![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How many electrons in 1st shell? |
2 |
|
|
How many electrons in 2nd shell? |
8 |
|
|
Electrons in more distant shells have what? |
Higher energy |
|
|
What are Valence electrons? |
Those electrons in the outermost shell |
|
|
What do Valence electrons do? |
Participate in chemical reactions and form bonds |
|
|
What is an Electrovalent Bond? |
Ionic bond |
|
|
What is a Covalent bond? |
Sharing of electrons |
|
|
What is a cation? |
Atom that loses an electron and becomes a positively charged ion |
|
|
What is an anion? |
An atom that gains an electron and becomes negatively charged |
|
|
Order from weakest to greatest strength bond |
Ionic Covalent Hydrogen |
|
|
What is an ionic bond? |
Electrons are stolen from another atom |
|
|
Example of Ionic bond |
Sodium Chloride (NaCl) |
|
|
Give an example of Nonpolar Covalent bonding |
H2 |
|
|
Define Nonpolar Covalent bonding |
Equal sharing of electrons |
|
|
Define Polar Covalent bonding |
Electrons shared unequally |
|
|
Give an example of a Polar Covalent Bond |
H2O |
|
|
Define Coordinate Covalent bonding |
One atom provides both electrons in a shared pair |
|
|
Define Hydrogen bond |
H atoms form polar bond with another atom taking on a slight + charge making it attract to any nearby negatively charged atoms |
|
|
Give an example of hydrogen bonding |
Water. H on one water molecule binds to the O on another water molecule |
|
|
Define solvent |
The majority of a solution. Something that dissolves another solution |
|
|
Define solute |
The solution or element that dissolves |
|
|
Define hydrophilic |
Water loving - soluble in water |
|
|
Define hydrophobic |
Water fear - insoluble in water |
|
|
Is water a solvent or solute? And what kind of compound will it dissolve? |
Solvent - polar compounds |
|
|
Define osmosis |
Movement of solvent (water) across a semipermeable membrane into an area of higher solute concentration |
|
|
Define osmotic pressure |
Pressure required to maintain equilibrium across the semipermeable membrane with no net movement of solvent |
|
|
Define osmolarity |
Solute concentration |
|
|
Define isotonic solution |
Solution that contains the SAME osmolarity as the surrounding environment outside |
|
|
Define hypotonic solution |
Osmolarity of the outside is lower than the inside |
|
|
Define hypertonic solution |
Osmolarity of the outside is higher than the inside |
|
|
What do each of the 3 solutions cause the cell to do? Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic |
Remain the same Swell Shrink |
|
|
Define acid |
Proton donor - concentration of H+ ions |
|
|
Define base |
Proton acceptor and also releases hydroxyl (OH) |
|
|
What is the pH of blood? |
7.35 - 7.45 |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
Prevents large changes in pH |
|
|
What does a buffer consist of? |
A weak acid and it's conjugate base A weak base and it's conjugate acid |
|
|
What is the Henderson-Hasselbach equation? |
pH = pKa + log[A-]/[HA] |
|
|
Name some different types of buffers |
Hemoglobin Bicarbonate Phosphate Protein |
|
|
Methyl |
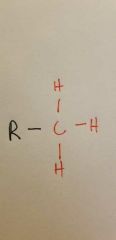
|
|
|
Ethyl |
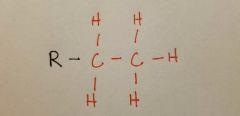
|
|
|
Phenyl |
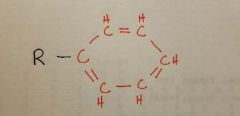
|
|
|
Aldehyde |
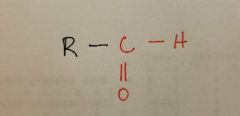
|
|
|
Ketone |
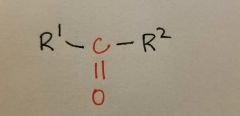
|
|
|
Carboxylate |
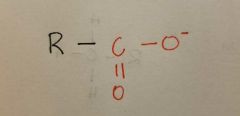
|
|
|
Hydroxyl |
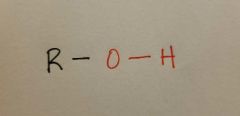
|
|
|
Enol |
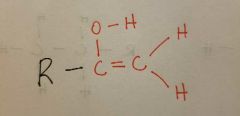
|
|
|
Ether |
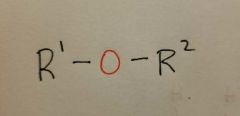
|
|
|
Ester |
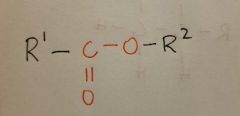
|
|
|
Acetyl |
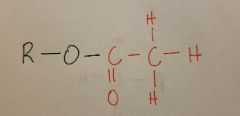
|
|
|
Amino |
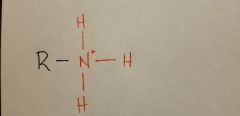
|
|
|
Amido |
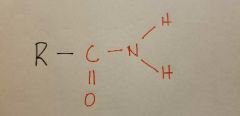
|
|
|
Sulfhydryl |
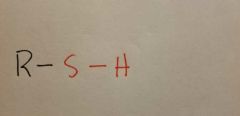
|
|
|
Disulfide |
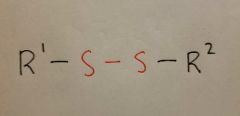
|
|
|
Thioester |
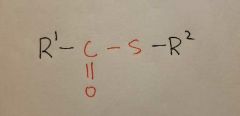
|
|
|
Phosphoryl |
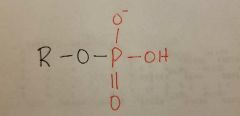
|
|
|
Phosphoanhydride |
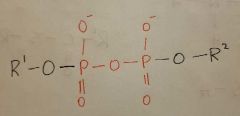
|

