![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
75 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
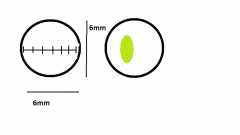
Using the left image as a reference, estimate the length and width of the shape in the right image. |
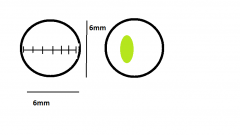
L: 2.6mm
W: 1.3mm Or L: 2600μm W: 1300μm (1μm = 1 micrometer = 0.001mm) |
|

Draw or imagine what this letter would look like when viewed in a compound light microscope.
|

The image will have been completely inverted on both the x - and y | axes.
|
|
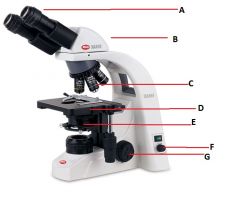
Identify these parts as best as you can.
|
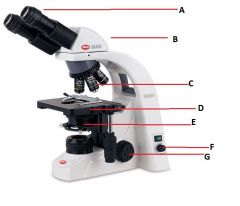
A) Eyepieces
B) Head C) Objective lenses D) Stage (Where it all happens) E) Condenser F) Lamp intensity knob G) Coaxial focus adjustment knob (Co- meaning together and -axial meaning axis form this word. This means that two objects, in the case focus adjustment knobs, share the same axis of rotation.) |
|
|
-------------------------------10x
Scanner (4x) - A Low power(10x) - B High Power(40x) - C Very High Power(100x) D Enter the values of A to D by multiplying the given values. |
A 40x
B 100x C 400x D 1000x Make sure to always include "x" after your value when writing the value of magnification. |
|
|
Staining of cells is a common procedure in labs.
Why do we do this? |

We stain cells since many organic tissues are difficult to view under a microscope.
Different parts of a cell will require different types of stain depending on the chemical composition and compatibility of these two. |
|
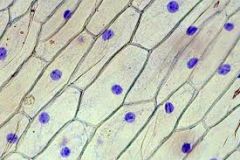
What is the name of the blue shapes display in the image above?
A- Pigments B- Nucleus C- Nucleolus D- Nucleoid |
B- Nucleus
The nucleus is often visible in eukaryotic cells when stained and viewed under a microscope. |
|

What is this common laboratory instrument called?
A- Microscope B- Electron microscope C- Dissecting microscope D- Optical transmission microscope |

