![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Steps of the scientific method |
♡Observation ♡Hypothesis ♡Prediction ♡Testing ♡Conclusion |
|
|
All cells have |
1. Cell membrane 2. Cytoplasm 3. DNA 4. Ribosome |
|
|
Eukaryotes |
Are subdivided by internal membranes into various membrane-enclosed organelles |
|
|
Prokaryotes |
Lack the kinds of membrane-enclosed organelles found in eukaryotic cells |
|
|
A system |
A combination of components thst form a more complex organization |
|
|
Emergent properties |
New properties that emerge as complexity increases |
|
|
If it's alive |
It has: ♡Cells ♡DNA ♡Metabolism ♡Homeostasis ♡Reproduction |
|
|
Some girls from our class play kickball daily |
Species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain |
|
|
Energy goes up |
As you go to higher levels of electron shells |
|
|
Covalent bond |
The sharing of valence electrons |
|
|
Ionic bond |
♡The attraction of cations and anions to each other ♡A strong DRY bond but weakens as it hydrates |
|
|
Hydrogen bond |
♡Weak bond ♡The attraction of hydrogen atoms on one molecule to partially negative areas of another |
|
|
Acid |
♡Any molecule that ADDS H+ to a solution ♡pH < 7.0 |
|
|
Base |
♡Any molecule that REMOVES H+ from a solution ♡Some directly do it by binding hydrogen ions and others indirectly by adding OH- which then makes water ♡pH > 7.0 |
|
|
Buffer |
Can either donate or accept H+ |
|
|
Van der Waals interactions |
♡Weak attractions that happen when atoms are very close together by fleeting charge differences ♡Collectively can be strong |
|
|
Non-polar Covalent bond |
Atoms share the electrons equally |
|
|
Polar covalent bond |
The atoms share the electrons unequally |
|
|
Electronegativity |
♡Pull of one atom on another ♡Oxygen and nitrogen are very strong so their presence is a sign of a polar bond |
|
|
Valence of elements |
♡Hydrogen: 1 ♡Oxygen: 2 ♡Nitrogen: 3 ♡Carbon: 4 |
|
|
Isomers |
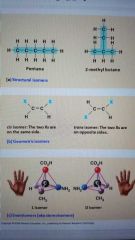
Molecules with the same molecular formula but different structures AND properties |
|
|
Functional groups |
♡Are chemically reactive groups of atoms as part of an organic molecule ♡Are involved in chemical reactions by the molecule ♡Give organic molecules distinctive chemical properties |
|
|
Hydroxyl |
♡Symbol: -OH ♡Ending: OL ♡Compound name: Alcohol [e.g. ethanol] |
|
|
Carbonyl |
♡Symbol: -COH & -OC ♡Ending: AL ♡Compound name: Aldehyde [e.g. proponal] & Ketone |
|
|
Carboxyl |
♡Symbol: -COOH ♡Ending: Acid ♡Compound name: Acid [e.g. acetic acid] |
|
|
Amino |
♡Symbol: -NH2 ♡Ending: Amine ♡Compound name: Amine [e.g. methylamine] |
|
|
Sulfhydryl |
♡Symbol: -SH ♡Ending: THIOL ♡Compound name: Thiol [e.g. methanethiol] |
|
|
Phosphate |
♡Symbol: -PO4 ♡Ending: Phosphate ♡Compound name: Phosphate [e.g. ATP] |
|
|
Types of Macromolecules |
♡3 are polymers 1. Carbohydrates 2. Proteins 3. Nucleic Acids ♡1 is not 1. Lipids |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
♡Elements: C,H, O ♡Monomer: Monosaccharide (glucose) ♡Functional groups: carbonyl and hydroxyl ♡Macromolecule: Polysaccharide ♡Functions: Energy source and structural ♡Formed by: dehydration rx ♡Broken down by: hydrolysis rx ♡Ex: starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin |
|
|
Sucrose |
Glucose and fructose |
|
|
Maltose |
Glucose and glucose |
|
|
Lactose |
Glucose and galactose |
|
|
Cellulose |
Held together by hydrogen bonds between hydroxyl groups attached to carbon atoms |
|
|
Phenylketonuria |
♡The enzyme hydroxylase turns phenylalanine into tyrosine which is peed out ♡People with PKU don't have this enzyme and so has a build up where phenylalanine builds up in the body |
|
|
Carbs-Fiber-Sugar= |
Starch |
|
|
Lipids |
♡Elements: C,H,O, and sometimes P ♡Functional group: carboxyl, phosphate, hydroxyl ♡Monomers: none ♡Macromolecules: fats, phospholipids, and steroids ♡Function: Energy storage ♡Formed by: dehydration rx ♡Broken down by: hydrolysis rx ♡Hydrophobic |
|
|
Fatty acid |
Long chain of hydrocarbon and a carboxyl group |
|
|
Fats |
Are made of 3 Fatty acids and glycerol |
|
|
Monounsaturated |
One double bond |
|
|
Polyunsaturated |
More than one double bond |
|
|
Saturated fatty acids |
♡Have the max number of hydrogen atoms possible and no double bonds ♡Can pack close together |
|
|
Unsaturated fatty acids |
♡Have one or more double bonds ♡Can't pack close together because of kinks in tails |
|
|
Hydrogenated |
Unsaturated oils that have become saturated by adding H atoms |
|
|
Omega fatty acids |
Are unsaturated and their first double bond is on the bond corresponding to the number in their name |
|
|
Phospholipid |
♡2 fatty acids and glycerol and phosphate and organic group ♡Elements: C,H,O, & P ♡Membrane structure |
|
|
Steroids/Sterols |
♡Elements: CHO ♡Membrane structure, hormones |

