![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define movement |
An action by an organism or part of an organism causing a change in position or place |
|
|
Define respiration |
The chemical reactions in cells that break down nutrient molecules and release energy for metabolism |
|
|
Define sensitivity |
The ability to detect or sense stimuli in the internal or external environment and to make appropriate responses |
|
|
Define growth |
A permanent increase in the size and dry mass by an increase in cell number cell size or both |
|
|
Define excretion |
Removal from organisms of the waste products of metabolism (chemical reactions in the cells including respiration), toxic materials and substances in excess of requirements |
|
|
Define reproduction |
The processes that make more of the same kind of organism |
|
|
Define nutrition |
Taking in of materials for energy, growth and development; plants need light, carbon dioxide and water ions; animals need organic compounds, ions and water |
|
|
Define species |
A group of organisms that can reproduce to produce fertile offspring -Group of individuals that look alike |
|
|
Define the binomial system |
An internationally agreed system in which the scientific name of an organism is made up of two parts showing the genus and the species |
|
|
Levels of classification in order: |
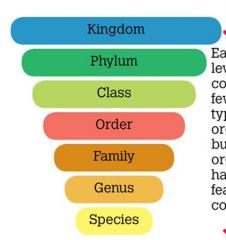
|
|
|
List the Kingdoms: |
-Animals -Plants -Fungi -Protoctists -Prokaryotes (bacteria) |
|
|
Feature used to place plants in their kingdom: |
-All plants are green and carry out photosynthesis (have chloroplasts) |
|
|
Features used to place animals in their kingdom: |
-multicellular -cells have no cell walls and no chloroplasts |
|
|
Features used to place prokaryotes in their kingdom: |
-consist of single cells -chromosomes not organised into a nucleus |
|
|
Features used to place protoctists in their kingdom: |
-unicellular (single celled) -chromosomes enclosed in a nuclear membrane to form a nucleus |
|
|
Features used to place fungi in their kingdom: |
-made up of thread-like hyphae rather than cells -many nuclei distributed throughout the cytoplasm in their hyphae |
|
|
Features used to put plants in to groups in the plant kingdom Ferns |
-land plants -stem entirely below the ground, forming a structure called a rhizome (roots grow horizontally downwards, sending up leaves at intervals, roots that grow from the rhizome are called adventitious roots) -stem and leaves have sieve tubes and water conducting cells (similar to xylem and phloem in flowering plants) |
|
|
Features used to put plants into groups in the plant kingdom Flowering plants |
-reproduce by seeds which are formed in flowers, seeds are enclosed in an ovary -divided into two subgroups: monocotyledons and dicotyledons |
|
|
Features used to put plants into groups in the plant kingdom
Flowering plants- Monocotyledons |
-long and narrow leaf shape -parallel leaf veins -one cotyledon -flower parts (petal, sepals, ovarys) in groups of threes |
|
|
Features used to put plants into groups in the plant kingdom
Flowering plants- Dicotyledons |
-broad leaf shape -network of branching leaf veins -two cotyledons -flower parts (petals,sepals,ovary) in groups of fives |
|
|
What are adventitious roots? |
-name given to roots that grow from the stem rather than other roots (in ferns, the roots grow directly from the stem below ground which forms a structure called a rhizome) |
|
|
Structure of a monocotyledon and dicotyledon leaves |
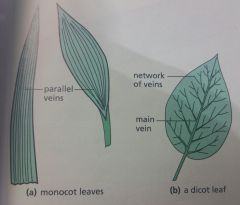
|
|
|
List the features of viruses |
-particles made up of genetic material (RNA or DNA) surrounded by a protein coat -not cells (no cytoplasm, nucleus, cell membrane, cell organeles) -genetic material is composed of a few genes that code for the proteins that form the coat |
|
|
Structure of a virus |