C- Dissecting microscope
Notice that this microscope does not have a stage as on a compound light microscope. |
|
|
If a particle is viewed under a microscope and observed as apparently vibrating in all directions in a random fashion, we can say that we are observing the phenomenon known as:
A- Brownian movement B- Diffusion C- Solubility D- Active transport |
A- Brownian movement
|
|
|
If you wanted to increase the speed at which NaCl (salt) diffused (spread through) a liquid, what factor could you play with to aid this?
|
Actually, there are many factors for a solvent that will affect the diffusability of the solute. Some are temperature, kinetic energy (shaking or stirring the solution), or the viscosity of the solution.
|
|
|
What is the difference between brownian movement and diffusion?
|
When a solute is deposited in a solvent, its overall set of molecules will have a tendency to spread in the direction of lower solute concentration.
Individual particle will still exhibit brownian movement, but the environment in which they will move at random will impinge directional restrictions. |
|
|
If two particles of differing mass are equally energized, which will move the furthest in the same amount of time during their diffusion in the same solvent?
The heaviest particle? The lighter particle? |
The lighter particle will move the furthest.
Consider using what strength you have to move two different objects. One of the objects is much heavier than the other. Which of the objects will you be able to move more easily and further in the same amount of time? Obviously the lighter object. |
|
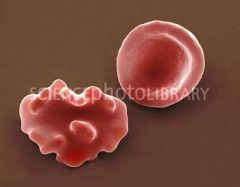
On the right is a healthy red blood cell. The cell on the right is also a blood cell but it is not so healthy.
Why is that? A It has contracted a disease B It is mutated C It has been subjected to a hypertonic environment D It has been subjected to a hypotonic environment |
C - The blood cell has undergone 'crenulation' from being subjected to a hypertonic environment. This means that there was a higher concentration of solutes outside of the cell. Hypertonicity when relative to the cytoplasm induces the outwardly diffusion of liquid from the cell.
Crenulation refers to the /\/\/\/\ shape of the cell walls. Crena is latin for notch. |
|
|
The term turgidity refers to what?
A The permeability of a cell's wall B The movement of particles in a fluid when heated C The tonicity a cell D The firmness of a membrane as a result of pressure from a liquid inside of it |
D Turgidity refers to how much pressure a plant cell exhibits on its cell walls is as a result from being filled with a liquid.
|
|
|
What is isotonicity?
A More solutes within relative to without a cell. B More solutes without relative to within a cell. C As many solutes within relative to without a cell. D The lack of solutes in both cells and the environment. |
C As many solutes within relative to without.
Iso- = equal -or-> = = = Agree? |
|
|
What is an allele?
A A visibly apparent characteristic B The sum of all the genetic material in a cell C A segment of DNA in the specific region on a chromosome D A variance in the genetic sequence at a specific locus |
D A variance in the genetic sequence at a specific locus.
The locus is the location in the chromosome where the genetic material attributed to a particular character can be found. Alleles, variations found at a locus (location), correspond to traits. |
|
|
If your genetic material at a specific locus is heterozygous are you more likely to exhibit the phenotypical expression of the L (dominant) or of the l (recessive) trait?
|
You would be more likely to exhibit the trait of the dominant -L- allele for that particular character.
|
|
|
DNA is composed of __ bases.
A 4 B 64 C 5 D 32 |
A 4
They are adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. |
|
|
"A" is adenine, "T" is thymine, and "G" is guanine, what is "C"?
|
Cytosine.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a restriction enzyme?
A To prevent loss of water from the cell membrane B A special type of enzyme that splits DNA at a specific location within a sequence C A mechanism by which cells absorb nutrients within their membrane to then digest them D To improve the movement of DNA strands within a gel in the process of gel electrophoresis. |
B A special type of enzyme that splits DNA at a specific location within a sequence.
EcoRI (pronounced, "eco R one") for example splits DNA between the G and the A in the sequence GAATTC. |
|
|
EcoRI is a restrictive enzyme that will split DNA between the G and the A in the sequence GAATTC.
How many strands of DNA would we be left with were to to subject the following sequence to the EcoRI enzyme? GTAAGAATTCTTTAGAATTCCGCCATTATCGAATTCAGGATCTTAC |
4 sequences would be given.
They are as follow: GTAAG AATTCTTTAG AATTCCGCCATTATCG AATTCAGGATCTTAC |
|
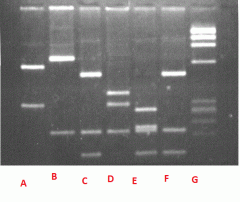
Suppose that C be the DNA obtained at a crime scene and that the other samples be of suspect DNA.
Which of the samples would be a match from the crime scene? |
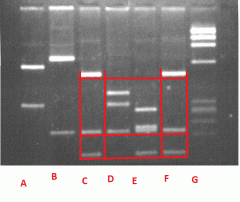
F would be the match to the crime scene C.
|
|
|
What is lysis?
A- The process of breaking down parts of a cell B- The separation of organelles using test tubes rotating at high velocity C- The procedure of preparing a wet mount using colorants D- The extraction of DNA from a cell for further experimentation |
A-
Cell lysing is the process of, for example, breaking down the plasma and nuclear membrane for the purpose of isolating DNA. |
|
|
What was the appearance of the DNA we obtained in test tubes after having subjected onion matter to lysing and isolation?
|
It had a white and stringy structure.
|
|
|
Suppose that we were to subject a sequence of 8 nucleotides to the process of gel electrophoresis.
Knowing that a single nucleotide would travel 30 mm in x amount of time, how far would our sequence travel in the same amount of time? So - 30mm / 8 = y Find the value of y. = ] |
y= 3.75 mm
|
|
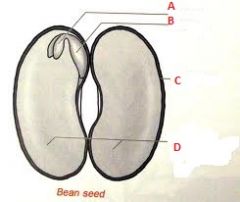
Associate the following terms to the letters above.
This is a dicot seed. Pericap, radicle, cotyledon, endosperm, plumule, seed coat. |
A- Plumule
B- Radicle C- Seed Coat D- Cotyledon |
|
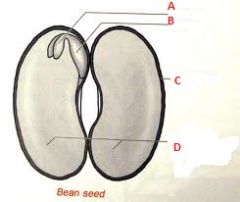
Associate the following terms to the letters above.
This is a monocot seed. Pericap, radicle, cotyledon, endosperm, plumule, seed coat. |
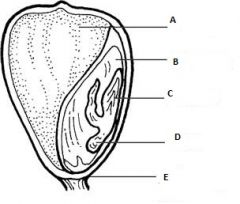
A- Endosperm
B- Cotyledon C- Plumule D- Radicle E- Pericarp |
|
|
What is the difference between a monocot and a dicot seed?
|
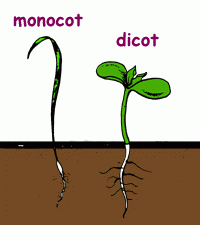
The cotyledons.
Mono-cots have one Di-cots have two |
|
|
Flowering vascular plants are known as:
A Perenials B Flowering plants C Endosperms D Angiosperms |
D- Angiosperms
New Latin, from Greek angeio-, from angeion, vessel, blood vessel. |
|
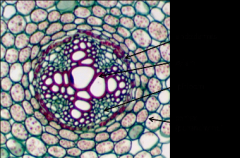
This cross section of a root is from a dicot or a monocot plant?
|
The X shape at the center of the root is characteristic of dicot plants.
|
|

