![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
7 Characteriestics of living organisims |
Cellular organization, Ordered complexity, Sensitivity, Growth /Reproduction, Energy Utilization, Evolutionary adapting, Homeostasis |
|
|
Prokaryote |
Has no nucleus, no membrane bound organelle (ex.bacteria) |
|
|
Eukaryote |
Does not have a nucleus, organelles, Complex. (ex:humans) |
|
|
The Science of life |
Organisms show hierarchical organization. (Population, Ecosystem, Biosphere) |
|
|
Animal kingdom |
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nervous |
|
|
Tissue>Organ>organ system>organism>population>species>community>ecosystem>Biopshere |
|
|
|
Deductive reasoning |
Generalized to specific (ex:mammals>hair) |
|
|
Inductive reasoning |
Specific observations to General (ex: Dog>Hair) |
|
|
Spontaneous generatioon |
Popped up out of nowhere |
|
|
Biogenesis/germ theory |
have to come from seomthing |
|
|
Reductionism |
To break a complex process down to its simplest parts |
|
|
Systems biology |
Focus on emergent properties that can't be understood by looking at simpler parts |
|
|
Darwin/ Thomas Malthus |
Survival of the fittest, Population increase geometrically, Humans can only increase their food supply arithmetically, fossil record, Earths age |
|
|
Comparative anatomy |
Did species have similar structure |
|
|
Homologous |
Same evolutionary Origin |
|
|
Analogous |
Structures of different origin used for same purpose (Butterflies and bird wing) |
|
|
Cell theory |
All organisms are composed of cells, cells are life's basic units , all cells come from pre-existing cells. (Bio-genesis/Germ theory) |
|
|
3 Domains |
[Bacteria, Archaea (Prokaryotes)] [Eukarya (Eukaryotes)] |
|
|
Evolutionary conservation |
All organisms come from same simple creater 3.5BYA |
|
|
Atomic structure |
Protons(+) Neutrons Electrons(-) |
|
|
Atomic number |
Number of protons in that atom |
|
|
Element |
any substance that cannot be broken down naturally |
|
|
Atomic mass |
Protons+neutrons |
|
|
Each proton/neutron has a mass of |
1 Dalton |
|
|
Electrons |
Negatively charged particles in orbitals |
|
|
Ion |
unbalanced atoms |
|
|
Cation |
loss of electrons- -> Positive charge (ca+ion) [+'v] |
|
|
Anion |
gain of electron -> Negative charge (aNion) [-'v] |
|
|
Isotopes |
Atom with different # of neutrons than protons. (Radioactive) |
|
|
Half life |
time it takes for one half of the atoms in a sample to decay |
|
|
Carbon 12 |
P-6 N-6 E-6 ( balanced ) |
|
|
Carbon 13 |
P-6 N-7 E-6 (isotope) |
|
|
Carbon 14 |
P-6 N-8 E-6 (isotope) |
|
|
Octet rule |
In shell L,M,N there are a max or 8 electrons. In shell K there is a max of 2 |
|
|
How many naturally occurring elements? |
90. Only 12 are found in living organisms. |
|
|
Redox reactions |
The kids or gain of one or more electrons |
|
|
Oxidation |
Loss of electron |
|
|
Reduction |
Gain of electron |
|
|
Covalent bonds |
Share electron, no net charge, polar/nonpolar |
|
|
Ionic bond |
Formed attraction of opposite charged ion, medium strength |
|
|
Hydrogen bonds |
Weakest bond |
|
|
Polar covalent bonds |
Unequal sharing of electrons |
|
|
Nonpolar covalent bonds |
Equal sharing of electrons |
|
|
Synthesis reaction |
Build up/ Require energy / Anabolic reaction (A+B=AB) |
|
|
Decomposition reaction |
Break down, release energy, catabolic reaction (AB-> A+B) |
|
|
Exchange reaction |
AB+CD-> AD+CB |
|
|
Reversible reaction |
A+B-><-AB |
|
|
Catabolic |
Break down |
|
|
Anabolic |
Build up |
|
|
Catalyst |
Enzyme that speed up a reaction |
|
|
Hydrophilic |
Water loving |
|
|
Hydrophobic |
Water repelling |
|
|
Acids and Bases |
0 - more acidic 7 neutral 14 more basic |
|
|
Salt |
Anything that breaks down and does not give you hydrogen is a salt |
|
|
Buffer |
Resist a change in pH |
|

Water to dioxide to carbonic acid to bicarbonate ion to hydrogen ion |
P |
|
|
Inorganic |
Carbon with any element that is not hydrogen |
|
|
Organic |
Carbon+hydrogen+anything else |
|
|
Carbon skeleton (hydrocarbon) |
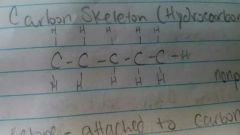
|
|
|
Ketone |
Attached to carbon |
|
|
Functional groups |
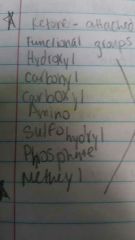
|
|
|
Isomers |
Molecule with the same molecular or empirical formula |
|
|
Stereo isomer |
Mirror image molecule |
|
|
Monomer for carbohydrates |
Monosaccharide |
|
|
Monomer for protein |
Amino acid |
|
|
Monomer for lipid |
Glycerol+fatty acid chain |
|
|
Monomer for nucleic acid |
Nucleotides( phosphate group) deoxyribose- no oxygen, ribose -oxygen |
|
|
Lyse |
Break apart |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Molecules with 1:2:1 |
|
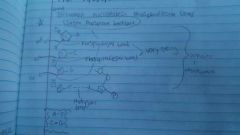
Dna |
L |
|
|
7 major protein functions |

** |
|
|
4 levels of protein |
Primary structure ( simple polypeptide chain) Secondary ( pleaded sheet ) tertiary (multiple foldings) quaternary (many tertiary all together) |
|
|
Translation |
Take rna and make a protein |
|
|
Lipids |
Insoluble in water |
|
|
hierarchal organization of life |
Atoms, molecule, organelle,cell ,tissue, organ, organ system, organism, population, community, ecosystem, biosphere |
|
|
Different bonds |
Covalent, polar covalent, ionic,hydrogen |
|
|
Endosymbiosis |
This theory suggests that mitochondria and plastids in eukaryotic cells were once independent prokaryotic cells. |
|
|
Prokaryote vs eukaryote |
The distinction between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is considered to be the most important distinction among groups of organisms. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. Differences in cellular structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes include the presence of mitochondria and chloroplasts, the cell wall, and the structure of chromosomal DNA. |

