![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the major forces causing genetic variation? |
Natural selection, genetic drift, migration, mutation |
|
|
|
What are the results of point mutations? |
SNPs |
|
|
|
Why are SNPs more often used than microsatellites? |
They are easier to determine, they give more accurate measurements since no calibration is needed for the of machines used (i.e. diff labs get the same results) because SNPs are consistent |
|
|
|
Where would you expect to find higher vs lower mutation rates? |
Higher rate in microsatellites, lower in genes |
|
|
|
What can give rise to supergenes? |
Inversions. The genes included in the inverted section tend to "stick together" - they tend to be linked (inversion means a diff in chr order - recombo can't really happen) |
|
|
|
What's allelic richness, A? |
A parameter of gen var. A=Average number of alleles per locus |
|
|
|
What can a model help us with? |
Define parameters, test hypotheses, generalize results, make predictions |
4 points |
|
|
Why could dissortative mating be selected for? |
To avoid inbreeding i.e. to avoid decrease of genetic variation and accumulation of deleterious alleles |
|
|
|
What causes a deviation from HWE? |
A violation of one of the assumptions, or incorrect genotyping (technical artifact) |
|
|
|
What's a null allele? What consequence do null alleles cause? |
An allele that doesn't create a detectable product in lab. Consequence: apparent access of homozygotes relative the HW proportions |
|
|
|
What's the Wahlund effect? |
A deficit of heterozygotes due to mechanical pop mixing |
|
|
|
What statistical test could we use to evaluate if our observations deviate enough from expected values to be considered valid and not just a coincidence? |
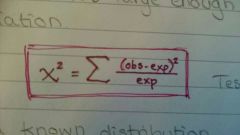
Chi2 |
|
|
|
How do you calculate the df for chi2? |
Number genotypes minus number of alleles |
|
|
|
What does the relative importance of forces acting on gen var depend on? |
Spatial and temporal scale, pop size |
|
|
|
How much gen var is lost for each generation (due to drift)? |
1/(2Ne) |
|
|
|
What is Ne? |
The effective pop size, the no. of ind. reproducing (in an ideal pop) |
|
|
|
Why is Ne often used in conservation? |
since pop.size is important if we want to ensure gen var is kept: if Ne is small then random effects has a stronger influence |
|
|
|
What is the formula for reduction in heterozygosity? |
-(1/(2Ne))Hi The change in heterozygosity from time i to i+1 |
|
|
|
What affects Ne? |
Unequal/skewed sex ratios pop size changes (pop bottlenecks, variation in reproductive success, fluctuating pop size |
Four causes
|
|
|
Which is the parameter of gen var that reduces the fastest? |
Allelic richness reduce faster than heterozygosity |
|
|
|
Which parameter of gen var is best to use, especially in a small sample, and why? |
Heterozygosity, since it is hard to find the rare alleles, especially in a small sample. |
|
|
|
How can we calculate the effective pop size when sex ratios are skewed? |
Ne=(4NmNf)/(Nm+Nf) where Nm=reproducing males and Nf=reproducing females |
|