This leaf is from a dicot or a monocot plant?
|

The leaf is from a dicot. The netlike veins are typical of dicot plants. Monocot plants have veins running in paralle in usually narrower leaves, like in blades of grass.
|
|
|
'Embryonic' tissue which may continue to divide throughout the life of a plant is known as:
A- Dermal tissue B- Meristem tissue C- Vascular tissue D- Phloem tissue |
B- Meristem tissue
They can be found in the apical meristem of roots and stems. Their function is growth and repair. |
|
|
Xylem tissue and Phloem tissue are two different types of vascular tissue. One of these two is composed of long, thick walled, dead cells.
Which is it? |
Xylem tissue.
They are responsible for the transportation of water throughout the organism. |
|
|
What type of tissue might we expect to find in the outermost layer of a stem?
A Vascular Tissue B Ground tissue C Meristem tissue D Dermal tissue |
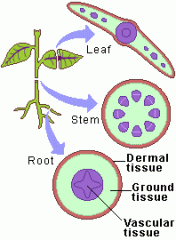
D Dermal tissue.
Dermal means skin. |
|
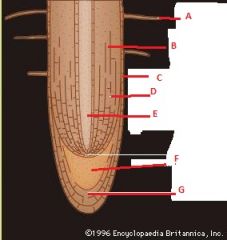
Identify these parts.
|
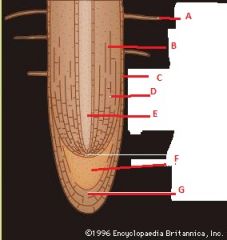
A Root Hair
B Cortex C Epidermis D Cortex E Vascular cylinder F Apical meristem G Root cap |
|
|
Were a stem to be hard and brown, would it more likely be a woody or herbaceous type of stem?
|

