![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What's the formation of Hydroxyl? |
-OH |
|
|
What's the formation of Carbonyl? |
>C=O |
|
|
What the formation of Carboxyl? |
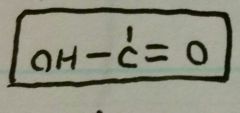
|
|
|
What kind of bonds are Hydroxyl, Carboxyl, Carbonyl, Phosphate, and Amino groups? |
Covalent |
|
|
Which basic covalent group is a donated acid? |
Carboxyl |
|
|
What basic covalent group is an accepting base? |
Amino |
|
|
What's the formation of Phosphate? |
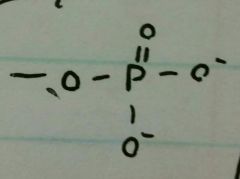
|
|
|
What is the formation of the Amino group? |
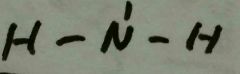
|
|
|
What's the charge on the oxygen side of a water molecule? |
Negative |
|
|
What are the three types of lipids? |
Fats, Steroids, and Phospholipids |
|
|
Name the three simple sugars. |
Glucose, Fructose, Galactose |
|
|
What's the monomer of carbohydrates? The polymer? |
Simple Sugars, and Polysaccharides. |
|
|
What's the monomer of proteins? The polymer? |
Amino Acids, and Polypeptides. |
|
|
What kind of bonds do macromolecules consist of? |
Covalent bonds. |
|
|
Does hydrolysis remove or attach a monomer to a polymer train? Does this use up or produce a molecule of H2O? |
Hydrolysis separates polypeptides by using up water. Dehydration Reactions connect them and produces water |
|
|
What stores more energy? Fats or carbohydrates? |
Fats. Almost twice as much. |
|
|
Steroids consist of how many fused rings? |
Four. |
|
|
What are the four levels of protein structure, from large to small? |
Quaternary, Tertiary, Secondary, Primary |
|
|
What are the two forms of secondary protein structure, and which is stronger? |
alpha helix and beta pleated sheet. Beta is stronger. |
|
|
What cellular object is responsible for protein folding? |
Chaperonin. |
|
|
Are all enzymes proteins? Are all proteins enzymes? |
All enzymes are proteins, but not all proteins are enzymes. |
|
|
What is an Amipathic molecule? |
A molecule with both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions. |
|
|
Side A: Low sugar, medium water. Side B: High sugar, medium water. Final outcome? |
Equal sugar, low water for Side A, high water for Side B. |
|
|
What happens to hypotonic animal cells? |
They burst from over-saturation. |
|
|
What is Tonicity? |
The ability of the surrounding environment to cause a cell to gain or lose water. |
|
|
What is the state of a hypotonic plant cell? |
Turgid (healthiest) |
|
|
What is an isotonic plant cell called? |
Flaccid. (Wilting) |
|
|
What state is a hypertonic plant cell in? |
Plasmolyzed. |
|
|
When small non-polar molecules pass through the cell membrane, that's... |
Passive Diffusion |
|
|
When a molecule passes through the membrane with assistance from a protein that also spans the membrane, that's... |
Facilitated diffusion. |
|
|
An NA+ pump is an example of what kind of protein? |
A carrier protein. |
|
|
Do electrogenic pumps hydrolyse or dehydration react ATP to produce energy, and what is that energy used for? |
Hydrolyse, and the energy is used to transport ions across the membrane (or to be fancy, translocate a net charge). |
|
|
What is it called when a cell is blended to be studied? |
Cell Fractionation |
|
|
Are prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells larger? |
Eukaryotic cells. |
|
|
Do prokaryotes have a nucleus? |
No. |
|
|
Do plant cells have centrosomes/centrioles? |
No, animal cells do. |
|
|
Is the plasmodesmata found in plant cells? |
Yes. |
|
|
Are lysosomes found in both types of cells? |
No, just animal cells. |
|
|
What are the holes in the nuclear envelope called? |
Nuclear Pores. |
|
|
How many chromosomes are in a human cell? |
46. |
|
|
Where is the ribosome factory? |
Nucleolus. |
|
|
What organelle takes mRNA, and transfers it into the primary structure of a protein? |
Ribosomes. |
|
|
What is the Smooth ER in a muscle cell called? |
The sarcoplasmic reticulum. |
|
|
What organelle regulates intracellular calcium? |
Smooth ER. |
|
|
