![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Null hypothesis |
Nothing happens, no significant change. |
|
|
Alternative hypothesis |
The opposite of original hypothesis |
|
|
Scientific method |
1) observation 2) form a question 3) form a hypothesis 4) conduct an experiment 5) analyze the data and draw a conclusion |
|
|
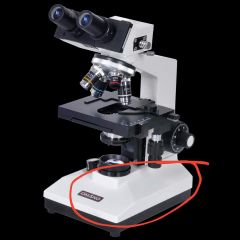
Base |
|
|
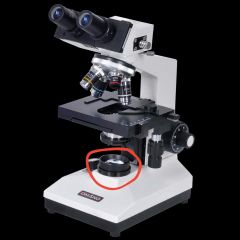
Substage light |
|

|
Fine focus knob |
|
|
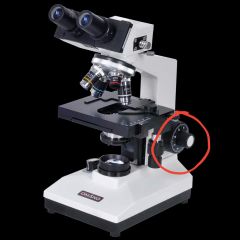
Coarse focus knob |
|

|
Arm |
|
|
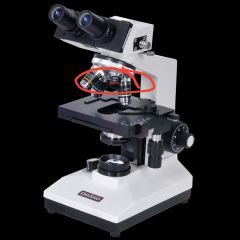
Objective lense |
|

|
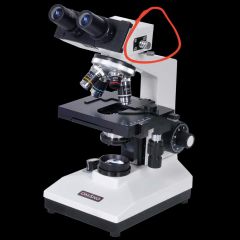
Revolving nose piece |
|
|
Body tube |
|

|
Eye piece |
|

|
Condenser |
|

|
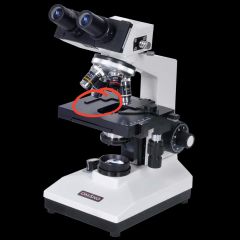
Iris diaphragm |
|
|
Mechanical stage |
|
|
Interphase |
Part of cell cycle where no division occurs Consists of G1, S, & G2 |
|
|
G1 |
First growth phase |
|
|
S phase |
Everything is copied DNA synthesis |
|
|
G2 |
Health and activity |
|
|
M phase |
Part of cell cycle where division occurs Consists of mitosis and cytokenises |
|
|
Mitosis |
Division of the nucleus whereby each daughter cell receives the same compliment of DNA that the parent cell possesed |
|
|
Cytokenises |
Actual splitting of the cell |
|
|
Prophase |
Nucleus disappears and the mitotic spindle apparatus forms 4 chromosomes present Replicated chromosomes 8 chromatids Diploid cell |
|
|
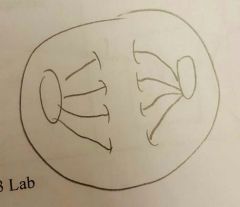
Metaphase |
Chromosomes line up down the middle and attached to the spindle fibers at the centromere 4 chromosomes present Replicated chromosomes 8 chromatids present |
|
|
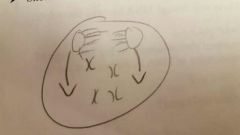
anaphase |
Chromatids split from each other and become individual chromosomes Unreplicated chromosomes 8 chromosomes present 0 chromatids present |
|
|
Telophase |
The nuclei reform and the cell starts to split 2 nuclei in the cell 8 chromosomes 0 chromatids |
|
|
Prophase |
|

|
Metaphase |
|
|
Anaphase |
|

|
Telophase |
|
|
Chromosome |
Long threadless DNA molecule found in nucleus |
|
|
Sister chromatids |
When two chromosomes are together they are sister chromatids |
|
|
Centromere |
Place where the pair of homogenous duplicated chromosomes are attached |
|
|
Microtubules |
Spindle fibers |
|
|
Cell plate |
Precursor to cell wall |
|
|
Somatic cell |
Any cell of a living organism other than the reproductive cells |
|
|
Gamete |
Mature happiness male or female German cell that is able to unite with another of the opposite sex in sexual reproduction to form a zygote |
|
|
Zygote |
Diploid cell resulting from the fission of two haploid gametes |
|
|
Ploidy |
Number of sets of chromosomes in a certain or in the cells of an organism |
|
|
Synapsis |
Homologous chromosomes pairs in meiosis I |
|
|
Haploid |
n=1 complete sets of chromosomes |
|
|
Diploid |
2n=2 complete sets of chromosomes |
|
|
Homologous recombinatiom |
Crossing over |
|
|
Recombinant chromosome |
Chromosome with genes from the other chromosome |
|
|
Independent assortment |
The Homologous pairs can switch with each other |

