![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Extinction events: |
End Ordovician Late Devonian End Permian End Triassic K/T (Cretaceous - paleogene) |
|
|
Three domains based on: |
Ribosomal RNA base sequences |
|
|
Fungal filament: |
Mycelium |
|
|
Extra cellular virus: |
Viron |
|
|
Deciduous gymnosperm: |
Larch + ginkgo |
|
|
Constanza et al know for: |
Ecosystem services costs |
|
|
Insect metamorphosis types: |
Hemimetabolous and holometabolous |
|
|
Earliest prokaryote fossil: |
3.5mil |
|
|
Arthropod success due to: |
Ability to change to environment |
|
|
Cladode: |
Flattened photosynthetic |
|
|
Cannot tell moss/liverwort apart by |
Thickness of leaves |
|
|
Arthropod cuticle made of : |
Chitin Proteins |
|
|
Major arthropod sub divisions: |
Chelicerata Myriapoda Crustacea Hexapoda Trilobitomorpha |
|
|
Percentage of animals that are Arthropoda: |
Around 85% |
|
|
Sleeping sickness caused by: |
Trypanosome protazoan |
|
|
Red algae is a: |
Rhodophyta |
|
|
Edicarian fossils |
600 mya |
|
|
Echinoderms have a unique |
Water vascular system |
|
|
Earliest avian fossil: |
150 mya from Jurassic |
|
|
Arthropod share with Annelids: |
Through gut, central nerve system and dorsal circulatory system |
|
|
Chordata defining features: |
Post anal tail Gill arches Pharyngeal slits Notochord Dorsal hollow nerve cord |
|
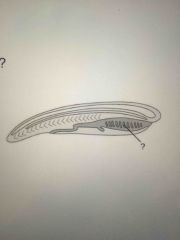
What is this? |
Pharyngeal slits |
|
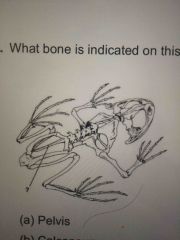
|
Urostyle |
|
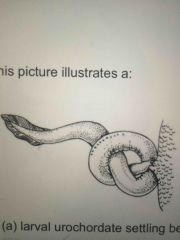
|
Hagfish feeding |
|
|
Bird species |
9,900 |
|
|
Flight needs: |
Lift and thrust |
|
|
Two theory's of flight evolution |
Ground up and trees down |
|
|
Two theory's of flight evolution |
Ground up and trees down |
|
|
Reasons for flight evolution |
Predators Prey Travel Niches Hind legs as weapons |
|
|
Two theory's of flight evolution |
Ground up and trees down |
|
|
Reasons for flight evolution |
Predators Prey Travel Niches Hind legs as weapons |
|
|
Features of avian skeleton: |
Keeled sternum Fused pelvis Beak and gizzard Short tail Uni are processes in ribs Limbs moved by central muscles |
|
|
disadvantages of flight |
Energetically costly Limits body size and morphology Can be lost |
|
|
Lancelet features |
Notochord Tail Pharyngeal slits Dorsal hollow nerve chord Filter feed using mucous net |
|
|
Tunicates |
Pharynx with slits Notochord Tail Dors hollow nerve chord Marine filter feeder adults benthic and sessile Planktonic larva are chordates |
|
|
Hagfish and lamprey features |
Large brain Skull Eyes Teeth |
|
|
Hagfish and lamprey features |
Large brain Skull Eyes Teeth |
|
|
Jaws |
Evolved mid Ordovician Allow efficient feeding |
|
|
Hagfish and lamprey features |
Large brain Skull Eyes Teeth |
|
|
Jaws |
Evolved mid Ordovician Allow efficient feeding |
|
|
Chondrichthyes (shark) features |
Cartilaginous skeleton Well developed jaw and paired fins Carnivore No swim bladder Good sense of smell and lateral line system Internal fertilisation Oviparous and viviparous |
|
|
Actinopterygii (fin fish) features |
Ossified skeleton Skin covered in scales and mucous Swim bladder Teleosts Most external fert. Ovoviviparous or viviparous |
|
|
Living organisms capable of: |
Growth Reproduction Metabolism |

