![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Transcription
|
the synthesis of an RNA molecule using DNA as a template, the information is transferred into a single strand DNA
|
|
|
RNA characteristics
|
- Primarily resides in the cytoplasm, uses the sugar ribose
- DNA uses thymine, RNA uses uracil - RNA is a single stranded molecule - Made continuously in the nucleus |
|
|
Ribosomal RNA
|
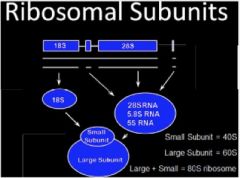
With various ribosomal proteins form the ribosomal subunit needed for protein synthesis
- Pieces needed 28 S, 5.8 S, 5 S (large subunit) - Piece for small subunit (18 S) Large (60 S) + Small (40 S) = 80 S ribosome |
|
|
Messenger RNA
|
Carry the genetic information from the nucleus to the ribosome for protein synthesis - "working copy of the genome"
|
|
|
Transfer RNA
|
- Amino Acid carriers and recognition molecules
- Identify mRNA nucleotide sequence and translate into the amino acid sequence of proteins |
|
|
Transfer RNA (tRNA) characteristics
|
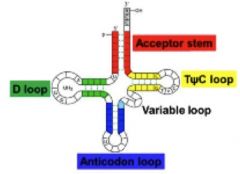
Clover shape with 4 distinct loops created by intra-strand h-bonding between complimentary bases
- D loop - TΨC loop - Anticodon loop - Variable loop |
|
|
D-Loop
|
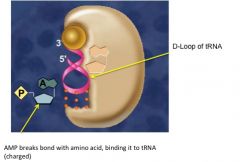
several modified bases (methylated cytosine and dihydrouridine) and acts as a recognition site for aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (these molecules attach an amino acid to the tRNA using the energy from a break between an AMP and the amino acid)
|
|
|
Anticodon Loop
|
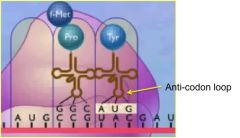
recognizes the complementary codon of the mRNA molecule. base pairing occurs between these 2 complimentary tri-nucleotide sequences
|
|
|
Variable Loop
|
provides structural stability
|
|
|
TΨC loop
|
COME BACK TO !!!
|
|
|
Acceptor Stem
|
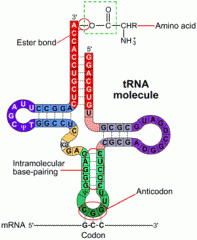
Each tRNA molecule has an acceptor stem that serves to link the amino acids. The last three bases are at the extreme 3' end are unpaired and always have the 5' -CCA -3' sequence. The AA is always attached via an ester bond
|
|
|
Promoter
|
sequence specific site, upstream of gene, region that starts transcription
|

