![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A useless or rudimentary body part that is thought to have been important in ancestral population but no longer has a known function is termed a(n)_________________. |
Vestigial structure |
|
|
what five elements refute the non-scientific approach and support descent with modification |
1. Species change over time 2. Lineages split and diverge 3. New life-forms derive from older forms 4. All life-forms are related 5. Te Earth - and life on Earth - are really, really old. |
|
|
A characteristic shared by two species (or other taxa) that is similar because of common ancestry |
Homology |
|
|
What are the three types of homology? |
1. structural homology 2. Ontogenetic homology 3. Molecular homology |
|
|
A characteristic that are similar but not derived from a common ancestor. |
Analogy |
|
|
Analgoies are a result of __________________ |
Convergent evolution |
|
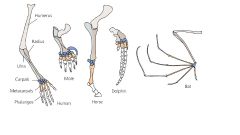
This image is an example of |
Homology |
|
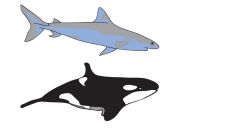
This image is an example of |
Analogy |
|
|
T/F: Based on the nested set of traits, we can infer the evolutionary history of common ancestry |
True |
|
|
Developmental (embryological) similiraities |
Ontogenetic Homology |
|
|
T/F: All vertebrates develop a similar body plan |
True |
|
|
All vertebrates develop a similar body plan. What are some body structures that they share |
Notochord, Body segments, pharyngeal pouches |
|
|
What do shared developmental structures (ontogenetic homology) say about different species? |
The shared developmental structures (ontogenetic homology) reflects shared evolutionary history |
|
|
What gene is said to be the genetic toolkit responsible for the control of homologous body plans across different species. |
Hox genes |
|
|
What genetic flaw do humans share with chimpanzee, but not with gorillas, orangutans and other primates? |
CMT1A |
|
|
Explain how sister chromatids could possibly result in one without a copy of a gene with the other having two copies |
In instances where there are repeat elements flanking genes, there is a possibility for missalignment during recombination and when the chromatids split, this could result in one sister chromatid without a gene and the other with two genes. |
|
|
T/F: the human genome has very few repeat elements |
False. The human genome is full of these repeat sequences |
|
|
Repeat sequences in the genome are often caused by |
Transposons |
|
|
T/F: often times repeat elements in a genome are parasitic
|
True |
|
|
Why are repeat elements in genomes bad? |
They could potentially lead to a loss or a gain of a gene during recombination. In both instances, diseases or undesirable phenotypes could result. |
|
|
Because of a CMT1A repeat sequence, humans have been shown to be most closely related to what species? |
Chimpanzees |
|
|
Genes that have no real function |
Pseudogenes |
|
|
By what process are pseudogenes produced? |
Reverse transcription |
|
|
How are pseudogenes formed? |
Pseudogenes (genes which have no function) are formed through transposons. The transposon is transcribed into RNA and then using reverse transcriptase returned back to DNA which is integrated back into the genome. |
|
|
Do older pseudogenes occur in a broader range of species? |
Yes, older pseudogenes are found among a broad taxa while young pseudogenes are only shared in a small group. We can tell the difference because the younger pseudogene will have very similar/identical sequences. |
|
|
Sediments originally deposited in horizontal layers |
Original horizontality |
|
|
In undisturbed strata, older layers lie beneath younger one |
Superposition |
|
|
Who proposed the principle of Uniformitarianism? |
James Hutton |
|
|
Describe Uniformitarianism |
Principle proposed by James Hutton, Uniformitarianism means the processes acting on the Earth's surface today were the same ones that had been acting upon it for all of history. If this principle is true, then Earth had to be millions, not thousands of years old. |
|
|
Based on relative dating, place the following dates from oldest to youngest:
1. Pennsylvanian 2. Devonian 3. Cambrian 4. Permian 5. Mississippian 6. Precambrian |
1. Precambrian 2. Cambrian 3. Devonian 4. Mississippian 5. Pennsylvanian 6. Permian |
|
|
Geologists can establish relative age of rocks based on the principles of ___________ |
Stratigraphy |
|
|
Relative age is difficult to determine just based on the principle of stratigraphy alone. What technique gave us the means of measuring numeric age? |
Radiometric dating |
|
|
Elements with different numbers of neutrons |
Isotopes |
|
|
T/F: Some isotopes are unstable and undergo radioactive decay, transforming into more stable isotopes |
True |
|
|
Why do radioactive isotopes decay? |
They decay in order to achieve a more stable state. |
|
|
Parent isotopes spontaneously decay at a constant rate to a daughter isotope |
Radioactive isotope |
|
|
At least how old is Earth? |
4.6 billion years old |
|
|
If potassium decays into Calcium (89%) and Argon (11%) with a half life of 1.3 billion years. How old is a rock that was found to have 2mg of Potassium and 0.22mg of Argon? |
Since after 1 half life 11% of the total potassium is lost as Argon we can take the amount of argon and divide it by 0.11. This gives us the amount of potassium lost as a result of Argon production. Then we add this number to the number of potassium found in the rock now to get the original amount of potassium. Determining the number of half lifes it took for the rock to reach that potassium number will give you the age of the rock. 0.22/0.11= 2mg of K to produce 11% of argon. 2mg K (amount lost) + 2mg K (Amount remaining) = 4mg. In order to reach 2mg of K from 4Mg of K it requires 1 half life meaning that the rock is 1.3 billion years old. |
|
|
If potassium decays into Calcium (89%) and Argon (11%) with a half life of 1.3 billion years. How old is a rock that was found to have 1mg of Potassium and 0.33mg of Argon? |
Since after 1 half life 11% of the total potassium is lost as Argon we can take the amount of argon and divide it by 0.11. This gives us the amount of potassium lost as a result of Argon production. Then we add this number to the number of potassium found in the rock now to get the original amount of potassium. Determining the number of half lifes it took for the rock to reach that potassium number will give you the age of the rock. 0.33/0.11= 3mg of K to produce 11% of argon. 3mg K (amount lost) + 1mg K (Amount remaining) = 4mg. In order to reach 1mg of K from 4Mg of K it requires 2 half life meaning that the rock is 2.6 billion years old. |
|
|
What radiometric method is used to date volcanic rock? |
Potassium-Argon |
|
|
What is the half life of the potassium-Argon radiometric method?