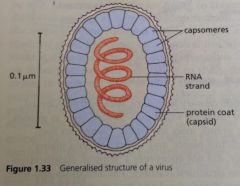
|
|
|
Features of (class) mammals (animal kingdom, vertebrates) |
-mouse -fur -four limbs -produce live young -eyes, ears with pinna (external flap) -warm blooded -females have mammary glands -four types of teeth |
|
|
Features of (class) amphibia (animal kingdom, vertebrates) |
-frog, newt -moist skin -four limbs -webbed back feet (make swimming more efficient) -produce jelly covered eggs in water -eyes and ears -cold blooded -lungs and skin for breathing |
|
|
Features of (class) fish (animal kingdom, vertebrates) |
-herring, shark -scales -fins (used for balance and movement) -jelly covered eggs in water (same as amphibians) -eyes, no ears -lateral line along body for detecting vibrations in water -cold blooded -gills for breathing |
|
|
Features of (class) reptiles (animal kingdom, vertebrates) |
-lizard, snake -dry skin, with scales -four legs (apart from snakes) -produce eggs with rubbery waterproof shell, laid on land -eyes and ears -cold blooded -lungs for breathing |
|
|
Features of (class) birds (animal kingdom, vertebrates) |
-robin, pigeon -feathers, scales on legs -two wings, two legs -produce eggs with a hard shell, laid on land -eyes ears -warm blooded -lungs for breathing -beak |
|
|
List the five classes of vertebrates: |
-fish -amphibia -reptiles -birds -mammals |
|
|
Features of (class) insects (animal kingdom, invertebrates, phylum arthropods) |
-dragonfly, wasp -three pairs of legs -body dived into head thorax and abdomen -one pair of antennae -two pairs of wings |
|
|
Features of (class) myriapods (animal kingdom, invertebrates, phylum arthropods)
|
-centipede, millipede -10+ pairs of legs (one pair per segment) -body not obviously divided into thorax and abdomen -one pair of antennae -simple eyes |
|
|
Features of (class) arachnids (animal kingdom, invertebrates, phylum arthropods)
|
-spider, mite -four pairs of legs -cephalothorax and abdomen -several pairs of simple eyes -chelicerae for biting and poisoning prey |
|
|
Features of (class) crustacea (animal kingdom, invertebrates, phylum arthropods)
|
-crab, woodlouse -5+ pairs of legs -cephalothorax and abdomen -two pairs of antennae -one pair of compound eyes -exoskeleton calcified to form a carapace (hard) |
|
|
Features of all arthropods (phyla) |
-jointed limbs -external skeleton called a cuticle -bodies segmented, with flexible joint which permit movement |
|
|
List the features in the cells of all living organisms |
-cytoplasm -cell membrane -DNA as genetic material -ribosomes for protein synthesis -enzymes involved in respiration |
|
|
Dichotomous key |
-used to identify unfamiliar organisms -simply the process of identification -made up of pair of contrasting features |
|
|
Explain that classification systems aim to reflect evolutionary relationships |
- |
|
|
Why is it important to classify organisms? |
-possible to identify those at risk of extinction -strategies can then be put in place to conserve threatened species |
|
|
Explain that classification is traditionally based on studies of morphology and anatomy |
morphology: study of the form or outward appearance of an organism anatomy: study of their internal structure as revealed by dissection |
|
|
Explain that the sequences of bases in DNA and of amino acids in proteins are used as a more accurate means of classification |
-each species has a distinct number of chromosomes and a unique sequence of bases in its DNA, making it identifiable and distinguishable -helps when different species are very similar morphologically and anatomically |
|
|
Explain that organisms which share a more recent ancestor have base sequences in DNA that are more similar that those that share only a distant ancestor |
-human and primate evolution -chimpanzees: 48 chromosomes humans: 46 chromosomes |
|
|
Diagram of a bacterium |
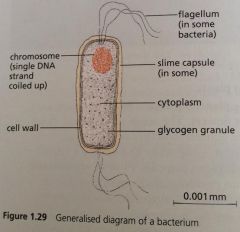
|

