhizoids -fungi gives plant water, dissolved nutrients, and antibiotics -plant gives fungi photosynthates -80% of plants are endomycorrhizal -12% of plants are ectomycorrhizal |
|
|
in mycorrhizae fungi gives plant |
water, dissolved nutrients, and antibiotics |
|
|
in mycorrhizae plants give fungi |
photosynthates (sugar) |
|
|
dissolved nutrients that fungi gives plant in mycorrhizae |
n, p, and k |
|
|
mycorrhizae is apart of |
mutualistic symbiosis |
|
|
mycology began in |
1700s |
|
|
kingdom fungi created in |
1969 contains 5 phyla -only know 5-6% of fungi on earth |
|
|
the 5 phyla of fungi |
-chytrids -zygote fungi -arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi -sac fungi -club fungi |
|
|
fungi does not need |
light to grow |
|
|
phylum chytridiomycota |
oldest, most primitive lineage of fungi -decomposers or parasites of plants, fungi, and animals -some unicellular -mostly freshwater, some found in soil |
|
|
oldest, most primitive lineage of fungi-decomposers or parasites of plants, fungi, and animals |
phylum chtridiomycota |
|
|
phylum zygomycota |
named for the sexually produced zygosporangia, a thick walled, black over wintering structure -includes parasites, commensal symbionts (insect endosymbionts) and molds -bread molds septa is only found in reproductive structures -used in pharmaceuticals to make birth control and anesthetics - used to make yellow pigment for margarine |
|
|
named for the sexually produced zygosporangia, a thick walled, black over wintering structure-includes parasites, commensal symbionts (insect endosymbionts) and molds-bread moldssepta is only found in reproductive structures-used in pharmaceuticals to make birth control and anesthetics- used to make yellow pigment for margarine |
phylum zygomycota |
|
|
sexual reprodcution of phylum zygomycota |
asexual reproduction disperses and germinates mating types which then goes through plasmogamy and creates a young zygosporangium (heterokaryotic) and then goes through karyogamy and produces a diploid nuclei and then goes through meiosis and back through cycle |
|
|
pilobolus |
explosive spore dispersal |
|
|
explosive spore dispersal -400x faster than a blink |
pilobolus |
|
|
the _____ contains spores of the pilobolus fungus |
sporangium |
|
|
phylum glomeromycota |
microscopic -ecolocially and commercially important group -forms mutualistic symbiotic relationships with the roots of 80% of all plants including many crops -endomycorrhizae or arbuscular mycorrhizae |
|
|
phylum ascomycota |
-can be marine, fresh water, or terrestrial -forms sac like sexual structures called asci wehre ascospores are produced internally -range in size from unicellular yeast to complex fruiting bodies -saptrotrophic, involved in mutualisms, or are pathenogenic on plants, animals, or other fungi -majority are lichens symbionts |
|
|
ascospores |
looks like peas - has sac like sexual structure called asci where ascospores are produced internaly |
|
|
phylum ascomycota human and ecological relevance |
edible mushrooms, yeast, cheese, human diseases, medicine, ergot, lichens |
|
|
cordyceps |
alien fungus of ascomycota |
|
|
phylum basidiomycota |
defined by the formation of club like sexual structures called basidia -meiosis occurs in basidia producing basidiospores |
|
|
meiosis occurs in _________ producing _________ |
basidia, basidiospores |
|
|
phylum basidiomycota is |
mostly sexual reproduction |
|
|
rusts and smuts |
plant parasies mycelium invades host and absorbs the nutrients sometimes causing tumors |
|
|
gilled mushrooms |
-poisonous(psychedelics) -edible -ecologically important -pharmaceutical and medicinal uses -hummungous fungus |
|
|
basidiomycota have |
rusts and smuts gilled boletes shelf fungi puffballs bird nest fungi stink horns |
|
|
lichens |
mutualistic association between a fungus and a green alga(cyanobacteria) |
|
|
lichens are made of |
green alga and fungus |
|
|
3 types of lichens |
-fruticose -crustose -foliose |
|
|
these are pioneer organisms, pollution indicators (not present where pollution is bad), and climate change indicators |
lichens |
|
|
lichens |
these are pioneer organisms, pollution indicators (not present where pollution is bad), and climate change indicators |
|
|
lichens usually consists of 3 or 4 layers |
-upper cortex- protective layer -algal layer- algal cells -medulla- made of hyphae -lower cortex- covered with rhizines to anchor lichen to substrate |
|
|
saprotrophic vs biotrophic |
saprotrophic = gets nutrients from dead organisms biotrophic= get nutrients from living organisms, can be parasitic, commensal, or mutualism |
|
|
phylum chytridiomycota |
chytrids are oldest morst primitve lineage of fungi |
|
|
phylum zygomycota |
bread molds, and pilbolus |
|
|
phlum glomeromycota |
endomycorrhizae |
|
|
phlyum ascomycota |
sac fungi, cordyceps |
|
|
phylum basidiomycota |
rusts, smuts, gilled mushroom, boletes, shelf fungi, puff balls, birds nest fungi, and stink horns |
|
|
lichens |
are fungi and photobiontf |
|
|
fungus helped plants evolve |
mychorrizae |

