![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Palmitic acid |
CH₃(CH₂)₁₄COOH
16:0
106 ATP from degradation |
|
|
Stearic Acid |
CH₃(CH₂)₁₆COOH
18:0
120 ATP from degradation |
|
|
Palmitoleic acid |
CH₃(CH₂)₅CH=CH(CH₂)₇COOH
16:1Δ9
Omega-7 fatty acid
104.5 ATP from degradation |
|
|
Oleic acid |
CH₃(CH₂)₇CH=CH(CH₂)₇COOH
18:1Δ9
Omega-9 fatty acid
118.5 ATP from degradation |
|
|
Linoleic acid |
CH₃(CH₂)₅CH=CH(CH₂)CH=CH(CH₂)₇COOH
18:2Δ9,12
Omega-6 fatty acid
Pro-inflammatory cytokines
116 ATP from degradation |
|
|
Linolenic acid |
CH₃CH₂CH=CH(CH₂)CH=CH(CH₂)CH=CH(CH₂)₇COOH
18:3Δ9,12,15
Omega-3 fatty acid
Anti-inflammatory cytokines
113.5 ATP from degradation |
|
|
Triacylglycerol |
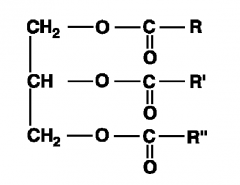
-Anhydrous molecule -Stores energy in adipose tissue -Glycerol backbone with 3 fatty acids |
|
|
TAG synthase complex |
-Active in liver and adipose cells -Formation of triacylglycerols from glycerol and activated fatty-acid components |
|
|
Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
TAG synthase complex step 1
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate + NADH --->
Glycerol-3-phosphate + NAD+ |
|
|
Glycerol kinase |
TAG synthase complex step 1 (alternate)
Dietary glycerol + ATP --->
glycerol-3-phosphate + ADP |
|
|
Glycerophosphate acyltransferase |
TAG synthase complex step 2
Glycerol-3-phosphate + FA-SCoA -->
Lysophosphatidate (LPA) + HSCoA
|
|
|
Lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase |
TAG synthase complex step 3
LPA + FA-SCoA -->
Phosphatidate + HSCoA |
|
|
Phosphatidate phosphatase |
TAG synthase complex step 4
Phosphatidate + H2O -->
Diacylglycerol (DAG) + Pi
|
|
|
Diacylglycerol acyltransferase |
TAG synthase complex step 5
DAG + FA-SCoA -->
Triacylglycerol + HSCoA |
|
|
VLDL |
Very Low Density Lipoprotein
-Constructed in liver tissue -Carries TAGs and Cholesterol-esters -Surrounded by phosphatidyl-choline and cholesterol monolayer -Apo-C II complexed lipoprotein -Deliver TAGs to adipose tissue |
|
|
CTP:PA transferase |
Phosphatidate activation for modification
Phosphatidate + CTP -->
CDP-Diacylglycerol + PPi |
|
|
Phosphatidyl inositol synthase |
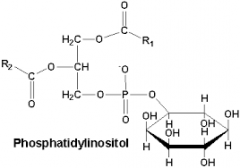
PI synthesis
CDP-DAG + Inositol -->
Phosphatidyl inositol + CMP
|
|
|
Phosphatidyl glycerol synthase |
PG synthesis step 1
CDP-DAG + Glycerol-3-P -->
Phosphatidyl glycerol-3-P + CMP |
|
|
Phosphatidyl glycerol phosphatase |
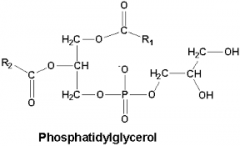
PG synthesis step 2
Phosphatidyl glycerol-3-P + H2O -->
Phosphatodyl glycerol + Pi |
|
|
Cardiolipin synthase |
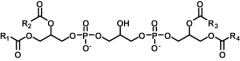
CL synthesis
CDP-DAG + Phosphatidyl glycerol -->
Cardiolipin + CMP |
|
|
Choline kinase |
PC synthesis step 1
Choline + ATP -->
Phosphocholine + ADP |
|
|
CTP:Phosphocholine transferase |
PC synthesis step 2
Phosphocholine + CTP -->
CDP-choline + DAG + PPi |
|
|
CDP-choline:DAG transferase |
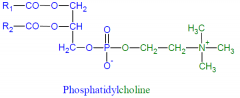
PC synthesis step 3
CDP-choline + DAG -->
Phosphatidylcholine + CMP |
|
|
Phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyl transferase |
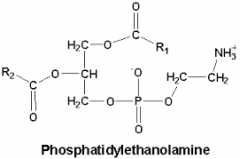
Methylation of PE to PC
PE + 3 S-adenosyl methionine -->
PC + 3 S-adenosyl homocysteine |
