![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Psuedostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium |
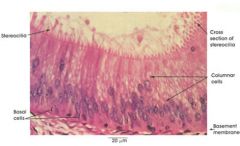
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Simple Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
|
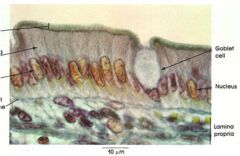
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
|
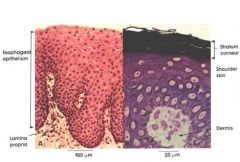
Name this tissue |
|
|
|
Stratified Non-Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
|
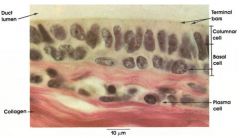
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Transitional Epithelium because the top layer has multiple shapes and some are wider than others.
|
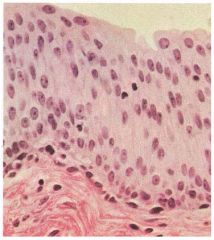
Name this tissue and give reasons why
|
|
|
|
Areolar Loose CT Proper. It looks like a spider web, has lots of space in the matrix between the collagen fibers and the elastic fibers.
|
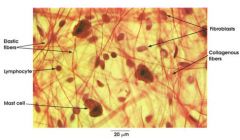
Name this tissue and give reasons why you say that.
|
|
|
|
Dense Regular CT Proper
|
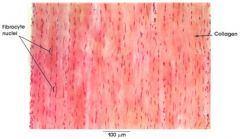
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Hyaline Cartilage
|
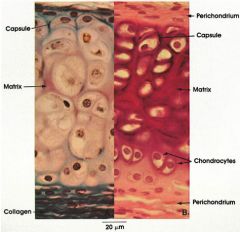
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Elastic Cartilage
|
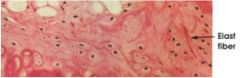
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Adipose Loose CT Proper because it says it has fat cell nucleus, fat globules and fat cell cytoplasms.
Also, the cells are round, with their nuclei off to the edge and only have 1 nuclei per cell. |
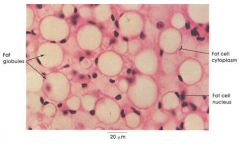
Name this tissue and why
|
|
|
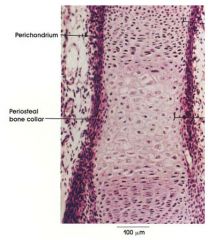
Name this tissue
|
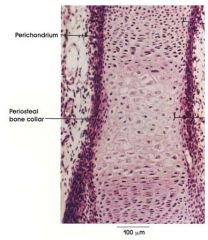
Hyaline Cartilage
|
|
|
|
Bone
|
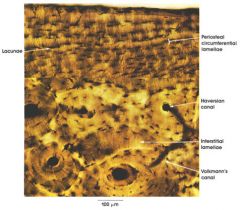
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Transitional Epithelium because the shape of top layer is not uniform
|
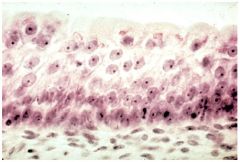
Name this tissue and why is it that tissue
|
|
|
|
Simple Columnar Epithelium
|
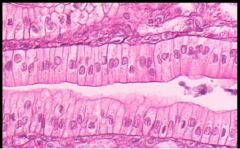
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
|
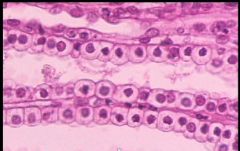
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Simple Columnar Epithelium
|
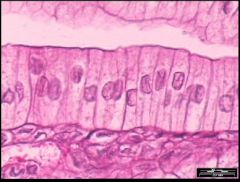
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Psuedostratified Columnar Epithelium
|
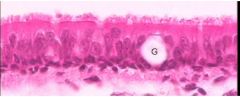
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
|
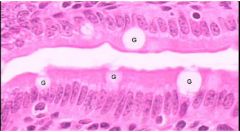
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Cornified stratified squamous epithelium for the epidermis
dense irregular ct proper for the dermis. The top layer of the epidermis is thin and wide. The picture also shows an apical side and a basal side, which makes it an epithelium for sure. The dark layer on top looks to be where the keratin is at. You can tell the layer below the stratified squamous epithelium is dense irregular CT because the collagen fibers are going in all kinds of directions. |
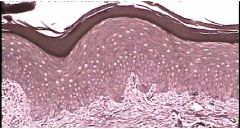
Name this tissue and give reasons why
|
|
|
|
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
|
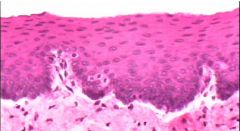
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Simple Columnar Epithelium
|
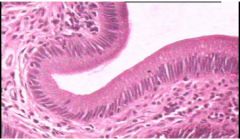
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Dense Regular CT Proper
|

Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Blood
|
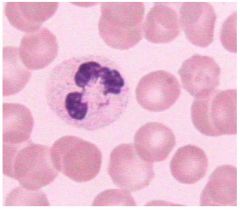
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Elastic CT Proper Dense
|
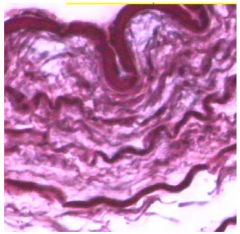
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Areolar Loose CT Proper
|
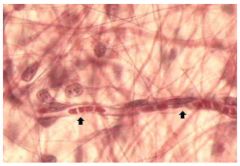
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Blood, Simple Squamous Epithelium, Smooth Muscle
|
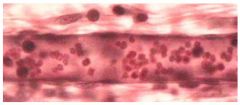
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Elastic C.T.
|
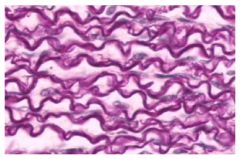
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
neural
|
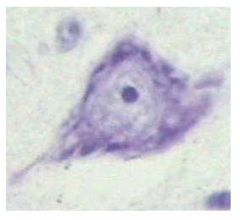
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Neural
|
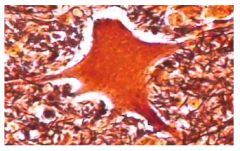
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Smooth muscle because the bottom part of this picture has long rounded (oval'ish looking) nucleus and there is a sheet of muscle going perpendicular to the one at the bottom
|
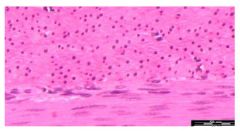
Name this tissue and why
|
|
|
|
Smooth Muscle
|
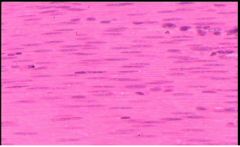
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Skeletonal Muscle
|

Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Skeletal Muscle because it has striations (lines on cell), no intercaliated discs (the joints found in cardiac muscle) and the nucleus has been pushed off to the edge of the cell. Also there are lots of nuclei per cell.
|

Name this tissue and why
|
|
|
|
Cardiac Muscle
|
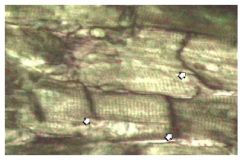
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Skeletal Muscle
|
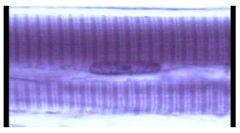
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Skeletal Muscle
|
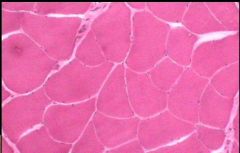
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Bone (zoomed out)
|
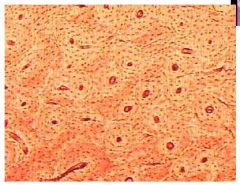
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
|
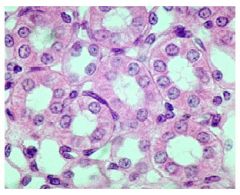
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Simple Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
Why? - epithelium because it has basal and apical side - simple because there is only one layer - columnar because it's tall - It's not psuedostratified because because it doesn't look like multiple layers |
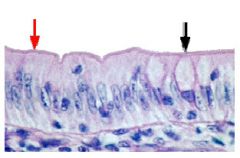
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
|
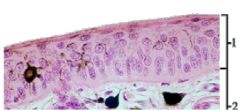
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Adipose Loose CT Proper
|
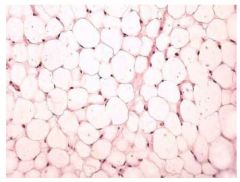
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium (inside kidney tubules)
|
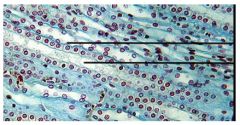
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Dense Irregular CT Proper
|
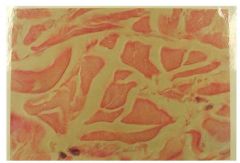
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Dense Regular CT Proper (because it
|

