![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
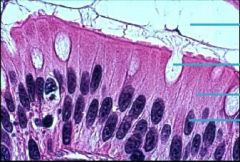
|
Goblet Cells
|
Epithelial
|
|
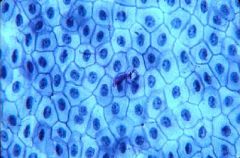
|
Mesothelium
|
Epithelial
|
|
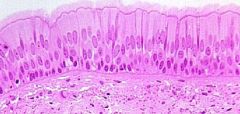
|
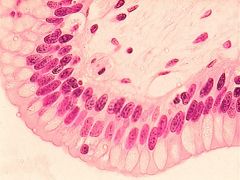
Pseudostratified Columnar
Epithelial |
Single layer of columnar shaped cells all touching basement membrane. Not all cells reach free surface. Ciliated
Protection, movement of materials if ciliated. If goblet cells then secretion. Nasal Cavity. Upper respiratory tract. Associated with goblet cells |
|
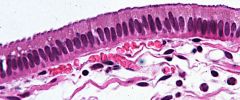
|
Simple Columnar
Single layer of column shaped cells attached to basement membrane. Nucleus towards basal region. May be ciliated. |
Epithelial
Secretion & Absorption. Protection from height of cell. Digestive tract. Glands. Associated with goblet cells. |
|
|
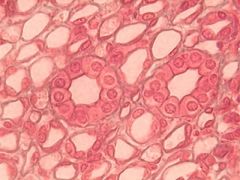
Simple Cuboidal
Single layer of cube shaped cells. All resting on basement membrane. Centrally located nuclei. Avascular |
Epithelial
Secretion & Absorption Renal tubules. Glands. Lower part of respiratory tree |
|
|
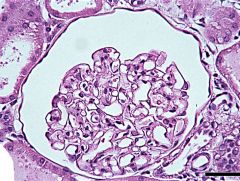
Simple Squamous
Single layered flattened squamous cells. Every cell touching basement membrane. Avascular |
Epithelial
Diffusion & Filtration Lining lumen of blood vessels. Capillaries made of only simple squamous serous membranes. Alveoli |
|
|
Stratified Columnar
two or more cell layers thick |
Epithelial
|
|
|
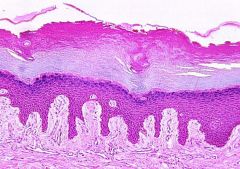
Stratified Squamous - Moist
Many layered, all cells in tissue alive. Moist, flattened cells. |
Epithelial
Protection Mouth, esophagus, parts of throat (pharynx and larynx) |
|
|
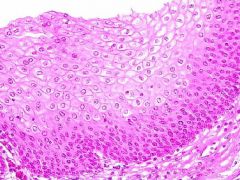
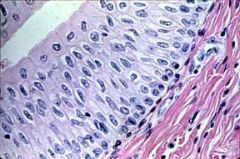
Stratified Squamous Keratinized
In keratinized, upper layer of cells dead and filled with waterproofing protein called keratin |
Epithelial
Protection Upper surface of skin, hair, nails, and callous skin |
|
|
Transitional Epithelium
a type of tissue consisting of multiple layers of epithelial cells which can contract and expand |
Epithelial
accommodate fluctuation of volume of the liquid in an organ or tube, such as the urinary bladder, and protect against the caustic effects of urine found in the urinary bladder, in the ureters, and in the superior urethra |
|
|
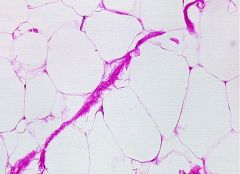
Adipose
Connective The fibroblasts have become fat cells. Will see more fat cells and less matrix. |
Connective
Storing yellow fat (insulator)(energy reserve). Protection (shock absorber) Surrounding heart, kidneys, part of hypodermis of skin |
|

|
Areolar (Loose)
Fibers loosely arranged in matrix. |
Connective
Packing agent All over body |
|
|
Blood
|
Connective
supply of nutrients and oxygen to tissues circulatory system |
|
|
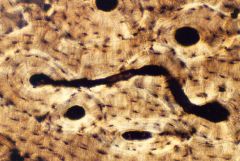
Bone - Haversian System
Connective tissue, second hardest tissue of body. Matrix is amorphous and fibrous (mostly collagenous) Types of cells: osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts Chondrocytes contained within lacunae |
Connective
Support, protection, movement (passive) Location: skeleton |