Woody stem.
|
|
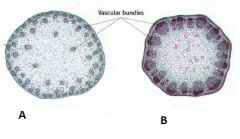
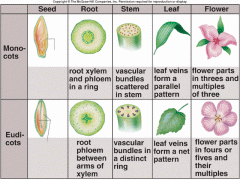
Considering the arrangement of vascular tissue in the cross section of these two stems, which do you think is from a dicot plant and which is from a monocot?
|
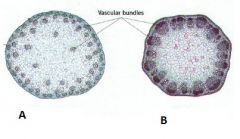
A Monocot
B Dicot I think that dicot plants, in general, seem to be more complex or advanced. We can see this here by the concrete organization of the vascular tissue compared to the more or less unorganized vascular tissue of the monocot. |
|
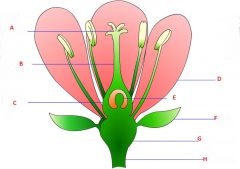
Attribute the following terms to their respectful location in the above image.
Pollen sack, Filament, Receptacle, Stem, Petals, Style, Stigma, Anther, Stamen, Ovary, Ovules, Sepals |
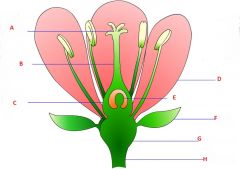
A- Stigma
B- Style C- Ovary D- Petals E- Ovules F- Sepals G- Receptacle H- Stem |
|
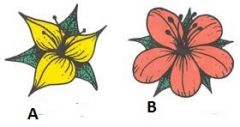
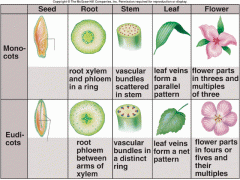
Which of these flowers is from a monocot plant and which is from a dicot plant?
|
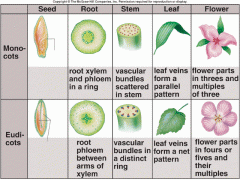
A- Monocot
B- Dicot |
|

