![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Two types of metabolic pathways |
Aerobic & Anerobic |
|
|
Eukaryotic cells perform ____________ resperation. Occurs inside the _________________. |
Aerobic; Mitochondrion. |
|
|
4 steps of cellular resperation |
1. Glycosis |
|
|
Goal of resperation: Convert __________ to ________+_____&_____. |
Glucose; Pyruvate + ATP & NADH. |
|
|
Glucose comes from... |
Plants |
|
|
During glycosis, glucose is broken down in the ____________. |
Cytoplasm |
|
|
Acetyl-COA: _________ are broken down into acetyl-COA & ________. |
Pyruvates; Co2 |
|
|
During Krebs cycle: Acetyl-COA is broken down, _______, ________, & ______ are produced. |
NADH; FADH; ATP. |
|
|
During ETP (ATP form.), ____ is converted to ATP. |
ADP; H2O; 36. |
|
|
3 stages of a cell's life cycle: |
1. Interphase |
|
|
3 reasons for mitosis: |
1. Growth |
|
|
Stage of mitosis when nucleolus disappears & duplicated chromosomes are visible. |
Prophase |
|
|
Stage of mitosis when duplicated chromosomes line up midway between spindle poles. |
Metaphase |
|
|
Stage of mitosis when sister chromatids of each chromosome are separated & pulled to opposite spindle poles. |
Anaphase |
|
|
Stage of mitosis when nuclear envelopes forms around each cluster of chromosomes. |
Telophase |
|
|
Division in animal cells happens on a ______ _________. |
Cleavage Furrow |
|
|
Division in a plant cell happens on a _______ _______. |
Cell Plate |
|
|
Cancer develops if: control over cell division is lost, causing ________ and if the cells become ____________. |
Neoplasms; Malignant. |
|
|
Term for when cancer cells invade other body parts. |
Metastasis |
|
|
Type of cells that go through mitosis |
Somatic/body cells |
|
|
Type of cells that go through meiosis |
germ/sex cells |
|
|
Total number of cells produced from mitosis: |
2 |
|
|
Total number of cells produced from meiosis: |
4 |
|
|
When 2 heterozygous individual's two traits are crossed, the ratio is __:__:__:__ |
9:3:3:1 |
|
|
Man who studied genetics & cross-fertilized pea plants. |
Gregor Mendel |
|
|
Observable traits in an individual (hair color, eye color, etc.) |
Phenotype |
|
|
P-_____________ |
Parents |
|
|
Way to calculate the probability of genotype outcomes on a chart. |
Punnett Squares |
|
|
Mendel's Law of Segregation: Observed a ratio of _______ for monohybrid crosses. |
3:1 |
|
|
"Genes are distributed independentally of other gene pairs. (Result of dyhybrid crosses.)" |
Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment |
|
|
Two non-identical alleles both fully expressed at the same time in heterzygotes, neither is dominant or recessive. |
Codominance |
|
|
One allele is not fully dominant over its partner. |
Incomplete Dominance |
|
|
One gene influences multiple traits. |
Pleiotrophy |
|
|
Genotype + environment = ____________ |
Phenotype |
|
|
__________+ environment = Phenotype |
Genotype |
|
|
Continuous traits in a population often follow a ____ curve. |
Bell |
|
|
3 components of DNA nucleotide |
1. Nitrogen Group |
|
|
The two pyrimidines: |
Thymine & Cytosine |
|
|
The two purines: |
Adenine & Guanine |
|
|
Enzyme in DNA replication that breaks hydrogen bonds between strands. |
DNA Helicase |
|
|
Enzyme in DNA replication that untwists the double helix. |
Topoisomerase |
|
|
Enzyme in DNA replication that joins free nucleotides into a new strand of DNA. |
DNA Polymerase |
|
|
Enzyme in DNA replication that joins DNA segments on the discontinuous strand. |
DNA Ligase |
|
|
The suffix "-ase" means the word is an... |
Enzyme |
|
|
DNA -> ______________ -> mRNA -> _________________ -> Protein |
Transcription; Translation. |
|
|
______ -> Transcription -> ________ -> Translation -> ________ |
DNA; mRNA; Protein. |
|
|
RNA uses __________ in place of thymine. |
Uracil |
|
|
Contains information transcribed from DNA |
mRNA |
|
|
Where polypeptide chains are built |
rRNA |
|
|
Delivers amino acids to ribosomes |
tRNA |
|
|
The genetic code consists of _____ (#) mRNA codons (triplets). |
64 |
|
|
Translation occurs in the... |
Cytoplasm |
|
|
The "start" codon. |
AUG |
|
|
Exchange of segments between nonsister chromatids of a tetrad during mitosis |
Crossing-Over |
|
|
Cancer-causing gene that transforms normal cells into a tumor. |
Oncogene |
|
|
The bell curve shows a __________ range of _________. |
Continuous; Variation. |
|
|
The ratio of genotypes of an offspring of 2 heterzygous parents. |
75% Dominant |
|
|
Mutation that causes adding or deleting one of the base pairs. |
Frameshift Mutation |
|
|
DNA is ___________ stranded, RNA is ______________ stranded. |
Double; Single. |
|
|
Recombinant DNA is made from 2 sources: One carries carries a gene of ___________, the other is a ____________. |
Interest; Carrier (vector). |
|
|
_________ ___________ organisms contain one or more genes introduced by artificial means |
Genetically modified. |
|
|
_____________ ______________ contain at least one gene from another species. |
Transgenic organisms. |
|
|
The alteration of a person's genes to alleviate an illness. |
Gene therapy. |
|
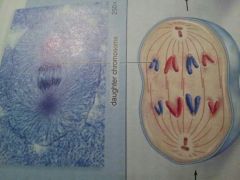
Which stage of mitosis is shown?
|
Anaphase
|
|
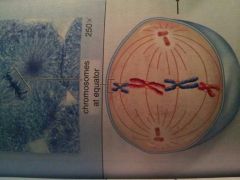
Which stage of mitosis is shown?
|
Metaphase
|