|
|
Phosphatidylserine synthase I |
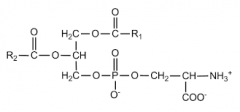
PS synthesis
PC/PE + serine -->
Phospatidylserine + Choline/ethanolamine |
|
|
Phosphatidylserine decarboxylase |
PE synthesis from PS
PS -->
PE + CO2 |
|
|
Sphingolipids |
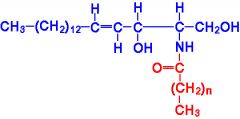
-Amphipathic membrane lipids -Sphingosine backbone from palmitate and serine derivatives containing a trans bond and a hydroxyl group on C3 -Different head groups with different charges, polarity, etc. |
|
|
Ceramide |
-Sphingolipid with one fatty acid |
|
|
Sphingomyelin |
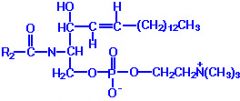
-Sphingolipid with phosphocholine on C1 -Major component in myelin sheath |
|
|
Cerebroside |
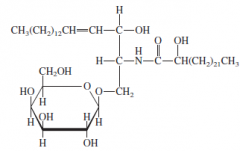
-Sphingolipids with glucose or galactose group of C1 -Polar head group -Isolated from nerve sheaths |
|
|
Ganglioside |
-Sphingolipid with complex oligosaccharide group on C1 |
|
|
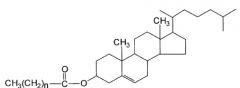
Cholesterol |
-Synthesized in liver from acetyl-CoA, promoted by insulin -Amphipathic due to polar OH group -Component of cell membranes -Synthesizes steroids and cortisol in adrenal tissue |
|
|
Thiolase (cytoplasmic) |
Cholesterol synthesis step 1
2 Acetyl-CoA <---> Acetoacetyl-CoA + HSCoA |
|
|
HMG-CoA synthase |
Cholesterol synthesis step 2
Acetoacetyl-CoA + Acetyl-CoA -->
B-hydroxy-B-methylglutary-CoA + HSCoA |
|
|
HMG-CoA reductase |
Cholesterol synthesis step 3
HMG-CoA + 2 NADPH + H+ -->
Mevalonate + HSCoA + 2 NADP+
Key regulatory enzyme Upregulated by insulin Downregulated by glucagon Inhibited by cholesterol |
|
|
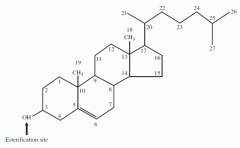
Acyl-CoA-Cholesterol acyl transferase |
Cholesterol ester biosynthesis
Cholesterol + Acyl-CoA -->
Cholesterol ester + HSCoA
Activated by cholesterol |
|
|
Lipoprotein lipase |
-Recognize surface proteins of VLDL/LDL and catalyze reaction:
TAG + 3 H2O --> 3 FA + glycerol
-Products cross over into tissues and resynthesized |
|
|
Acyl-CoA synthetase |
Fatty-acid activation
FA + CoA + ATP --> Acyl-CoA + AMP |
|
|
LDL |
Low Density Lipoprotein
-Carries cholesterol-esters -Surrounded by phosphatidyl-choline and cholesterol monolayer -Apo-B 100 complexed lipoprotein -Deliver CEs to extrahepatic tissue |
|
|
Cholesterol esterase |
Uptake of cholesterol
CE + H2O --> Cholesterol + 1 FA |
|
|
Bile Salts |
-Synthesized in liver -50% of new cholesterol converted to bile salts -Stored in gall bladder, delivered to small intestine -Isolate TAGs for digestion -95% returned to liver from small intestine via receptors |
|
|
Oxidation of cholesterol by Cytochrome P450 |
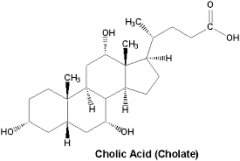
Bile salt synthesis |
|
|
Covalent attachment of glycine to cholic acid |
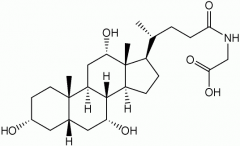
Bile salt synthesis |
|
|
Covalent attachment of taurine to cholic acid |
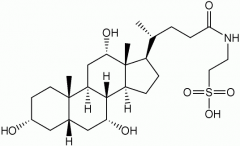
Bile salt synthesis |
|
|
Cholestyramine |
-Non digestible positively charged polymer -Attracted to charged bile salts (taurocholic acid) -Block re-absorption of bile salts |
|
|
HDL |
High Density Lipoprotein
-Synthesized in liver and intestinal cells -Protein rich particle scavenges excess cholesterol in the bloodstream -Contains LCAT -Cholesterol converted to CEs and transported back to liver