How many petals might we expect to find in a flower of the plant to which this leaf belongs?
A- 3 B- 6 C- 5 D- 4 |
C- 5
The plant is from a dicot-type of plant. Dicots typically have 5 petals in their flowers. |
|
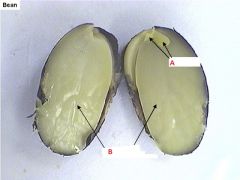
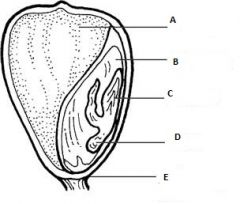
Name the indicated structures.
Is this a monocot or a dicot seed? |
A- plumules
B- Cotyledon This is a dicot seed, we know this from the presence of two cotyledons. We can assume that the leaves of this plant will have web-like veins. |
|
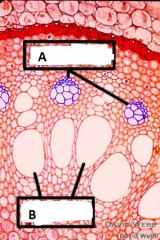
In this cross section of a root both types of vascular tissue, phloem and xylem, are indicated. Which is which?
|
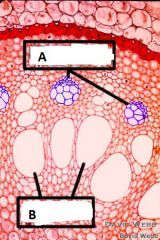
A Phloem
B Xylem |
|
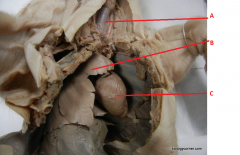
What is are the names of the indicated organs?
|
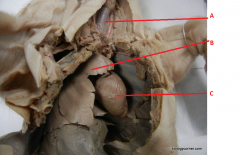
A- trachea
B- Lung C- Heart |
|
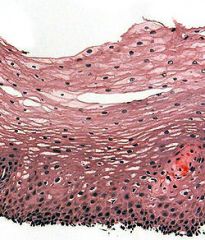
Epithelial tissue is a type of tissue that covers the surface of certain organs or organisms.
Which type of epithelial tissue is this one? A- stratified squamous B- stratified columnar C- simple squamous D- simple cuboidal |
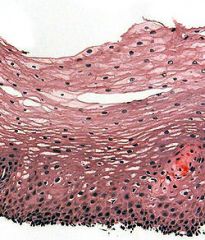
A- Stratified squamous epithelial tissue
The area on the bottom of the image is called the germinal layer. Cells here do perform division. |
|
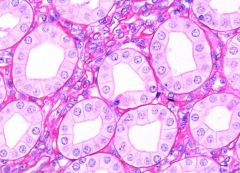
`Which type of epithelial tissue is this?
A- stratified squamous B- stratified columnar C- simple squamous D- simple cuboidal |
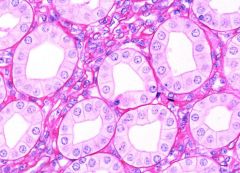
D- Simple cuboidal.
These often make up tubular structures as can be seen in the image. They also have large nuclei. |
|
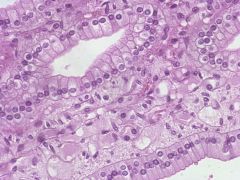
`Which type of epithelial tissue is this?
A- stratified squamous B- stratified columnar C- simple squamous D- simple columnar |
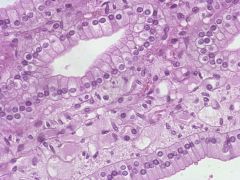
D- Simple columnar
The squarish or rectangular shape that can be observed when view above is typical of this type of epithelial tissue. |
|
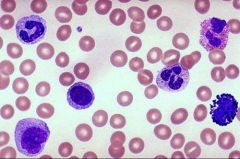
The large cells with big nuclei in the above image of blood are known as what?
A- Erythrocytes B- Thrombocytes C- Leukocytes D- Red blood cells |
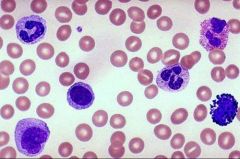
C- Leukocytes or white blood cells
The smaller cells in the image are erythrocytes, or red blood cells. |
|
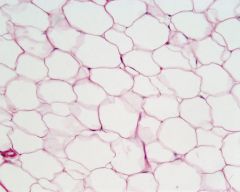
Which type of connective tissue is displayed in the image above?
A- Adipose tissue B- Loose connective tissue C- Fibrous connective tissue D- Smooth muscle tissue |
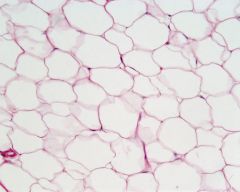
A- Adipose tissue
This is what fat is composed of. |
|

Would you consider the image above to be loose connective tissue or fibrous connective tissue?
|

