![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The Process of Science
|
The Scientific Method
|
|
|
|
Part of the Scientific Method
|
1. observation
2. hypothesis 3. testing the hypothesis 4. conclusion 5. theory |
|
|
|
Define the Scientific Method
|
An orderly process for solving problems and seeking answers
|
|
|
|
1. Observation
|
- use of all senses
- data from other scientists - leads to asking questions |
|
|
|
2. hypothesis (inductive reasoning)
|
- possible explanation for 'why' or 'how'
- makes a prediction: 'if'- 'then' - must be testable |
|
|
|
What are the three types of Chemical bonding?
|
Ionic bonding
Covalent bonding Hydrogen bonding |
|
|
|
What is Ionic bonding?
|
a bond formed between two oppositely charged ions
|
|
|
|
Define ion
|
an atom or group of atoms with a net charge
|
|
|
|
How do you form an ion?
|
atoms will lose or gain one or more electrons in order to form an ion.
|
|
|
|
What is hydrogen bonding?
|
a bond formed between negative side of one molecule and positive side of another
|

|
|
|
Four types of Macromolecules
|
carbohydrates
lipids nucleic acids proteins |
|
|
|
Three types of carbohydrates
|
monosaccharides
disaccharides polysaccharides |
|
|
|
What are polysaccharides?
|
long chains of monosaccharides
|
|
|
|
Three types of polysaccharides
|
starch
glycogen cellulose |
|
|
|
Cellulose
|
Structural carbohydrate in plant cell walls
|
|
|
|
Five types of Lipids
|
fatty acids
triglycerides phospholipids waxes steroids |
|
|
|
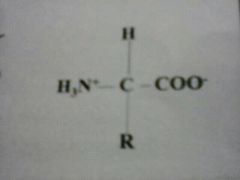
proteins are composed of
|
amino group
NH3+ Carboxyl group COO- R group variable |
|
|
|
dipeptide
|
Two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond
|
|
|
|
phospholipids are composed of
|
2 non polar fatty acid tails
polar head (glyserol molecule plus one phosphate group PO4-³ And nitrogen group |
|
|
|
function of phospholipids
|
structural molecule in cell membranes
|
|
|
|
What are steroids
|
four fused carbon rings
|
|
|
|
function of steroids
|
many hormones, structural molecule in animal cell membranes
|
|
|
|
What are triglycerides
|
glycerol molecule plus 3 fatty acids
|
|
|
|
function of triglycerides
|
food source, food storage, insulation...
|
|
|
|
Polypeptides are...
|
Kong chains of amino acids
|
|
|
|
example of third level polypeptide
|
glob in in hemoglobin, enzymes
|
|
|
|
nucleotides are composed of ....
|
phosphate group (PO4-³)
five sided sugar (pentose) nitrogen base |
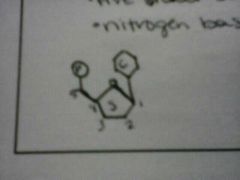
base
|
|
|
Three types of nucleic acids are
|
RNA
DNA ATP |
|
|
|
What is RNA
|
single stranded polymer of nucleotides
|
functions during protein synthesis
|
|
|
What is DNA
|
double stranded polymer of nucleotides
|
|
|
|
What is ATP
|
Adenosine Triphosphate
single adesine nuclei tide with three phosphate groups |
|
|
|
Five protein components
|
channel proteins
carrier protein receptor protein recognition protein enzymatic protein |
|
|
|
components of lipids
|
phospholipids
cholesterol glycolipids |
|
|
|
glycolipids
|
short polysaccharide made with lipid and carbohydrate. animal membranes only
|
|
|
|
function of glycolipids
|
mark cell as self
|
|
|
|
enzymatic protein
|
acts as catalyst
|
|
|
|
three special cases of osmosis
|
turgor
plasmolysis inhibition |
|

