![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Glucose Structure |
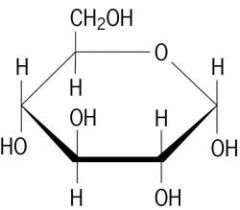
|
|
|
Fructose Structure |
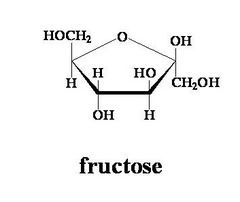
|
|
|
What type of bonds make oligo or poly saccharaides?
|
Glycosidic bonds
|
|
|
What does it mean when a sugar is an alpha or beta isomer?
|
C1-OH is linked
|
|
|
What do B-1,4 glycosidic bonds produce?
|
Cellulose. Long straight glucose chains.
|
|
|
Can animals make cellulose?
|
No
|
|
|
Name common disaccharides?
|
Maltose, sucrose, lactose
|
|
|
What does an alpha-1,4 linkage make?
|
Helical chain of glucose
|
|
|
What is the preferred fuel for some tissues?
|
Carbs
|
|
|
Glycolysis is it a conserved pathway?
|
Yes
|
|
|
How many steps are there in the glycolysis pathway?
|
10 steps
|
|
|
Ultimately, what will glycolysis give you?
|
2 Pyruvate and 2 ATP
|
|
|
What is the first step of glycolysis and what do you need to know?
|
Hexokinase, you go from Glucose to G-6P. You spend 1 ATP. Delta G = Big Negative
|
|
|
What is the second step of glycolysis and what do you need to know?
|
Phosphoglucose Isomerase. G-6P to F-6P. Delta G = small negative
|
|
|
What is the third step of glycolysis and what do you need to know?
|
Phosphofructokinase. F-6P to F-1,6-B-P. You spend 1 ATP. Delta G = Big negative
|
|
|
What are the reactions called in stage one of glycolysis?
|
Hexokinase, Phosphoglucose Isomerase, Phosphofructokinase.
|
|
|
What is the result of stage 2 of Glycolysis?
|
Hexose bisphosphate to 2 triose monophosphate.
|
|
|
What is the fourth step of glycolysis and what do you need to know?
|
Aldolase. F-1, 6-BP will change into DHAP and GAP. Delta G = Small negative
|
|
|
What is the 5th step of glycolysis and what do you need to know?
|
Triose phosphate isomerase. DHAP turns into GAP. Delta G = small positive
|
|
|
What are the reactions called in stage two of glycolysis?
|
Aldolase and Triose phosphate isomerase.
|
|
|
What is the end result of stage 3?
|
2 NADH produced, 4 ATP produced, and pyruvate production
|
|
|
What is the 6th step of glycolysis and what do you need to know?
|
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. GAP turns into 1,3-BPG. You go from NAD+ and Pi to NADH and H+. It is an ox-phos reaction. Oxidation = glyceraldehyde and exergonic. Phosphorylation = endergonic. Delta G = small negative
|
|
|
What is the 7th step of glycolysis and what do you need to know?
|
Phosphoglycerate Kinase. 1,3-BPG turns into 3-Phosphoglycerate. ADP to ATP. Excergonic part of reaction: Transfer of phosphate from 1,3-BPG. Delta G = small positive
|
|
|
What is the 8th step of glycolysis and what do you need to know?
|
Phosphoglycerate mutase. You go from 3 phosphoglycerate to 2 phosphoglycerate. It’s a rearrangement. Delta G = small positive
|
|
|
What is the 9th step of glycolysis and what do you need to know?
|
Enolase. 2 Phosphoglycerate turns into phosphenolpyruvate. You lose an H2O. Delta G = small negative
|
|
|
What is the 10th step of glycolysis and what do you need to know?
|
Pyruvate Kinase. Phosphenolpyruvate turns into pyruvate. ADP turns into ATP. Delta G = Big Negative
|
|
|
What does the hexokinase reaction require?
|
Mg2+
|
|
|
How does it allow the OH group to make the nucleophilic substitution?
|
It arranges the two substrates close enough for a reaction to occur
|
|
|
What are the kinase reaction in glycolysis?
|
Hexokinase, Phosphofructokinase, phosphoglycerate kinase, pyruvate kinase.
|
|
|
Is the phosphate on 1,3-BPG made by a kinase reaction?
|
No
|
|
|
So Phosphoglucose Isomerase is a multistep reaction. You only need to know how to draw the cyclic forms, but how does the reaction work?
|
The cyclic part is opened. You take a hydrogen off of one part of the molecule, you put it back in a different place, you close the molecule
|
|
|
What are the isomerase reactions?
|
Phosphoglucose isomerase, triose phosphate isomerase, phosphoglycerate mutase.
|
|
|
What do isomerases do?
|
Take a group from substrate and give it back to the same molecule in a different place
|