It is fibrous connective tissue. This image is from a tendon.
|
|
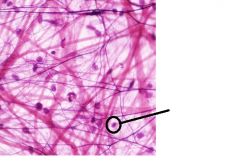
Here is an image of loose fibrous tissue.
What is the name of the designated structure? A- Areolar B- Chondrium C- Cell D- Fibroblasts |
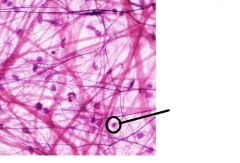
D- Fibroblasts
These are cells with large nuclei found in loose connective tissue. |
|
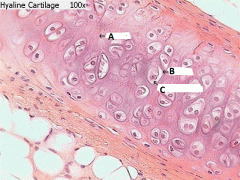
Here is an image of cartilage tissue.
Cells found within the tissue are called -chondrocytes, the substance (matrix) in which they are suspended is known as -chondrium, and each cell has its own encasing known as a -lacuna. Attribute these terms to the labels in the image. A- B- C- |
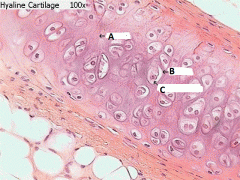
A- Chondrium
B- Lacuna C- Chondrocytes |
|
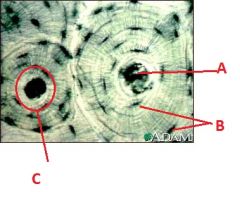
Label this image of bone tissue using the information from page 7.5 of your lab manual.
|
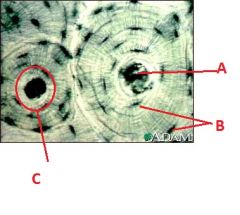
A-Central canal
B-Osteocytes C- Osteum |
|
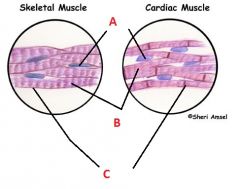
Associate the following terms to their appropriated label.
Sarcolemma, Sarcoplasm, Nucleus. |
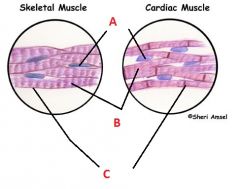
A- Nucleus
B- Sarcoplasm C- Sarcolemma |
|
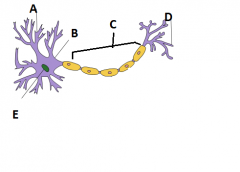
Label this figure of a neuron using the following terms:
Nucleus, Axon, Axon terminal, Cell body, dendrites. |
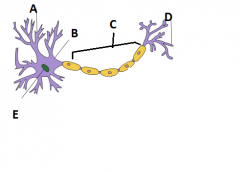
A- Dendrites
B- Cell body C- Axon D- Axon terminal E- Nucleus |
|
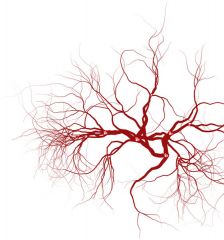
Which organ is in this image?
What is it responsible for? |
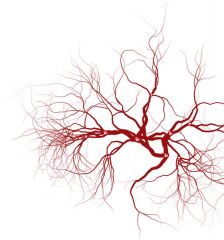
These are veins.
They are responsible for carrying the oxygen-deprived blood back to the heart. |
|
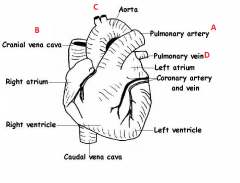
Which of these structures are receiving blood and which are responsible for sending it back into the body?
Receiving - Resending- |
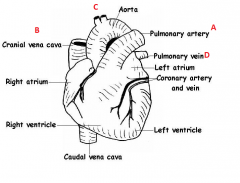
Receiving - B, D
Resending - A, C |
|
|
Name the 3 main domains.
|
They are Archaea, Eukarya, and Bacteria.
|
|
|
In scientific nomenclature, how many terms make up the name of an animal?
What are these two terms representative of? |
2 names. Example: Homo Sapien
The first is the genus and the second is the species. |
|
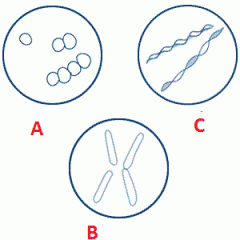
Associate the following terms to their appropriated letter.
Bacillus, coccus, spririllum. |
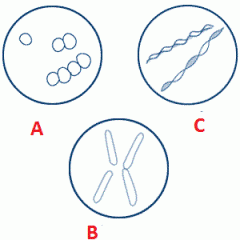
A- Coccus
B- bacillus C- Spirillum |
|
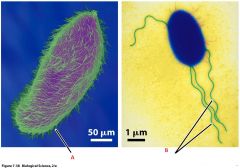
Here are two motile unicellular organisms.
What are the names of the structures that allows them to move about? |
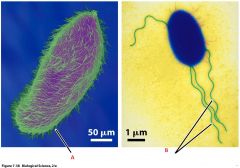
A- Cilia
B- Flagella |
|
|
Cyanobacterias are distinct for being entirely photoautotrophic.
What does this mean? A- They obtain energy from sunlight B- They do not obtain energy from sunlight C- They are in a symbiotic relationship with a photosynthesizing organism D- Their functioning is hindered by sunlight |
A- They obtain energy from sunlight.
|
|
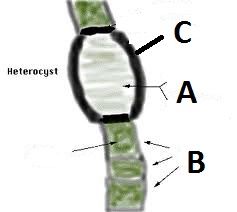
Here is a heterocyst, a type of cell created by certain species of cyaniobacteria for the purpose of obtaining nitrogen.
Knowing that cyanobacteria are photoautotrophs, meaning that they obtain energy from the sun, sometimes with chloroplasts, which part of this cell do you think is the heterocyst cell and which part is the cyanobacteria? |
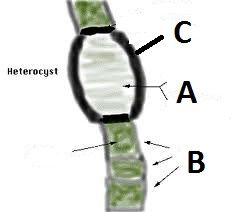
A- Is the heterocysts
B- Is the cyanobacteria We know this because the green is typical of photoautotrophic organisms. |
|