|
|
|
Lecithin-cholesterol acyl transferase |
Esterification of cholesterol
Cholesterol + lecithin --->
Cholesterol ester + Lysolecithin |
|
|
Plasmalogen |
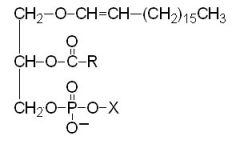
-Found in myelin sheaths -X = CH2-CH2-NH3+
|
|
|
Prenyl group |
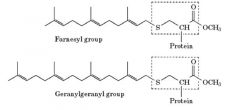
-Synthesized from squalene -Bulky |
|
|
pancreatic TAG lipase |
Digestion of dietary fats
TAG + 2 H2O -->
Monoacylglyceride (A2 position) + 2 FA
**Colipase cofactor |
|
|
Orlistat |
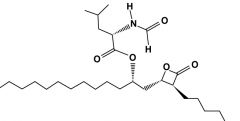
Competitive inhibitor of TAG lipase |
|
|
Pancreatic A2 lipase |
Digestion of dietary fats
MAG + H2O --> glycerol + FA
|
|
|
Chylomicrons |
-Less dense than VLDL/LDLs, but much larger -Constructed in intestinal cells -90% TAG composition, 4% CE composition -Deliver TAGs to adipose, muscle and mammary tissue -Return to liver for recylcling |
|
|
Perilipin |
Storage protein associated with phospholipid monolayer surrounding TAGs in adipose tissue |
|
|
Hormone Sensitive Lipase |
-HSL -Break down stored TAGs in adipose tissue (when activated) |
|
|
Protein kinase A |
Mobilization of TAGs in adipose tissue
-Activated by cAMP via hormone signaling from glucagon/epinephrine
perilipin/HSL ---> phosphorylated perilipin/HSL
|
|
|
Serum albumin |
-Bind free FAs in bloodstream for transport ~10 FAs per protein |
|
|
Carnitine acyl-transferase I |
Fatty acid degradation
Carnitine + Acyl-CoA --> Acyl-carnitine + HSCoA
-Located on outer surface of outer mitochondrial membrane -Key regulatory step -Inhibited by Malonyl-Coa |
|
|
Carnitine carrier protein |
-Located on inner mitochondrial membrane -Antiport exchange -Acyl-carnitine into mitchondrial matrix in exchange for carnitine(mit) |
|
|
Carnitine acyl-transferase II |
Fatty acid degradation
Acyl-carnitine + HSCoA --> Acyl-CoA + carnitine |
|
|
Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase |
β-oxidation of Fatty acids step 1
Acyl-CoA + FAD -->
trans Δ2 Enoyl-CoA + FADH2 |
|
|
Enoyl-CoA hydratase |
β-oxidation of Fatty acids step 2
trans Δ2 Enoyl-CoA + H2O -->
L-3-hydroxylacyl-CoA |
|
|
Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase |
β-oxidation of Fatty acids step 3
L-3-hydroxylacyl-CoA + NAD+ -->
3-ketoacyl-CoA + NADH + H+ |
|
|
Thiolase (mitochondrial) |
β-oxidation of Fatty acids step 4
3-ketoacyl-CoA + HSCoA -->
Acyl-CoA + Acetyl-CoA |
|
|
Δ3,Δ2 Enoyl-Coa isomerase |
β-oxidation of Fatty acids (skip step 1)
cis Δ3 Enoyl-CoA --> trans Δ2 Enoyl-CoA |
|
|
2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase |
β-oxidation of Fatty acids
trans Δ2, cis Δ4 Enoyl-CoA + NADPH + H+ -->
trans Δ2 Enoyl-CoA |
|
|
Propionyl-CoA carboxylase |
β-oxidation of Fatty acids
Propionyl-CoA + HCO3- + ATP -->
D-Methylmalonyl-CoA + ADP + Pi
*biotin cofactor |
|
|
Methylmalonyl-CoA epimerase |
β-oxidation of Fatty acids
D-Methylmalonyl-CoA --> L-Methylmalonyl-CoA |
|
|
Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase |
β-oxidation of Fatty acids
L-Methylmalonyl-CoA --> Succinyl-CoA
*B12 coenzyme |
|
|
Pepsin |
Digestive enzyme, active in the stomach at pKa = 2 |
|
|
Aminopeptidase |
Digestive enzyme active in the intestine, breaks down oligopeptides |
|
|
