![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
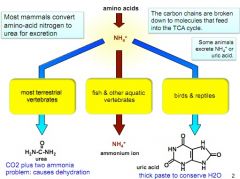
plot out how different animals get rid of ammonia
|
|
|
|
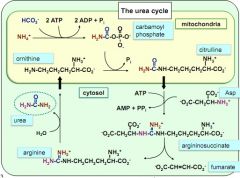
draw the Urea cycle
|
|
|
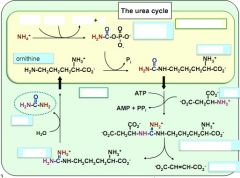
fill in the blanks
|
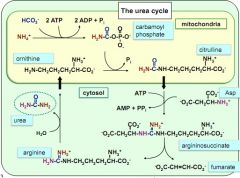
|
|
|
formation of carbamoyl phosphate
|
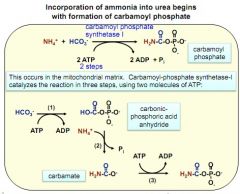
|
|
|
structure of ornithine
|
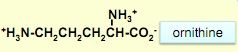
|
|
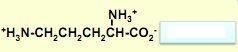
what's this?
|
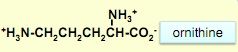
|
|
|
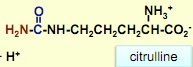
Draw out citruline
|
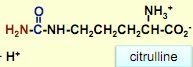
|
|
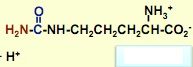
What's this?
|
|
|
|
draw out aspartate
|
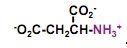
|
|
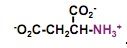
What's this?
|
aspartate
|
|
|
draw out argininsuccinate
|
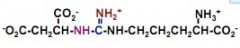
|
|
|
draw out argininsuccinate
|
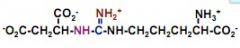
|
|

