![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Oxidative deamination by glutamate dehydrogenase |

|
|
|
|
Urea cycle |

|
C -----> CAAO |
|
|
Rotenone , barbiturate , piericidin |
Inhibitors of complex 1 in etc cycle |
|
|
|
Oligomycin |
Inhibitor of atp synthesis in ETC cycle ( inhibitor of F0 & F1 protein) |
|
|
|
Cyanide , co , H2S , azides |
Inhibitors of complex 4 in etc cycle |
|
|
|
Antimycin , british antilewsite |
Inhibitors of complex 3 in etc cycle |
|
|
|
Hexokinas Glucokinase Phosphofructokinase Pyruvatekinase |
Key enzyme of glycolysis |
|
|
|
Citrate synthase Isocitrate dehydrogenase Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase |
Key enzyme of TCA cycle (citric acid cycle) |
|
|
|
Flouroacetate Malonate |
Inhibitors of TCA cycle |
Flouroacetate->citrate synthase Suicide Malonate->succinate dehydrogenase Competitive |
|
|
Pyruvate carboxylase
Phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase
Fructose 1-6 bisphosphatase
Glucose -6-phosphatase |
Key enzyme of gluconeugenesis |
|
|
|
Acetone , acetoacetate , beta-hydroxy butyrate |
Ketone body |
|
|
|
Acromegaly |
Increase Growth hormone causes of diabetes mellitus |
|
|
|
Cushing's syndrome |
Increase corticosteroid hormone causes of diabetes mellitus |
|
|
|
Pheochromocytoma |
Increase adrenalin hormone causes of diabetes mellitus |
|
|
|
Hyperthyroidism |
Increase thyroid hormone causes of diabetes mellitus |
|
|
|
Gastaional diabetes |
Diabetes mellitus during later stage of pregnancy |
|
|
|
Amphibolic role of TCA cycle |

|
|
|
|
Glycosuria |
Suger into urine |
|
|
|
Rapaport leubering cycle |

BGP SHUNT |
|
|
|
Protein kinase |
Its kind of enzyme that cause of activating glycogen phosphorylaze (terminator of glycogen) |
|
|
|
Phosphatase |
Remove 1 phosphate group |
|
|
|
Phosphorylaze |
Add 1 phosphate group |
|
|
|
Aspartate |
Produce Oxaloacetate |
|
|
|
Alanine |
Produce Pyruvate |
|
|
|
Anaplerosis |
T |
|
|
|
-CH2- |
Methylene group |
|
|
|
S-adenosylmethionine(SAM) |
Active form of methionine |
|
|
|
Other name of Polysaccharide |
Glycan |
|
|
|
Glycine |
-Is only symmetric aminoacid -Because this reason its not optically active H | NH2---C---COOH | H |
|
|
|
Proline |
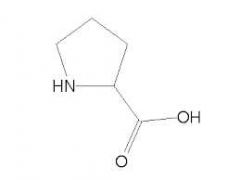
Is an imino acid(have NH group instead of NH2) |
|
|
|
Zwitterion |
Ion which have both negetive and positive charge amino acid note page 4 |
|
|
|
Amide group |
It contain --CONH2 |
|
|
|
Native protein |
A protein with 3D structure under natural condition |
|
|
|
Iso electric ph (PI) |
The ph that pr have minimum solubility in it |
|
|
|
Pituitry stalk Hypothalamus stalk |
Connection betwn pituitry and hypothalamus |
|
|
|
Serine hydroxy methyl transferase |
Its an enzyme that change serine to glycine |
|
|
|
Glycine synthase |
Is an enzyme that make glycine of co2 and nh3 |
|
|
|
Glyoxalate |
Its a ketoacid that react with glutamate and make glycine and alpha keto glutarate during transamination reaction |
|
|
|
Threonine |
Its a hydroxy amino acid that make glycine in the presence of threonine aldolase |
|
|
|
Benzoic acid |
Its a food preservative that is detoxified by glycine |
|
|
|
Zigma amino levulinic acid |
Its an intermediate in changing glycine to heme (heme bio synthesis) |
|
|
|
Creatine phosphate |

Is formed from glycine and arginine and s adenosyl methionine in kidney and liver |
|
|
|
Phosphoadenosine phosphosulfate (PAPS) |
Doner of sulfate groups for the synthesis of sulfated mucopolysaccharides |
|
|
|
UDP choline |
Is a doner of choline for the synthesis of lecithin |
|
|
|
Replication |
DNA produce DNA |
|
|
|
Transcription |
DNA produce RNA |
|
|
|
Translation |
RNA to protein |
|
|
|
Linoleic acid (C18 , delta 9,12 , omega-6) |
One of the essential fatty acid |
|
|
|
Arachidonic acid(C20 , delta 5,8,11,14 , omega 6) |
One of the essential fatty acid p5 note |
|
|
|
Eicosanoid |
Biologically important compounds that drived from essential fatty acid |
|
|
|
Phynoderma(toad skin) |
Deficiency of essential fatty acid in body Rough and thickend skin |
|
|
|
Glycerophospholipids |
Phosphatidyl choline (lecithin) Phosphotidyl ethanolamine(cephalin) Phosphotidyl serine Phosphotidyl inositol Cardiolipin |
|
|
|
Linolenic acid(C18 , delta9,12,15 , omega3) |
One of the essential fatty acid |
|
|
|
Enzyme |
Enzyme are biological catalysts which are protein in nature |
|
|
|
Natural substrate |
Is the substrate that have least km value (more affinity) |
|
|
|
Optimum tempreature |
The tempreture at which the velocity is maximum (enzyme) |
|
|
|
Km significance |
Kinetic constant Affinity Indicate the natural substrate Iso enzyme differ Mechanism of enzyme inhibition Enzyme assays |
|
|
|
Metalloenzyme |
Are the enzyme which require metal ions (cofactor) for their activity these enzyme hold metal tightly |
|
|
|
Active site |
Small region at which the substrate bind and catalysis take place |
|
|
|
Catalytic resudues |
The amino acid that present at the active site |
|
|
|
Absolute specificity of enzyme |
Certain enzyme act only on one sunstarate |
|
|
|
Group specificity of enzyme |
The act on closy relatrd group of substarate |
|
|
|
Michaelis menten equation |
Vmax [S] Vi = ------------------ Km+[S] |
|
|
|
Transport protein |
Transferrin TBPA RBP TBG Hepatoglobin Hemopexin Lipoprotein Alpha 1 acid glycoprotein |
|
|
|
Hypoalbuminemia |
Kwashiorkor(nutritional deficiency) Cirrhosis(liver diseases) Albumin loss Loss due to burns Urinary loss |
|
|
|
Neoplasm |
Tumor |
|
|
|
Van den bergh reaction |
Its one of the colorometrically measurement Bilirubin + diazorized sulphanic acid | | V Azo bilirubin ( purple) |
|
|
|
Hippuric acid synthesis test |
Test base on detoxification |
|
|
|
The pruduct of stomach of digestion of protein |
Peptone proteoses |
|
|
|
Colipase |
A protein secreted by pancreas act as cofactor for pancreatic lipase |
|
|
|
Tyrosine product |
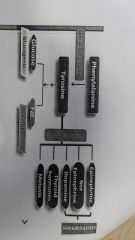
|
|
|
|
Hbs sickle shape anamia |
Due to substitution of glutamate by valine |
|
|
|
Rothera's test |
Is a test for recognizing keton body in urine |
|
|
|
SAM |
S-adenosyl methionine |
|