|
|
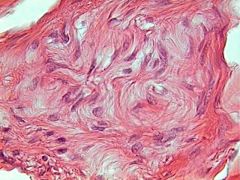
Dense Irregular
Tightly packed bundles of fibers in all directions. |
Connective
Distribute pressure in many directions. Dermis |
|

|
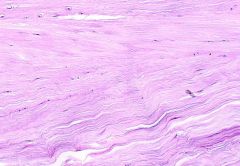
Dense Regular
The fibers are tightly packed and cells squeezed between. Regular because all oriented in one direction. |
Connective
Distribute pressure in one direction. Ligaments and tendons |
|
(EXCLUDE)
|
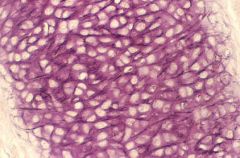
Elastic Cartilage
|
Connective
outer ear, larynx, and epiglottis |
|
(EXCLUDE)
|
Fibrocartilage
|
Connective
If hyaline cartilage is torn all the way down to the bone, the blood supply from inside the bone is sometimes enough to start some healing inside the lesion. In cases like this, the body will form a scar in the area using a special type of cartilage called fibrocartilage. found in the pubic symphysis, the annulus fibrosus of intervertebral discs, meniscus, and the TMJ. |
|
|
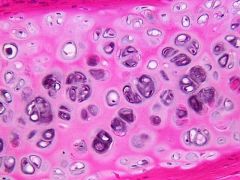
Hyaline Cartilage
All characteristics of cartilage. Fibers are primarily collagenous |
Connective
Hyaline cartilage exists on the ventral ends of ribs; in the larynx, trachea, and bronchi; and on the articular surface of bones. |
|
|
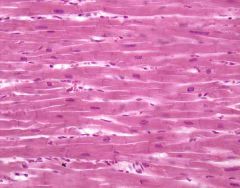
Cardiac
Striated, single nucleus per cell (central). Cells branched provides strong network of cardiac muscle. Intercalated discs (speeds up contraction). Involuntary. Myogenic (beats by itself without need of nervous system stimulation) |
Muscle
Myocardium of Heart only (middle layer of heart wall) |
|
*
|
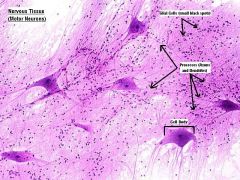
Nervous Tissue
2 cell types (neuron= functional unit) and (neuroglia= supportive cells) |
Nervous
Monitor changes in environment and allow body to respond to changes CNS (brain + spinal cord) & Peripheral (all nerves outside CNS) |
|
|
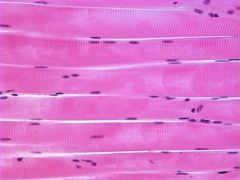
Skeletal Muscle
Multinucleated fibers, striated. Fastest contracting voluntary muscle. |
Muscle
Movement of skeleton Attached to bone |
|
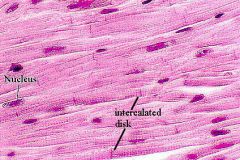
|
Cardiac
Striated, single nucleus per cell (central). Cells branched provides strong network of cardiac muscle. Intercalated discs (speeds up contraction). Involuntary. Myogenic (beats by itself without need of nervous system stimulation) |
Muscle
Myocardium of Heart only (middle layer of heart wall) |
|
*
|
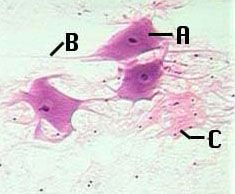
Nervous Tissue
2 cell types (neuron= functional unit) and (neuroglia= supportive cells) A= Cell body (neuron) B= Axons and Dendrites C= Glial Cells |
Nervous
Monitor changes in environment and allow body to respond to changes CNS (brain + spinal cord) & Peripheral (all nerves outside CNS) |
|
|
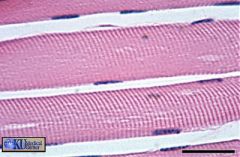
Skeletal Muscle
Multinucleated fibers, striated. Fastest contracting voluntary muscle. |
Muscle
Movement of skeleton Attached to bone |
|
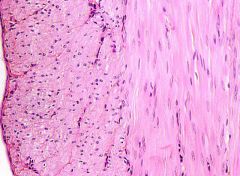
|
Smooth Muscle
Only non-striated muscle we covered |
Muscle
Involuntary & regulates the blood flow in capillary beds of various organs and tissues Located in wall of blood vessels (except heart) |
|
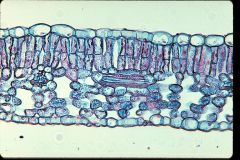
Monocot or Dicot?
