![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what can make aromatic amino acids, and what is the important intermediate?
|
plants and bacteria can synthesize aromatic amino acids. humans must get it in the diet.
the important intermediate is sshikimic acid |
|
|
draw out shikimic acid. What is it an intermediate for?
|
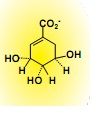
intermediate for bacteria or plants creating aromatic amino acids
|
|
|
what do phenylalanine and tyrosine break down into?
|
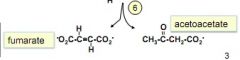
fumarate and acetoacetate
|
|
|
steps 1 and 2 plus end of Trp/Phe breakdown
|
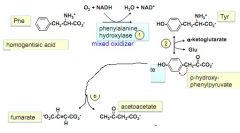
|
|
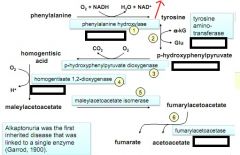
disorders in Tyrosine / Phenylalanine breakdown
|
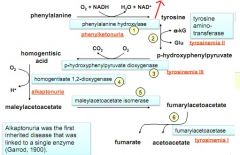
|
|
|
what problems does phenylketonuria present? and how can you prevent them?
|
causes severe intellectual disability. can be fixed by restriction of phenylalanine in the diet
|
|
|
map out phenylketonuria problem
|
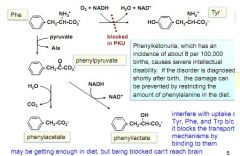
|
|
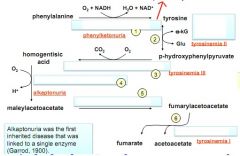
Fill in the missing enzymes
|
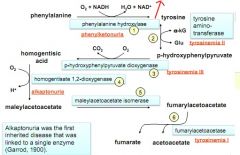
|
|
|
draw out the cofactor of phenylalanine hydroxylase. what is it called and what kind of enzyme is phenylalanine hydroxylase?
|
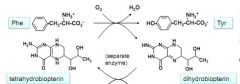
mixed-function oxidase
|
|
|
what AA enzymes have homologous structures?
|
phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan hydroxylases
|
|
|
structure of AA hydroxylases
|
active site w/ Fe and His, Glu and H2O ligands
all have tetrahydrobiopterin cofactor |
|
|
what do you use to make dopamine. what causes the rate limiting step?
|
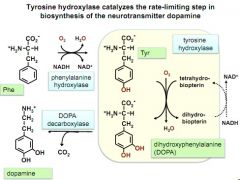
|
|
|
what is used in creation of serotonin? what catalyzes the rate limiting step?
|
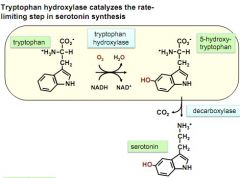
|
|
|
how is an action potential created?
|
vesicles containing inducer fuse w/ plasma membrane to release. They float down to receptors.
|
|
|
what does insufficient dopamine synthesis lead to?
|
parkinson's disease
|
|
|
parkinson's disease attributes
How do you treat it? |
due to insufficient dopamine
if substantia nigra is damaged they can't make enough characterized by tremors and muscular rigidity treat w/ dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) |
|
|
what can lead to schizophrenia?
|
dopmanime receptors firing too often.
drugs inhibiting receptors help out with the symptoms |
|
|
how does dopamine get removed?
|
can be repackaged in vesicles, or diffuses into other cells to be remetabolized
|
|
|
draw out dopeamine inactivation
|
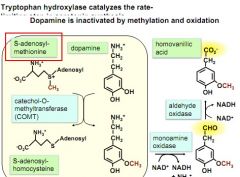
|
|
|
how can the gene for catechol-O-methyltransferase vary?
|
single-nucleotide polymorphism affects the stability. methionine is unstable, valine is stable
|
|
|
What risks are associated with 108-Met COMT?
|
obsessive-compulsive disorder in men
rapid cycling bipolar disorder depressive disorder aggressive or suicidal behavior in schizophrenia |
|
|
what creates velocardiofacial syndrome? (VCFS)
|
people who lack the COMT gene on one copy of chromosome 22
|
|
|
what happens to people who are missing COMT gene or one copy of chromosome 22
|
velocardiofacial syndrome (VCFS)
|
|
|
how is missing COMT gene created and what is a treatement?
|
mispairing in homologous recombination
inhibitor of tryosine hydroxylase helps -> reducing dopeamine |
|
|
problems with high levels of COMT
|
rapid removal of dopeamine may interfere w/ short term memory
|

