![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the four types of biomolecules? |
Nucleic Acids, Proteins, Lipids, Carbohydrates |
|
|
What is DNA? What is RNA? |
DNA is the instructions for making proteins it has base pairs and a double stranded helix. IT uses base pairs a,t,g,c. RNA is the copy of the DNA instructions it is what is used to make the proteins it has no pairs is single stranded. a,u,g,c |
|
|
What are Proteins? What are their structure? |
Proteins are the essential unit for almost all structures and functions. They regulate and preform most cell and body functions. Chains of amino acids. |
|
|
what is the structure of an amino acid chain? |
Hooked together and folded into 3d shapes to make proteins |
|
|
Are lipids hydrophobic or hydrophillic? What does that mean? |
Lipids are hydrophobic meaning they are not water soluable. |
|
|
how any types of lipids are there? what are they what are their diffrences? |
Phospholipids-major component of cell membrane, 2 fatty acids, phosphate head is hydrophillic while fatty acid tails hydrophobic. form membranes spontanously with water. Triglycerides-important for long term storage of energy, 3 fatty acid tails , glycerol head, hydrophobic, most common fat in the blood,protection and insulation
|
|
|
What does a phospholipid look like? |
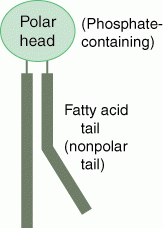
|
|
|
What does a triglyceride look like? |
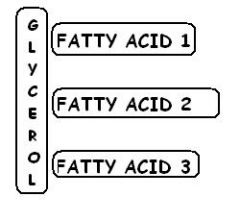
|
|
|
what is the major component of the cell membrane? |
Phospholipids |
|
|
what are the two kinds of triglycerides? |
saturated and unsaturated |
|
|
Saturated fats |
straight fatty acids, solid ex: krisco, lard linked to cardiovascular disease and plaque in arteries |
|
|
unsaturated fats |
bent fatty acids, liquid ex: olive oil, canola oil |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
sugars and starches composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxegen (CH2O)n |
|
|
Glucose |
Most abundant sugar in the blood. Glucose= (CH2O)6 =C6H12O6 3 types monosacarides, polysacarides, and disacarides |
|
|
Monosacarides |
simple sugars |
|
|
polysacarides |
more than two sugars ex:starch broken down to glucose to be used by cells |
|
|
disacarides |
two monosacarides |
|
|
lactose |
sugar in milk disacaride most mamals stop producing lactase and become lactose intolerant |
|
|
glycogen |
long highly branched chain of glucose molecules stored in muscle and liver cells imediate source of glucose during intense muscle activity |
|
|
Starch |
long chain of glucose molecules similar to glycogen but not as highly branch major component of root vegtables and grain |
|
|
cellulose digestion |
cows,horses, sheep, and goats bacteria in digestive system break down cellulose humans can't digest cellulose (dietary fiber) |
|
|
what is blood glucose level? |
supply brain with energy source uses only glucose for energy needs constant supply no stored fuel 60 percent of glucose used by body at rest |
|
|
what makes glucose levels soar? |
sugary or refined foods too much caffine body reacts to rapid dramatic increase |
|
|
What are the main ideas of cell theory? |
1.All living things are composed of cells 2.The cell is the basic unit of life 3.Cells arise from pre-existing cells |
|
|
What is a cell? |
smallest biological unit of life preforms all activities of life. Cells do things through chemical reactions. |
|
|
Diffrences between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell |
Prokaryotic: small, simple, bacteria
Eukaryotic: larger, more complex, plants and animals |
|
|
What makes up a Prokaryotic cell? |
Ribosomes, cell membrane, free floating DNA
NO nucleus or seperate compartments |
|
|
What makes up a Eukaryotic cell? |
Ribosomes, organelles, cell membrane, DNA inside membrane bound nucleus |
|
|
What is the cell membrane? |
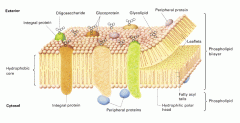
Interactive boundry between cell and it's enviornment. surrounds all cells, phospholipis bilayer and proteins. |
|
|
What is the structure of the cell membrane? |
It is fluid lipids and proteins move within the bilayer |
|
|
What do all cells have? |
Cytoplasm, genetic material, and cell membrane |
|
|
Passive transport |
Requires no cellular energy. down concentration gradient ex: diffusion and facilitated diffusion. |
|
|
Active transport |
Requires cellular energy moving against the concentration gradient uses pump proteins |
|
|
What is endocytosis? |
requires cellular energy vesicle transport into the cell |
|
|
What is Exocytosis? |
Transport out of the cell requires cellular energy |
|
|
What is ATP? |
The energy currency of the cell |
|
|
What is the formula for photosynthesis? |
Carbon dioxide+ Water+ sunlight = glucose + oxegen |
|
|
What is the formula for cellular respiration? (hint: reverse of Photosynthesis) |
Glucose+ Oxygen = Carbon Dioxide + Water +ATP |
|
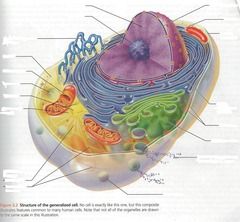
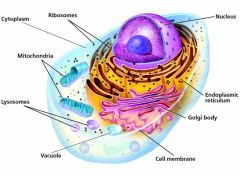
Label the animal cell. |
|
|
|
Cell Wall |
Ridgid Wall around membrane Provides support Contains cellulose |
|
|
How is a chromosome formed? |

DNA is replicated and then wrapped around histones and condensed forming the x shaped structure |
|
|
What are the phases of mitosis? |
P- Prophase (DNA Condenses) M- Metaphase (chromosomes line up) A- Anaphase (chromosomes pulled apart) T- Telophase (membrane decondenses) |
|
|
What is cytokenisis? |
The formation of the 2 cells after mitosis has taken place |
|
|
What are the 3 checkpoints of the cell cycle? |
G1- Check for cell size and health, DNA damage G2-Check DNA replication for mistakes and damage M- Check spindle fiber alignment and attachment |
|
|
What is cancer? |
Mutations in genes for cell cycle regulatory proteins = uncontrolled cell division. Can be treated with early detection
|
|
|
In Meiosis how many time is DNA copied? How many times do the cells split? |
DNA is copied once Cells split twice |
|
|
What does sexual reproduction do? |
promotes genetic diversity new combinations of genes important to species adaptation and survival |
|
|
What are the mechanisms for recombining genes? |
Independent assortment Crossing over Random fertilization
|
|
|
What is non-mendelian inheritance? |
it does not follow a dominant/ recessive pattern 3 types incomplete dominance, multiple genes, x-linked |