H+ symport |
Transporter for di and tripeptides from intestinal lumen into intestine cells |
|
|
Na+ symport |
Transporter for amino acids from intestinal lumen into intestine cells |
|
|
Alanine aminotransferase |
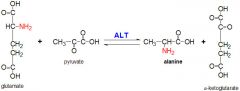
|
|
|
Glutamate dehydrogenase |
Urea cycle step 1
Glutamate + H2O + NADP+ -->
α-ketoglutarate + NADPH + H+ + NH4+ |
|
|
Carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase |
Urea cycle step 2
NH4+ + 2 ATP + HCO3- -->
Carbamoyl-phosphate + 2 ADP + Pi
Key regulatory enzyme Activation strategy 1: Acyl-P Channelling mechanism Allosterically activated by N-acetyl-glutamate |
|
|
N-acetyl-glutamate synthase |
Urea cycle regulatory step
Acetyl-CoA + glutamate -->
N-acetyl-glutamate + CoA |
|
|
Ornithine transcarbamylase |
Urea cycle step 3
Carbamoyl-P + ornithine --> citrulline + Pi |
|
|
Ornithine/Citruline translocase |
Urea cycle step 4
Citrulline + H+ ---->
<---- Ornithine (1+ charge)
Across mitochondrial membrane |
|
|
Arginino succinate synthetase |
Urea cycle step 5
Citrulline + ATP + aspartate -->
Argininosuccinate + AMP + PPi
Activation strategy 2: AMP |
|
|
Argininosuccinase |
Urea cycle step 6
Argininisuccinate <---> arginine + fumarate |
|
|
Arginase |
Urea cycle step 7
Arginine + H2O --> ornithine + urea |
|
|
Urea |
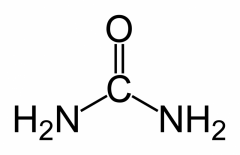
Waste product excreted by mammals in the kidneys |
|
|
Glutamate synthetase |
Glutamine biosynthesis
Glutamate + ATP + NH4+ -->
Glutamine + ADP + Pi
Activation strategy 1: Acyl-P |
|
|
Glutamate kinase |
Proline biosynthesis step 1
Glutamate + ATP --> γ-glutamyl-phosphate + ADP
Activation strategy 1: Acyl-P |
|
|
γ-Glutamyl-phosphate dehydrogenase |
Proline biosynthesis step 2
γ-glutamyl-phosphate + NADPH + H+ -->
Glutamate semialdehyde + NADP+ + Pi |
|
|
5PC reductase |
Proline biosynthesis step 3
Glutamate semialdehyde + H2O <---> 5PC + NADPH + H+ --->
Proline + NADP+ |
|
|
Asparagine synthetase |
Asparagine biosynthesis
Aspartate + ATP + Glutamine + H2O -->
Asparagine + PPi + AMP + Glutamate
Activation strategy 2: AMP |
|
|
3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase |
Serine biosynthesis step 1
3-PGA + NAD+ --> 3-phosphohydroxy pyruvate + NADH + H+ |
|
|
3-phosphoserine aminotransferase |
Serine biosynthesis step 2
3-phosphohydroxy pyruvate + glutamate -->
3-phosphoserine + α-ketoglutarate
PLP coenzyme |
|
|
3-phosphoserine phosphatase |
Serine biosynthesis step 3
3-phosphoserine + H2O --> serine + Pi |
|
|
Serine hydroxy methyl transferase |
Glycine biosynthesis
Serine + THF -->
Glycine + H2O + N5,N10 methylene THF |
|
|
PRPP synthetase |
Nucleic acid biosynthesis
Ribose-5-P <--> β-D Ribose-5-P + ATP -->
PRPP + AMP
Activation strategy 3: PPi |
|
|
Adenylosuccinate synthetase |
AMP biosynthesis step 1
Inosinate + aspartate + GTP -->
adenylosuccinate + GDP + Pi
Activation Strategy 1: Pi |
|
|
Adenylosuccinate lyase |
AMP biosynthesis step 2
Adenylosuccinate --> Adenylate (AMP) + fumarate |
|
|
IMP dehydrogenase |
GMP biosynthesis step 1
Inosinate + H2O + NAD+ -->
Xanthylate |
|
|
GMP synthetase |
GMP biosynthesis step 2
Xanthylate + Glutamine + H2O + ATP -->
Guanylate (GMP) + Glutamate + AMP + PPi
Activation Strategy 2: AMP activation
|

