![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
define systematics?
|
the scientific study of biological diversity and its evolutionary history
|
|
|
define taxonomy?
|
the identification, naming, and classifying of species.
|
|
|
Who is known as the father of botany?
|
Theophrastus (370-285 B.C.)
|
|
|
Phylogenetic tree:
|
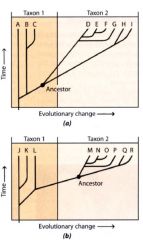
depict the genealogic relationships between taxa as hypothesized by a particular investigator.
|
|
|
monophyletic:
|
(of a group of orgnaisms) descended from a common ancestor or ancestral group, especially one not shared with any other group.
|
|
|
polyphyletic:
|
(of a group of organisms) derived from more than one common evolutionary ancestor or ancestral group.
|
|
|
paraphyletic:
|
group contains its last common ancestor but does not contain all the descendants of that ancestor or ancestral group, but not including all the descendant groups.
|
|
|
homologous:
|
structures which have a common origin but not necessarily a common function.
|
|
|
analogous:
|
structures from the result of convergent evolution. Structures with similar functions and superficial appearances but have an entirely different evolutionary background.
|
|
|
Cladistics:
|
- most widely used method of classifying organisms today
- a form of phylogenetic analysis that explicitly seeks to understand phylogenetic relationships - focuses on the branching of one lineage from another in the course of evolution. - attempts to ID monophyletic groups (clades) |
|
|
Cladogram:
|
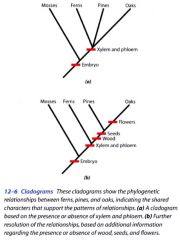
provides a graphical representation of a working model (hypothesis) of the phylogenetic relationships of a group of organisms.
|
|
|
Principle of parsimony:
|
- fundamental principle of cladistics
- cladogram should be constructed in the simplest, least complicated and most efficient way - preferred to have more statements of homology and fewest of analogy. |
|
|
molecular clock:
|
uses the rate at which proteins (nucleic acids) shared by different groups of organisms changed over time as an indication of when those groups diverged from a common ancestor.
|
|
|
serial endosymbiotic theory:
|
both mitochondria and chlorplast are believed to be the descendants of bacteria that were taken up and adopted by some ancient host cell.
|
|
|
endosymbionts:
|
organism that lives within another, dissimilar organism.
|
|
|
Phagocyte:
|
"eating cell"
a cell capable of engulfing large particles such as bacteria. |
|
|
Origin of a photosynthetic eukaryotic cell from a heterotrophic prokaryote
|
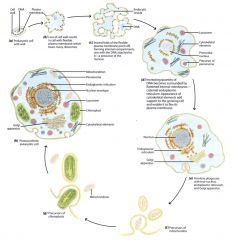
a) most prokaryotes contain a rigid cell wall, initial step in the transformation was a loss of the prokaryote's ability to form a cell wall
b)/c) now has ability to increase in size, change shape, engulf extracellular objects by infolding of the plasma membrane (endocytosis), resulting in the formation of endocytic vesicles. d)/e) internalization of a patch of the plasma membrane to which DNA was attached was the probable precursor of the nucleus. increased quantity of DNA. Cytoskeleton developed to provide inner support for the wall-less cell. f) mitochondria had their origin as bacterial endosymbionts, which ultimately transferred most of their DNA to the host's nucleus. g) chloroplasts also are descendants of bacteria. |
|
|
Some characteristics of plants:
|
- multicellular
- composed of eukaryotic cells that contain vacuoles and are surrounded by cell walls that contain cellulose. - get nutrition through photosynthesis. |
|
|
describe the reproduction in plants:
|
reproduction in plants is primarily sexual, with cycles of alternating haploid and diploid generations.
|
|
|
gametophyte:
|
the haploid, gamete-producing generation in plants.
|
|
|
sporophyte:
|
the diploid, spore-producing generation in plants.
|
|
|
What may be the reason that the sporophyte is the larger,complex, nutritionally independent generation in vascular plants:
|
Diploidy permits the storage of more genetic information generation in vascular plants.
|

