![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are genes? |
unit of inheritance that determine the traits (characteristics) passed from one generation to the next |
|
|
What are alleles? |
Variants of a gene Ex: genes that determine pea pod shape |
|
|
What is a genome? |
The entire collection of all genetic material in a microbe |
|
|
2 DNA strands intertwine to form a ______ _____. |
Double Helix -each strand is complimentary & anti-parallel |
|
|
A always binds to ____ in DNA. C always binds to ____ in DNA.
|
A - T C - G |
|
|
What is Chargaff's Rule? |
%A = %T %G = %C |
|
|
Where does DNA carry the genetic information? |
In its sequence |
|
|
Where do eukaryotic cells keep chromosomes? |
Condensed & packaged into the NUCLEUS |
|
|
What kind of chromosomes do prokaryotes have? |
Single, circular chromosomes |
|
|
What are plasmids? |
- Small circular extra-chromosomal DNA - Carries genes with non-essential functions (antibiotic resistance) (not part of the chromosome) |
|
|
What is the central dogma of biology? |
DNA (Genes) --> RNA (Messages) --> Protein (Products) |
|
|
What is replication? |
DNA copying itself |
|
|
What is transcription? |
DNA making RNA |
|
|
What is translation? |
RNA making protein |
|
|
What is semiconservative replication? |
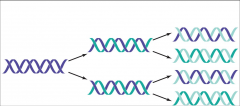
Each strand serves as a template for replication |
|
|
What does a helicase do? |
"unzips" DNA (replication fork forms) |
|
|
What is DNA polymerase (DNAP)? |
the replicating enzyme |
|
|
DNA synthesis occurs ___' to ___' |
5' to 3' |
|
|
2 types of strands formed during replication? |
Lagging & Leading |
|
|
What direction does DNAP move? |
towards the helicase |
|
|
Which strand is fragmented because it has to go back every time DNA is unzipped? |
the lagging strand |
|
|
What is the origin (oriC)? |
A specific DNA sequence at which replication begins |
|
|
What is the terminus (terC)? |
A DNA region at which each replication fork ends during replication |
|
|
How does replication initiate? |
DNA polymerase and helicase bind to DNA at oriC and begin replication |
|
|
Replication is _____________? |
Bidirectional: two complexes of DNA polymerase set off in opposite directions (greek letter theta) (also called "Theta" replication" |
|
|
Where do both copies of replicated DNA reside after separation? |
in its own new daughter cell |
|
|
Describe RNA synthesis (transcription) |
1. DNA sends messages to ribosomes 2. mRNA message is made by RNA polymerase 3. Promoters control transcription |
|
|
________+_______= RNA polymerase |
Core + Sigma |
|
|
What is the core responsible for? |
assembling RNA |
|
|
What is sigma responsible for? |
- Finding promoters on the DNA strands where the RNA polymerase can bind - each sigma recognizes a specific promoter sequence & determines which messages get sent |
|
|
What are promoters? |
DNA sequences that indicate where to start transcription (start the message) |
|
|
What 2 things are part of a promoter? |
-35 box & -10 box |
|
|
Promoter sequences are NOT ______? |
identical |
|
|
How do you determine the consensus sequence for "sigma"? |
average all the promoter sequences |
|
|
What do promoters vary in? |
strength-which is determined by consensus |
|
|
Stronger promoters are closer to _________. |
consensus |
|
|
What are 2 things strong promoters do? |
- call over lots of RNA polymerases - microorganism will create lots of messages (lots messages= lots of protein later on) |
|
|
What does RNA polymerase unwind a small piece of DNA into? |
single strands |
|
|
What will nucleotides base pair with? |
the complementary DNA |
|
|
What does RNA polymerase do? |
polymerizes RNA, duh. |
|
|
What is RNA transcript complementary to? |
DNA template strand |
|
|
What does RNA polymerase use one strand of as a template? |
DNA |
|
|
What does rRNA (ribosomal) do? |
forms structure of the ribosome, recognizes messages, assembles proteins |
|
|
_____ is central to protein synthesis. |
RNA |
|
|
What does tRNA (transfer)? |
activates amino acids and reads the mRNA message |
|
|
What does mRNA (messenger) do? |
carries the message from the DNA (gene) |
|
|
Protein synthesis= __________ |
Translation |
|
|
What is a protein's shape/function determined by? |
its primary sequence of amino acids |
|
|
How many different amino acids are there? |
20 |
|
|
Protein + rRNA --> Prokaryotic 70S |
30S + 50S (smaller than eukaryotic and shaped differently) |
|
|
Protein + rRNA --> Eukaryotic 80S |
40S + 60S |
|
|
There is one unique mRNA strand for each unique _______. |
protein |
|
|
A cell can make multiple copies of the same protein from one ________. |
mRNA |
|
|
Each amino acid matches a unique tRNA with what a specif ____________ _____________? |
nucleotide sequence |
|
|
During translation initiation, the ribosome assembles on the mRNA at a specific spot called the ____________. |
shine-dalgarno sequence |
|
|
During translation initiation, where do activated tRNA's arrive? |
at the ribosome |
|
|
During translation elongation, a peptide bond is formed between what? |
the two amino acids |
|
|
During translation elongation, how many nucleotides does the ribosome slide down the mRNA? |
three nucleotides |
|
|
During translation elongation, what is formed when NEW activated tRNA arrives? |
ribosome forms another peptide bond (the cycle repeats) |
|
|
During translation elongation, protein is syntheiszed from _________ to _________ as the cycle repeats. |
N-terminus to C-terminus |
|
|
During translation termination, a mRNA sequence called a ______ _______ terminates protein syntheis. |
stop codon |
|
|
During translation termination, what happens to the protein and the ribosome? |
-the protein is RELEASED -the ribosome DISASSEMBLES |
|
|
What is the translation start site? |
the message starts 6-9 bases in the 3' direction of the SHINE-DALGARNO SEQUENCE |
|
|
What is the specific start site? |
a CODON: AUG |
|
|
What is always the first amino acid in translation? |
Methionine (Met) |
|
|
What is a codon? |
a series of three nucleotides |
|
|
How is a particular amino acid specified? |
By recruiting the appropriate tRNA |
|
|
A start codon sets the ________ which determines all subsequent codons. |
frame |
|
|
After each peptide bond is formed, the ribosome slides ____ bases down the mRNA strand. |
3 |

