![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
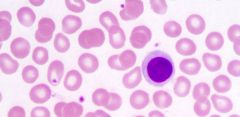
|
- lymphocyte (agranular)
|
|
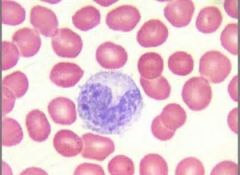
|
- monocyte (agranular) - leave cell and form macrophages |
|
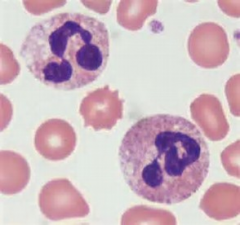
|
- neutrophil (granular)
|
|
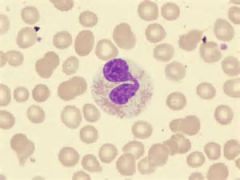
|
- eosinophil (granular) - red background |
|
|
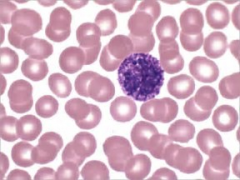
- Basophil (granular)
|
|
|
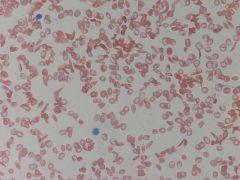
- Sickle cell anemia - cells sickle, form clusters, and clog capillaries - patients cant handle high altitude |
|
|
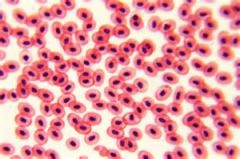
- frog blood - nucleated RBC, unlike most animals |
|
|
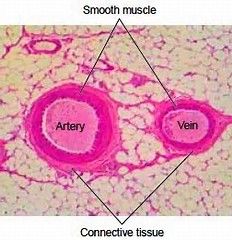
- artery and vein cross section - artery has a wider muscle than vein |
|
|
granular
|
- type of Leucocytes - Neutrophils: engulf bacteria - Eosinophils: allergic and parasitic reactions - Basophils: histamine (causes dilation of the blood vessels) for inflammation |
|
|
agranular
|
- type of Leucocytes - Lymphocytes: antibodies - Monocytes: macrophages (scavenging cells) |
|
|
functions of the CS
|
- transport gases (O2, CO2) - transport nutrients and waste - transport water - transport hormones - component of immune system - helps regulate homeostasis |
|
|
CS requires
|
- Fluid: -RBC, WBC - Plasma (water, salts, nutrients, plasma proteins (fibrinogen) - Platelets (formation of blood clots) - Pump - Vessels |
|
|
Lack circulatory system
|
- Hydra, corals, flatworms
|
|
|
Open CS
|
- insects, spiders, crustacean, and most mollusks - have heart and arteries, but no capillaries or veins - hemolymph |
|
|
Closed CS
|
- earthworms, birds, mammals, (vertebrates) - system made up of tubes - blood never leaves the vessels |
|
|
pulmonary circuit
|
- deoxygenated blood is pumped from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart
|
|
|
systemic circuit
|
- blood is pumped from the heart to the rest of the body and back to the heart
|
|
|
Ventricle with a thicker wall
|
- Left ventricle - needs a larger muscle to pump blood through the entire body (systemic circuit) |
|
|
Erythrocytes
|
- RBC - contain hemoglobin - transport oxygen |
|
|
Leucocytes
|
- WBC - immune response and defense - granular and agranular types |
|
|
arteries
|
- thick wall of smooth muscle - transport away from heart |
|
|
veins
|
- skinnier wall of smooth muscle - valves move blood through vessel - transport toward the heart |
|
|
heart
|
- pump of CS - 4 chambers - right side = systemic - left = pulmonary - valves prevent backflow - atrioventricular, pulmonary, aortic (semilunar) |
|
|
coronary arteries and veins
|
- provide oxygen to heart
|
|
|
apex
|
- base of heart
|
|
|
placenta
|
- organ made of both mother and fetal tissues through which gases and nutrients pass between mom and baby - mass of capillaries - also secretes hormones |
|
|
umbilical cord
|
- connects fetus to placenta - two arteries carry deox blood away from fetus - one vein carries ox blood back to fetus from placenta - allantoic stalk connects to allantois (sac that acts as a dump for metabolic wastes of the fetus) |
|
|
ductus venosus
|
- location in which umbilical vein from placenta and joins the posterior or inferior vena cava |
|
|
ductus arteriosus
|
- connection between pulmonary artery and aorta - allows most of the blood to go to the fetus body, bypassing the lungs but sends enough to continue development |
|
|
foramen ovule
|
- opening in the septum between right and left atria - allows blood in RA to go straight to LA, bypassing the lungs - closes in first year of birth (small hole can cause migraines) |
|
|
4 veins of brachiocephalic
|
- internal jugular - external jugular - cephalic vein - right subclavian |
|
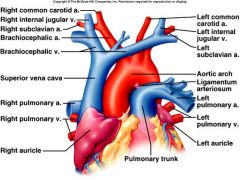
|
R/L brachiocephalic vein Internal jugular External jugular Cephalic vein Subclavian vein Brachiocephalic trunk Subclavian artery Common carotid artery Hepatic portal system Celiac arteryRenal arteries |