what's this?
|
argininosuccinate
|
|
|
draw fumarate
|

|
|

what's this?
|
fumarate
|
|
|
draw arginine
|
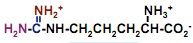
|
|
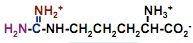
what's this?
|
arginine
|
|
|
draw urea
|
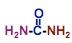
|
|
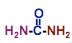
what's this?
|
urea
|
|
|
how many phosphate anhydride bonds does the formation of urea take up?
|
takes up 4 phosphate anhydride bonds
2 for making carbamoyl phosphate 1 in making argininosuccinate 1 for hydrolyzing argininosuccinate |
|
|
draw out simply how aspartate is regenerated from fumarate
|
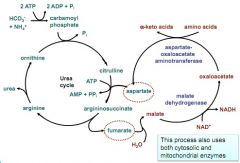
|
|
|
complex urea cycle + oxidation in mitochondria
|
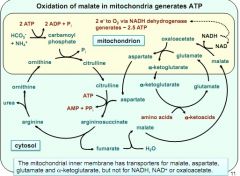
|
|
|
complex urea cycle + oxidation in mitochondria
|
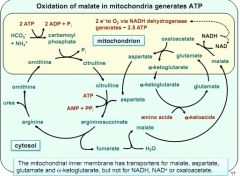
|
|
|
example of proton gradient in urea cycle transport, and what disease it may cause if not working correctly
|
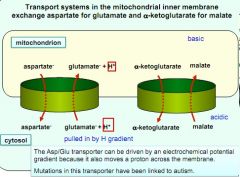
|
|
|
NADH cycles and transport
|
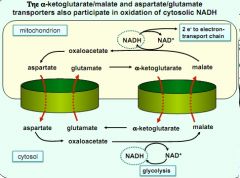
|
|
|
model for small-molecule transporters?
|
E. coli lactose permease
transports TDG |
|
|
most abundant protein in the mitochondrial inner membrane?
|
ATP/ADP exchanger (translocase)
exports ATP carries a proton into the matrix w/ each ATP/ADP exchange |
|
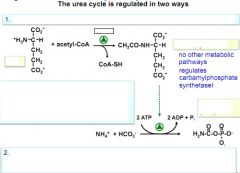
Urea regulation
|
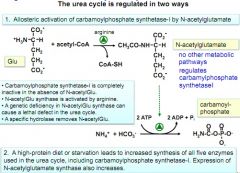
|
|
|
Urea cycle disorders
|
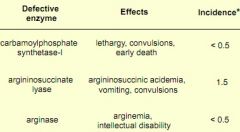
|
|
|
defect in carbamylphosphate synthetase I creates what disorder?
|
lethargy, convulsions, early death
|
|
|
defect in argininosuccinate lyase creates what disorder?
|
argininosuccinic acidemia, vomiting, convulsions
|
|
|
defect in arginase creates what disorder?
|
arginemia, intellectual disability
|
|
|
pharmacological treatment for some urea cycle defects
|
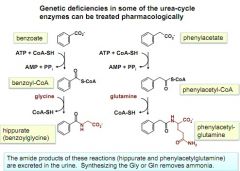
|
|
|
urea cycle defect that can also lead to autism?
|
single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the gene for mitochondrial, Ca2+ dependent Asp/Glu exchanger
main transporter in the brain |
|
|
what is Arginine also a precursor for that seemingly has nothing to do with urea cycle?
|
arginine is a precursor of nitric oxide (NO)
|
|
|
What is the role of NO?
|
short-lived messenger that controls blood pressure, clotting, and neurotransmission. Binds guanylyl cyclase and activates production of c-GMP
|
|
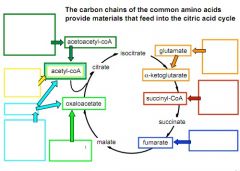
amino acids feeding in to the TCA cycle
|
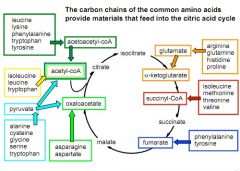
|
|
|
AA that are neither glucogenic or ketogenic
|
Glutamate
|
|
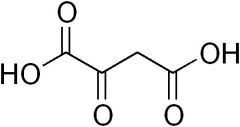
AA that lead to oxaloacetate
|
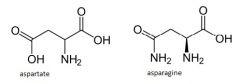
asparagine
aspartate |
|
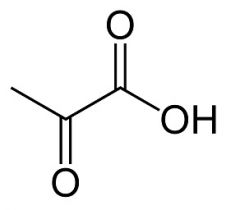
AA that lead to pyruvate
|
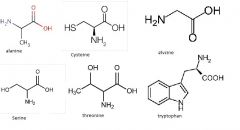
alanine
cysteine glycine serine threonine tryptophan |
|
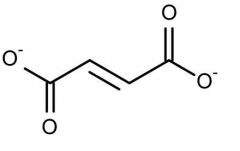
AA that lead into fumarate
|
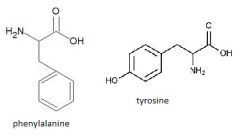
phenylalanine
tyrosine |
|
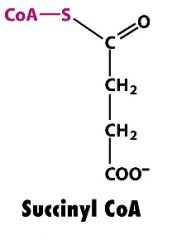
AA that lead into succinyl-CoA
|
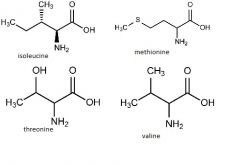
isoleucine
methionine threonine valine |
|
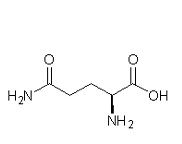
AA that lead to glutamate then alphaketoglutarate
|
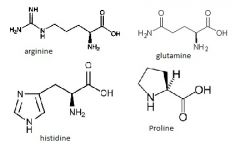
arginine
glutamine histidine proline |
|
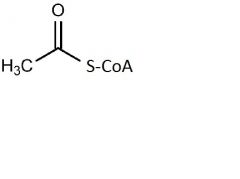
AA that run into acetyl CoA
|
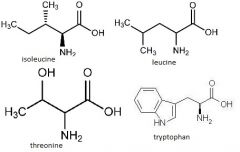
isoleucine
leucine threonine tryptophan |
|

AA that lead into acetoacetyl-CoA
|
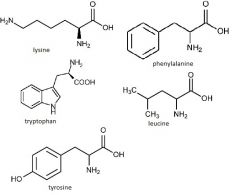
leucine
lysine phenylalanine tryptophan tyrosine |
|
|
Essential amino acids
|
Arginine
Histidine Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Valine (RHVMILKFTW) Really HeaV MILK For The Win |
|
|
What is serine formed from? draw it out
|
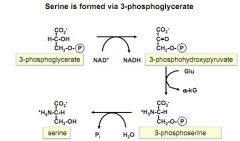
|