Name this tissue
|
Dense regular has long skinny nucleus and the smooth muscle has more wider nucleus. Also with smooth muscle, it needs a sheet of muscle going the opposite direction. You may or may not see it, but if you do see it, it's definitely a smooth muscle.
|
|
|
Adipose Loose Proper CT
|
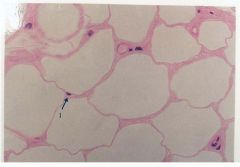
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Bone
- Osteon - Canalicui - Osteocyte - Concentric Lamellae - Haversions (central canals) - Volkmanns (perforated canals) - interstital lamellae - Ground substance Not shown here - Circumferential Lamellae - Sharpey's fibers (holds periosteum to compact bone) |
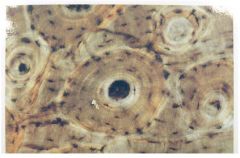
Name this tissue and all the parts of this tissue that you see
|
|
|
|
Elastic Cartilage
|
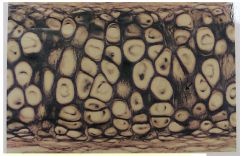
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Transitional Epithelium
|
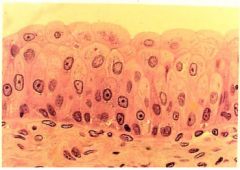
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Blood & simple squamous epithelium
|
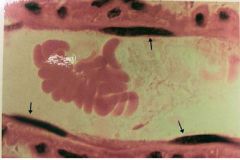
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Simple Squamous Epithelium
|
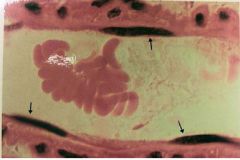
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Reticular CT
|
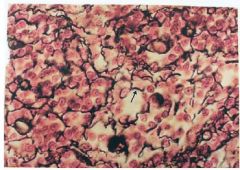
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Pseudostratified Epithelium
|
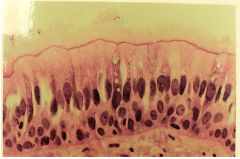
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Cardiac Muscle
|
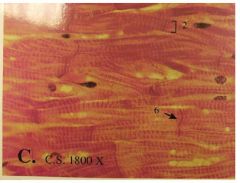
Name this tissue
|
things to look for:
- single cell - splitting into freeway like things - intercalated discs (the joints of the muscles) |
|
|
Skeletal Muscle
|
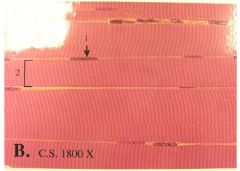
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Areolar CT
|

Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Hyaline Cartilage
|
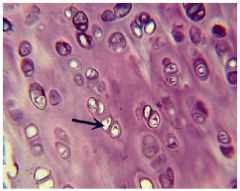
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Elastic Cartilage because there is chondracytes inside lacunaes and there are lots of elastic fibers in the ground substance
|
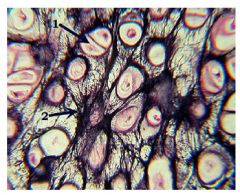
Name this tissue and why
|
|
|
|
Fibrocartilage
|

Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Hyaline Cartilage
|
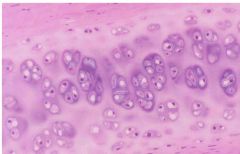
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Hyaline Cartilage because the cells are inside a lacuane and hyaline cartilages don't stain dark so the matrix looks smooth.
|
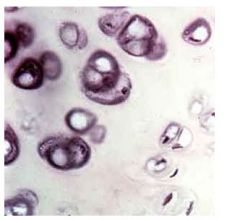
Name this tissue and why is it that tissue
|
|
|
|
Dense Regular CT Proper (nucles is wiggly)
|

Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Reticular
|
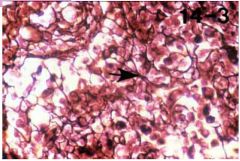
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Elastic Cartilage because it has chondracytes in lacunaes and lots of elastic fibers.
|
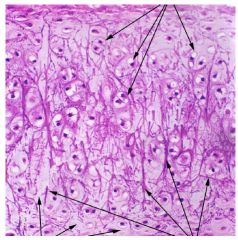
Name this tissue and why
|
|
|
|
Fibrocartilage
|
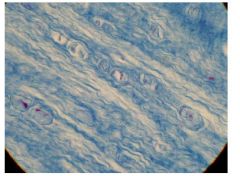
Name this tissue
|
|
|
|
Areolar CT
|
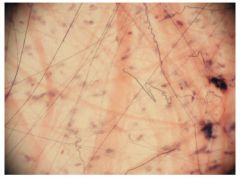
Name this tissue
|
|

