![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Herbaceous stems are made of |
And epidermis, vascular tissue, and either ground tissue or cortex and pith. |
|
|
Permits gas exchange |
Protective layer covered by a water conserving cuticle |
|
|
Stomata |
Permits gas exchange |
|
|
Pith, cortex |
A ground tissue at the center of the herbaceous you to cut them that consist of large, then world parenchyma cells that function primarily in storage. |
|
|
Herbaceous eudicot stem arrangement |
Have the vascular bundles arranged in a circle (cross-section), and have a distinct cortex and pith. |
|
|
Monocot Stem arrangement |
Have vascular bundles scattered in ground tissue |
|
|
Spongy mesophyll layer |
This layer contains cells with chloroplasts and is a major site of photosynthesis. |
|
|
Upper epidermis layer
|
A single layer of clear cells that allows light to pass through and prevents the loss of water.
|
|
|
Palisade layer
|
This layer contains long columnar cells that are packed tightly together. These cells contain chloroplasts and are the main cells carrying out photosynthesis.
|
|
|
Lower epidermis layer
|
A single layer of clear cells that contains stomates and guard cells.
|
|
|
Stomate
|
An opening in the lower epidermis that allows carbon dioxide into the leaf and water and oxygen out of the leaf. Transpiration is the loss of water by a leaf.
|
|
|
Guard cells
|
Pairs of these cells containing chloroplasts are found on the lower epidermis of the leaf and are responsible for forming stomates. During the day these cells produce sugar by photosynthesis, causing their walls to curve inward and away from each other and creating a space between the cells called a stomate. At night the process is reversed and the stomate closes.
|
|
|
Air space
|
__ _____ are found in the spongy mesophyll layer and function in the exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen.
|
|
|
Xylem in Vascular Tissue |
Vessel Members: Water & mineral transport, support. Mostly in advanced angiosperms
Tracheids: Water & mineral transport, support. Mostly in gymnosperms and lower angiosperms Sclerenchyma Cells: Fibers & Sclereids: support, protection Xylem Parenchyma Cells: storage, short distance transport Laticifers: secretion, storage of secondary metabolites Resin & Gum Duct Epithelial Cells: secretion |
|
|
Phloem In Vascular tissue |
Sieve Tube Members & Companion Cells: transport of sugars, organic nitrogen compounds, and growth regulators in angiosperms
Sieve cells, Albuminous Cells: transport of sugars, organic nitrogen compounds, and growth Sclerenchyma Cell: Fibers, Sclereids: support, protection Phloem Parenchyma Cells: storage and short-distance transport Laticifers: secretion and storage of secondary metabolites Resin & Gum Duct Epithelial Cells: secretion |
|
|
Rhizomes
|
A horizontal shoot that grows just below the surface. Vertical shoots emerge from axillary bud.Bulbs
|
|
|
Bulbs
|
Vertical underground shoots consisting mostly of enlarged bases of leaves that store food.(eg:onion)
|
|
|
Stolons
|
Horizontal shoots that grow along the surface. Enable a plant to reproduce asexually, as plantlets form at nodes along each runner(eg: strawberries)
|
|
|
Tubers
|
Enlarged ends of rhizomes or stolons specialized for storing food(eg: potatoes)
|
|
|
Relationship
|
A stem is an organ consisting of an alternating system of nodes and internodes, Many plants have modified stems
|
|
|
Eudicot vs monocot stem |
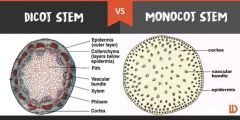
|
|
|
dicot vs monotcot |
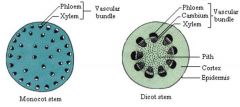
|