|
1.3 billion years |
|
|
Igneous and metamorphic rock are dated using what radiometric method? |
Uranium-lead |
|
|
U-238 to Pb-206 half life is |
4.5 billion years |
|
|
What radiometric method is used to date bones, wood, shells, cloth, and animal droppings? |
Carbon-14 |
|
|
Carbon-14 dating half life is |
5730 years |
|
|
Name the large divisions of Eons? |
1. Hadean 2. Archaean 3. Proterozoic 4. Phanerozoic |
|
|
list the large divisions of Eons from oldest to youngest |
1. Hadean 2 Archean 3. Proterozoic 4. Phanerozoic |
|
|
During what Eon was early life first observed? |
Proterozoic |
|
|
Hadean, Archean, and proterozoic are referred to as the _____________ |
Precambrian |
|
|
Phanerozoic means |
Visible life |
|
|
Life originated from what era |
Proterozoic |
|
|
What are the eras that fall under The Phanerozoic Eon? |
1. Paleozoic (ancient life) 2. Mesozoic (middle life, also called the age of dinosaurs) 3. Cenozoic (life, also called the age of mammals) |
|
|
This eon means "ancient rock" |
Archean |
|
|
What are the periods that fall under the Paleozoic Era |
1. Cambrian 2. Ordovician (first vertebrate organism - fish) 3. Silurian (first land plants) 4. Devonian (first amphibians) 5. Carboniferous (first reptiles) 6. Permian |
|
|
During what period did the first vertebrate organisms appear? |
Ordovician |
|
|
During what period did the first land plants appear? |
Silurian |
|
|
During what period did the first amphibians appear |
Devonian |
|
|
During what period did the first reptiles appear? |
Carboniferous |
|
|
This Era means ancient life |
Paleozoic |
|
|
This Era means middle life, also called the age of dinosaurs |
Mesozoic |
|
|
This Era means recent life, also called the age of mammals |
Cenozoic |
|
|
What are the periods that fall under The Mesozoic Era.
|
1. Triassic 2. Jurassic 3. Cretaceous |
|
|
The first dinosaurs appeared in this period |
Triassic |
|
|
First dinosaurs appeared in this Era |
Mesozoic |
|
|
The first amphibians were seen during this era |
Paleozoic |
|
|
The first mammals appeared during this period |
Cretaceous |
|
|
The first mammals appeared during this era |
Mesozoic |
|
|
Processed pseudogenes are useful for testing Darwin's theory of descent with modification because they: A. Accumulate mutations at a constant rate and thus older processed pseudogenes should be shared by a greater variety of species B. Can be utilized for examining phylogenetic relationships among asexually reproducing organisms C. Are distributed in organisms that are found in similar environments D. Demonstrate phylogenetic relationships of divergence because they do not accumulate |
A. Accumulate mutations at a constant rate, and thus older processed pseudogenes should be shared by a greater variety of species |
|
|
The purposeful breeding of a specific trait |
Artificial Selection |
|
|
What is Darwin's first postulate? |
The individuals within a population differ from one another (variation within a population) |
|
|
What is Darwin's second postulate? |
The differences are, at least in part passed from parents to offspring (Variation is heritable) |
|
|
What is Darwin's third postulate? |
Some individuals are more successful at surviving and reproducing than others (differential fitness) |
|
|
What is Darwin's fourth postulate? |
The success in survival and reproduction is associated with variant traits that are heritable |
|
|
What are Darwin's postulates and why were they proposed? |
Darwin proposed four postulates necessary for Natural Selection to occur. |
|
|
Name all of the postulates proposed by Darwin necessary for Natural Selection to occur |
1. The individual within a population differ form one another (variation within a population) 2. The differences are, at least in part passed from parents to offspring (variation is heritable) 3. Some individuals are more successful at surviving and reproducing than others (differential fitness). 4. The success in survival and reproduction is associated with variant traits that are heritable. |
|
|
T/F: Natural selection leads to adaptation and by extension decent with modification |
True |

