![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How do you remember what assays are used for DNA, protein or RNA?
|
SNOW DROP
|
|
|
With Southern blotting, what kind of electrophoresis gel do you use?
|
agarose
|
|
|
With Southern blotting, the fragment is denatured using...
|
a strong alkali solution
|
|
|
Southern blotting: After DNA fragments are denatured into single strands with alkali, they are transferred onto a...
|
nitrocellulose or nylon sheet
|
|
|
Southern blotting: Once on a nitrocellulose or nylon sheet, ssDNA fragments are...
|
hybridized with a probe
|
|
|
The Northern, Southern and Western blots all follow what 5 steps?
|
1. Fragmentation
2. Separation 3. Denaturation 4. Blotting 5. Hybridization w/probe Frank Sat Down By Hannah |
|
|
What kind of probes are used in the 3 blotting techniques?
|
Southern (DNA) and Northern (RNA) = DNA probe
Western (protein) = Antibody probe |
|
|
DNA is denatured before or after transferring (blotting) it onto a nitrocellulose paper?
|
before
|
|
|
What is needed for DNA sequencing?
|
4 tubes
ONE dideoxynucleotide (ddATP, ddTTP, ddGTP, or ddCTP) per tube four normal deoxynucleotides (dATP, dGTP, ...) in each tube DNA polymerase in each tube Primer in each tube Single stranded DNA template in each tube Magnesium to shield DNA's negative charge |
|
|
What is a dideoxynucleotide?
|
it's the same as a DNA nucleotide except it lacks the hydroxyl group; therefore you cannot elongate a DNA chain with it
|
|
|
Using DNA sequencing, nucleotide synthesis terminates when a __________ is incorporated into the growing chain.
|
ddNTP
|
|
|
Describe the Sanger Method
|
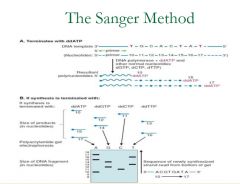
|
|
|
How can we amplify specific DNA sequences?
|
1. DNA cloning
2. Libraries 3. PCR |
|
|
A bacteria is transformed while a eukaryote is ______________ when you insert a DNA sequence into the genome.
|
transfected
|
|
|
When you insert a sequence into a host like a bacteria and allow it to grow and divide naturally to amplify the DNA, this method is called...
|
DNA cloning
|
|
|
With a bacteria host, the 3 possible vectors include...
|
1. bacteriophage
2. plasmids 3. cosmids - genetically engineered like plasmid but bigger NOTE: A vector is used to insert the sequence into DNA |
|
|
With a eukaryotic host, the 4 possible vectors include...
|
1. retroviruses
2. adenoviruses 3. free DNA 4. DNA coated w/lipid bilayer (liposome) |
|
|
The genomic library has (larger/small) fragments than cDNA. The cDNA library has (larger/smaller) fragments.
|
larger
smaller |
|
|
Rank the capacity of these vectors for foreign DNA for the genomic library:
1. Bacteriophage 2. BACs (engineered bacterial DNA) 3. YACs (engineered yeast DNA) |
bacteriophage < BACs < YACs (largest)
|
|
|
What is the vector of choice for foreign DNA for the cDNA library? How is the cDNA library obtained? cDNA corresponds to _______________________.
|
plasmid
cDNA is obtained from mRNA using reverse transcriptase. corresponds to a specific stage of differentiation of the cell |
|
|
Which library corresponds to a specific stage of differentiation of a cell?
|
cDNA library
|
|
|
PCR requires:
|
1. isolated DNA
2. 2 types of primers that are not complementary to each other w/NO TANDEM REPEATS 3. 4 dNTPs 4. Heat stable DNA polymerase (because you will heat DNA to open it) 5. Magnesium to protect the negative charge of DNA |
|
|
DNA polymorphisms are...
|
variations of DNA within the same species (hair color)
|
|
|
Polymorphisms result from (3):
|
1. point mutations
2. deletions 3. insertions |
|
|
What techniques can be used to detect polymorphisms (5)?
|
1.Restriction fragment length polymprophisms (RFLPs)
2. Detection of mutations by allele-specific oligonucleotide probes 3. testing for mutation by PCR 4. Detection of polymorphisms caused by repetitive DNA 5. DNA chips/DNA microarray |
|
|
Detection of polymorphisms: RFLPs?
|
DNA is cut by restriction enzymes, which cut at specific sites. If there are fragments that are larger or smaller than others, this is due to a mutation that abolishes the normal restriction site. These fragments with different lengths are called restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs).
|
|
|
RFLPs can be used for genetic testing because mutations causing diseases affect a restriction site in what 2 ways?
|
in a coding region
outside of a coding region but still associated with the abnormal gene causing the disease |
|
|
RFLPs: the mutation that causes sickle cell anemia abolishes a restriction site for the enzyme ___________ in the __________ gene, making a RFLP that is larger than the RFLP for a normal individual.
|
-Enzyme: Mstll
-Gene: Beta-globin |
|
|
What can oligonucleotide probes be used to identify mutations?
|
Two probes: one is complementary to sequence in normal allele, another is complementary to sequence in mutated allele. Sequence of interest amplified by PCR and then DOT BLOTTED onto nitrocellulose paper. Paper is treated with radioactive probe (32P). Incubated and washed; XRAY film made. Analysis of xray: shows if allele of interest is normal or mutated; for carriers, both normal and mutated alleles will be detected; for affected pts, only mutant probe will hybridize.
|
|
|
When you detect mutations by allele specific oligonucleotide probes, the xray film of a carrier will show...
|
both normal and mutated alleles will hybridize
|
|
|
When you detect mutations by allele specific oligonucleotide probes, the xray film of an affected pt will show...
|
only the mutant probe will hybridize
|
|
|
In addition to DNA sequencing, ______________ can be used to detect cystic fibrosis.
|
allele-specific oligonucleotide probes
|
|
|
When testing for cystic fibrosis using oligonucleotide probes, one probe binds to the mutant _________ gene while the other binds to the ___________ gene.
|
-mutant deltaF508 gene
-normal gene |
|
|
When a sequence containing a mutation is used as a primer for PCR, normal DNA (will/will not) hybridze with the primer. Will amplification take place?
|
will not
no amplification |
|
|
_____________ can be used as primes to test clinically for several mutations in a short time.
|
Oligonucleotides for different mutations
|
|
|
Polymorphisms can be detected due to repetitive DNA because the human genome has __________________. These ___________ can be digested by restriction enzymes and the fragment sizes differ in size from one individual to another.
|
variable number tandem repeats (VNTR)
|
|
|
VNTR patterns can be used to ______________.
|
identify individuals/family relationships/forensic analysis
|