What is this eukaryotic cell known as?
Notice the slit running down its hard "shell", and the green colour typical of photoautotrophic organisms. |

A diatom.
|
|

Here is an image of brown algae, a multicellular eukaryote. One of these letters is pointing at the part know as the "receptacle" responsible for the production of gametes (sexual cells) which the other letter is pointing at the "bladder" responsible for suspending the organism within the water.
|

A- Receptacle
B- Bladder |
|

A- Is this organism multicellular or unicellular?
B-In which domain would you fit it (bacteria, eukarya)? C- What is the purpose of the hair-like structures covering the edges of this organism? D- Judging by its colour, what can we assume is one of its characteristics? |

A- Multicellular
B- Eukarya C- Cilia, for movement. D- We can assume that it is photoautotrophic. |
|

This is ab ameoba.
What is the name of the organism's protrusions? A- Cilia B- Achinetes C- Holdfasts D- Pseudopodia |
D- pseudopodia
Pseudo- - false -Podia - relating to legs |
|

In which kingdom would you classify this organism as being in?
A- Stramenopila B- Alveolata C- Fungi D- Animalia |

C- Fungi
Here is a zygosparngium. |
|

In which kingdom would you classify this organism (Volvox)?
A- Rhodophyta B- Chlorophyta C- Alveolata D- Euglenozoa |
B- Chlorophyta
|
|
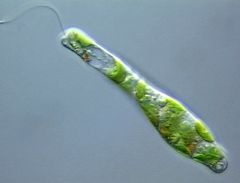
In which kingdom would you classify this organism?
A- Rhodophyta B- Chlorophyta C- Alveolata D- Euglenozoa |
D- Euglenozoa
|
|
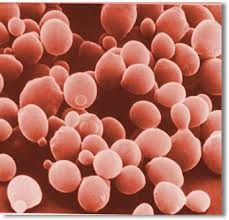
The above cell is sometimes difficult for scientists to classify due to their specialized life cycles.'
These cells can be seen reproducing asexually by a process called "budding". What type of cell is this? In which kingdom are they classified? |
Yeast cells.
Fungi kingdom. |
|

This appears to be a single organism, in fact it is not. There is a fungus and probably a green algae benefiting from one another in a special relationship of mutual gain.
What type of relationship is this? |
It is known as a mutual symbiotic relationship.
|
|

Here is a glass sponge. What type of symmetry is it exhibiting?
A- Bilateral B- Radial C- none |
B- Radial
|
|
|
An organism with an endoskeleton, radial symmetry, and a 1-chambered heart would fall into which phylum within the animalia kingdom?
|
Echinodermata
|
|
|
What is the simplest phylum within the animalia kingdom to have organ systems made of specialized tissues?
|
Platyhelminthes - Flatworms.
Platy- is greek for flat. Similar to "plat" in french. |
|
|
Without looking at your notes. Which phylum of the animalia kingdom do you belong to?
|
Chordata.
Lab 10 was devoted to this phylum. |
|
|
Under which phylum might you expect to find octopi?
Are they bilaterally or radially symmetrical? |
They fall under the mollusca phylum.
They are bilaterally symmetrical. |

