![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Population |
an interbreeding group of organism of the same species occupying a particular habit |
|
|
Birth rate |
Number of new individuals derived form reproduction per unit time |
|
|
Negative feedback |
Process that brings about a reversal of any change in conditions |
|
|
Equilibrium species |
Species that control their population by competition rather than reproduction or dispersal |
|
|
Fugitive species |
Rely on large capacity for reproduction and dispersal to increase numbers |
|
|
Phases of 1 step growth curve + it's description |
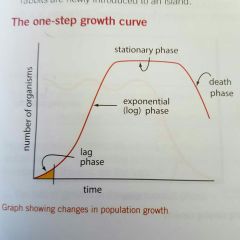
Lag phase, Exponential phase, Stationary phase, Death phase Growth pattern is Sigmoid (S- shape) curve |
|
|
Environment resistance |
Environmental factors that slow down population growth |
|
|
Immigration |
Movement of individuals into a population of the same species |
|
|
Biotic factors |
Part of the environment of an organism that is living- pathogens, predators |
|
|
Carrying capacity |
Maximum number around which population fluctuates in a given environment |
|
|
Abiotic factors |
A part of the environment of the organism that's is non-living ( Air temp, oxygen avaibility) |
|
|
Measuring animal abundance methods |
-Capture-mark-recapture (Lincoln index) -kick sampling in a stream and counting aquatic invertebrates caught in net down stream |
|
|
Plant Abundance |
Quadrat to calculate mean, in known area Estimate % cover of a in which individuals are hard to recognise Estimate % frequency |
|
|
Distribution |
Area/Volume in which the organism of a species are found |
|
|
Kite diagrams- what does it show? |
% area cover of the species across the belt transect |
|
|
Ecosystem |
A characteristic community of interdependent species interacting with abiotic components of their habitat |
|
|
Habitat |
Place in which an organism lives |
|
|
Biomass |
Mass of biological material in living/ recently living organisms |
|
|
Community |
Interacting population of 2 or more species in the same habitat at the same time |
|
|
Trophic level |
Feeding level; number of times the energy has been transferred between sun and successive organism along a food chain |
|
|
Saprobiont |
A micro-organisn that obtains it's food from the dead or decaying remains of other organism |
|
|
Gross primary productivity |
The rate of production of chemical energy in organic molecules by photosynthesis in a given area in a given time |
|
|
Net primary productivity |
Energy in plants biomass which is avaible to the primary consumer |
|
|
Primary productivity |
Rate at which energy is converted into biomass by producer |
|
|
Secondly productivity |
Rate this which consumers convert chemical energy from their food into biomass |
|
|
Succession |
Change in structure and species composition of a community over time |
|
|
Climax community |
New species invades and replaces existing ones until eventually a stable community is formed and no further changes occur |
|
|
Primary succession |
Changes in structure and species composition of a community over time in an area that had not been previously colonised |
|
|
Pioneer species |
First species to colonise a new area in an ecological succession |
|
|
Sere |
Sequence of stages in succession |
|
|
Seral stage |
Stage of sere |
|
|
Secondary succession |
Changes in community following the disturbance or damage to a colonised habitat |
|
|
Niche |
Role and position a species has in its environment including all interactions with biotic and abiotic factors of its environment |
|
|
Abundance |
Number of individuals in a species in a given area/volume |

