![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the genetic code?
|
relationship between sequence of nucleotides in DNA/RNA and sequence of amino acids in a protein
|
|
|
How many possible codons are there?
|
-64 (4 power of 3) possible codons yet only 20 amino acids (AAs)
-all AAs except methionine (Met) and tryptophan (Trp) are specified by more than one codon |
|
|
Even though there are many codons that specify an amino acid, one codon NEVER specifies more than one
amino acid. (T/F) |

True
|
|
|
Genetic code is almost universal (T/F)
|
True
|
|
|
_______ or _______ of bases that shift the reading frame can lead to novel proteins that are beneficial, or they can be disastrous.
|
Loss, gain
|
|
|
How does an mRNA codon specify an amino acid?
|
An adapter molecule holds the amino acids in place while interacting directly and specifically with a codon in mRNA
|
|
|
What is an adapter molecule?
|
tRNA!
|
|
|
There's a different aminoacyl tRNA synthetase and one or more tRNAs for each amino acid (T/F)
|
true
|
|
|
What do tRNAs look like?
|
Clover leaf
|
|
|
Where in the tRNA are the binding sites for AAs?
|
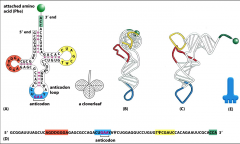
CCA sequence at 3’ end
|
|
|
How does tRNA become aminoacyl tRNA?
|
-ATP and AA bind to aminoacyl tRNA synthase (enzyme)
-2 phosphorous bonds leave the ATP (making it AMP) which now attaches to the AA -Once the AMP and AA bind together, the AA becomes activated -tRNA specific to the AA in the enzyme binds to the active site -The AA and tRNA will bind together, and AMP will fall off -aminoacyl tRNA leaves enzyme and is ready for translation |
|
|
What is the wobble hypothesis?
|
Proposes that the anticodon of tRNAs can still bind successfully to a codon (on mRNA) whose third position requires a nonstandard base pairing
This explains how one tRNA is able to base pair with more than one type of codon |
|
|
What are the components of a ribosome (eukaryotic)?
|
-small subunit
-large subunit |
|
|
Translation begins when?
|
The anticodon of a ‘charged’ tRNA binds to a codon in mRNA
|
|
|
Translation ends when?
|
That amino acid forms a peptide bond with growing chain
|
|
|
Once translation is ongoing, ______ of the 3 binding sites within the ribosome are occupied by a tRNA at any given time.
|
2
|
|
|
What are the 4 sites within a ribosome?
|
A site- acceptor site
P site- where peptide bonds form E site- where tRNAs no longer bound to an amino acid leaves |
|
|
Which subunit moves first during the process of translation (translocates)?
|
Large
|
|
|
Are ribosomes ribozymes?
|
Yes
|
|
|
What initiates translation?
|
The initiator tRNA loaded with met binds to small ribosomal subunit (loaded with proteins known as translation initiator factors); binds tightly to P site of small ribosomal subunit (only initiator tRNA can do this)
|
|
|
What happens after the initiation of translation?
|
Step 2: the initiator tRNA loaded with an AA moves along the mRNA with the small subunit in search for the first AUG
Step 3: when AUG is found, the initiation factors dissociate and the large ribosomal subunit binds Step 4: next charged tRNA can move into A site, and strand synthesis can begin |
|
|
What terminates translation?
|
The presence of a STOP codon in the mRNA
|
|
|
What happens when a stop codon reaches the A site?
|
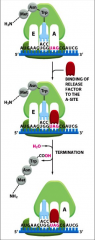
The stop codon will bind a release factor that alters catalytic activity, causing addition of a water rather then forming a peptide bond. Polypeptide chain is finished, and subunits fall off the mRNA
|
|
|
Proteins are made on?
|
Polyribosomes
|
|
|
How can you speed up the process of translation of an mRNA?
|
If another ribosome hops on the mRNA and starts translating the same message as soon as the first one is out of the way. This is common in both bacteria and eukaryotes
|
|
|
When do proteins fold?
|
Begins during translation, long before termination and disassembly of ribosomes
|
|
|
Does folding of proteins occur ‘spontaneously’?
|
Yes
|
|
|
What are molecular chaperones?
|
They bind to ribosome near ‘tunnel’ where growing peptide exits and helps protein develop its appropriate structure
|
|
|
What are Post-Translational Modifications (PTMs)?
|
Chemical modification of protein structure which generally involves addition of functional groups/small molecules to protein
|
|
|
Post-translational modifications increase protein diversity (T/F)
|
True
|
|
|
Overview of Protein Synthesis in Eukaryotes
|
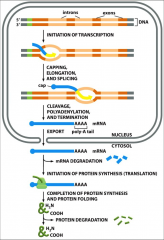
|