|
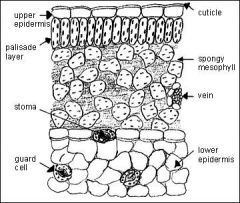
Dicot Leaf
|
|
|
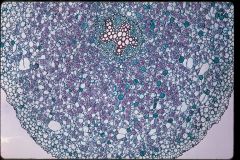
Monocot or Dicot?
|
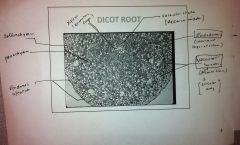
Dicot Root
|
|
|
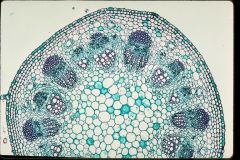
Monocot or Dicot?
|
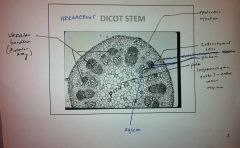
Dicot Stem
|
|
|
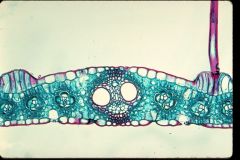
Monocot or Dicot?
|
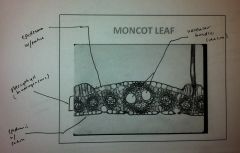
Monocot Leaf
|
|
|

Monocot or Dicot?
|

Monocot Root
|
|
|
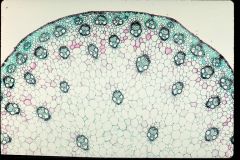
Monocot or Dicot?
|
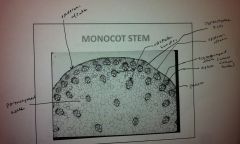
Monocot Stem
|
|
|
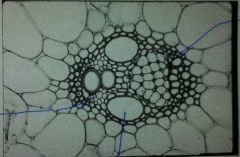
Monocot or Dicot?
|
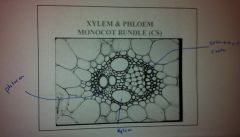
Monocot
|
|
|
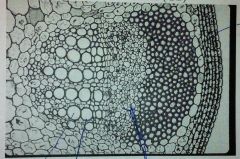
Monocot or Dicot?
|
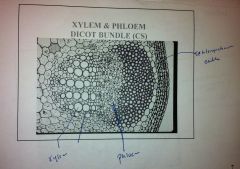
Dicot
|
|
|
|
Muscle consists of what 2 proteins?
|
contains contracting proteins: actin and myosin which if regularly arranged will make the muscle appear striated
|
|
|
|
Composition and Functions of Connective Tissues?
|
Types:
Connective tissue proper Cartilage Bone Vascular |
Functions:
support, protection, fillers, transport, energy reserve |
|
|
Composition and Function of Cartilage?
|
Chondrocytes reside in lacunae within a matrix of mucopolysaccharides and fibers
|
functions: form and protection
|
|
|
*
Types of connective tissue |
Connective tissue proper
Cartilage Bone Vascular |
|
|
|
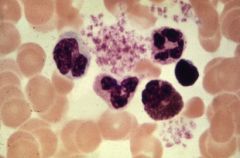
Function of erythrocytes, leucocytes, and thrombocytes
|
Part of vascular tissue (blood)
Erythrocytes= oxygen transfer Leucocytes= immune system Thrombocytes= blood clotting (platelets) |
|

