![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Founder Effect |
A few individuals colonise a new region carrying a small amount of the alleles of the larger population |
Few Colonise |
|
|
Genetic Bottleneck |
A drop in allele variety due to a large decrease in population size |
Evolutionary event reduces population size |
|
|
Affinity for Oxygen |
Hb with high aff takes up O2 easily and releases it less readily(at GES) left Hb with low aff takes up O2 less easily but releases it more readily(at resp tissues) right |
GES - left Resp tissues- right |
|
|
Associating + Disassociating |
A- process which Hb combines with O2 in the lungs D- process which Hb releases O2 in the tissues |
Oxy diss curve- S shape ... First molecule is hard to load the next 3 load easily |
|
|
Starch |
Storage molecule in plants Coiled Insoluable Can be hydrolysed to form alpha glucose |
|
|
|
Glycogen |
Storage molecule in animals Short chains Readily hydrolysed into alpha glucose |
|
|
|
Cellulose |
Parrallel chains of B- glucose joined by hydrogen bonds forms microfibrils for strength |
|
|
|
Mitosis |
Cell division where 2 daughter cells are produced that have the same number of chromosomes as the parent |

|
|
|
Semi conservative replication |
DNA helicase breaks Hbonds linking base pairs, double helix seperates into two strands unwinds each exposed polynucleotide strand acts as a template complementry nucleotides attracted to and are joint by enzyme dna polymerase to form missing strand Now one new and one original strand |
|
|
|
I PMAT |
I- cell dna replicication P- chromosomes shorten and thicken to become visible, nuclear envelope disappears M- chromosomes align at the equator of cell, Spindle Fibres form A- sister chromatids move to opp poles T- nuclear envelope reforms so two new identical cells |
|
|
|
Spiracles |
Pores on the body surface of insects that open and close to allow gases to diffuse in and out |
|
|
|
Gill lamellae |
Parts of the fishes gill that inc surface area and where blood flows through for gas exchange |
|
|
|
Countercurrent exchange |
Blood and water flow in opposite directions to maintain a diffusion gradient |
|
|
|
Arteries |
Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart ✳small lumen ✳thick muscle ✳elastic layers Aorta Pulm Artery- deoxy to lungs |
|
|
|
Veins |
Blood vessel that carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart Large lumen Thin muscle Elastic layers Have valves to stop backflow Vena cava Pulm Vein- oxy blood back to heart from lungs |
|
|
|
Tissue fluid |
Fluid that surrounds the cells of the body it supplies nutrients to the cells and removes waste products |
|
|
|
Apoplastic pathway + Symplastic |
A- Route through the cell walls which water and minerals are transported into the plant. Most water as its simpler Stopped by casperian strip which blocks the endodermis S- route through the cytoplasm and plasmodesmata of plant cells by which water and minerals are transported |
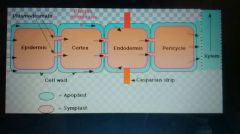
|
|
|
Cohesion |
Water molecules stick together by hydrogen bonds Cohesion- tension= transpiration pull on the water puts the xylem under pressure |
|