What organelle synthesizes lipids? |
Smooth ER. |
|
|
What organelle metabolizes carbohydrates? |
Smooth ER. |
|
|
What organelle makes glycoproteins? |
The Rough ER |
|
|
What organelle distributes transport vesicles? |
Rough ER. |
|
|
Where is the membrane factory of the cell? |
Rough ER. |
|
|
What organelle modifies ER products? |
Golgi apparatus. |
|
|
What organelle manufactures polysaccharides and carbohydrates? |
Golgi. |
|
|
On the golgi apparatus, is the Cis side the receiving or shipping side? |
Receiving. Trans is the shipping side (starts with same letter). |
|
|
What organelle digests macromolecules? |
Lysosomes (animal cell only). |
|
|
What are the enzymes inside of lysosomes called? What are they made of? |
Hydrolytic enzymes, proteins. |
|
|
What is it called when one cell or cell piece engulfs another? |
Phagocytosis. |
|
|
What is it called when a lysosome breaks down its own cellular components? |
Autophagy. |
|
|
What do contractile vacuoles do? |
Pump excess water out of the cell. |
|
|
What products are produced from cellular respiration? |
CO2+H2O |
|
|
How many membranes do mitochondria have? What are the bumps inside of it called? |
Two. Cristae. |
|
|
What is the winding internal part of the mitochondria called? |
The mitochondrial matrix. |
|
|
What are the three things contained in mitochondria? |
Enzymes, ribosomes, and mitochondrial DNA. |
|
|
Aerobic cellular respiration: Glucose and Oxygen = ...? |
CO2, H2O, and Energy |
|
|
What is the jelly like substance within a chloroplast? |
The stroma. |
|
|
What is one full stack of thylakoids called? |
A granum. |
|
|
What do peroxisomes do? |
Detoxification. |
|
|
What are microtubules made of, and how big are they in regards to other cytoskeletal structures? |
Tubulin, thickest. |
|
|
What are microfilaments made of, and how big are they in regards to other cytoskeletal structures? |
Actin, smallest. |
|
|
What are intermediate filaments made of, and how big are they in regards to other cytoskeletal structures? |
Keratin, medium. |
|
|
Where do microtubules grow out of? |
The centrisome (near the nucleus). |
|
|
What cytoskeletal structure controls muscle contraction and cytoplasmic streaming? |
Microfilaments. |
|
|
What cytoskeletal structure anchors the nucleus and organelles? |
Intermediate filaments. |
|
|
What cytoskeletal structure controls organelle movement? |
Microtubules. |
|
|
What cytoskeletal structure forms the nuclear lamina? |
Intermediate filaments. |
|
|
What two cytoskeletal structures are not permanent structures? |
Microtubules and microfilaments. |
|
|
In direct cellular communication, the _____ exists between them in animal cells, and the _____ in plant cells. |
Gap junction (lost in tumors!), and the plasmodesmata. |
|
|
_____ are secreted by a sender cell in cellular communication. |
Ligands. |
|
|
Which of the following is not a type of cellular communication? Direct, local, paracine, synaptic, long-distance, plasmotic |
Plasmotic. |
|
|
What type of communication involves a secreting cell and secretory vesicles? |
Paracine. |
|
|
What cell signalling method involves neurotransmitters? |
Synaptic. |
|
|
What type of cellular communication involves hormones travelling in the bloodstream? |
Long distance, hormonal, endocrine. |
|
|
What are the three processes of cellular communication? |
Reception (of ligand), Transduction (with relay molecules), Response. |
|
|
What happens when an intracellular steroid receptor combines with a steroid such as testosterone? |
RNA/DNA production. |
|
|
What process does a Tyrosine Kinase Receptor use to turn on a signalling pathway? |
Phosphorilation. |
|
|
What does a kinase do to a protein? |
It takes the phosphate group from ATP to turn on the protein. |
|
|
What does the opposite of kinases? |
Phosphatases. |
|
|
What are second messengers? (Ligands are first messengers) |
Small non-polar molecules and ions (like cAMP or Ca2+) easily diffused to activate proteins after initial ligand response. |
|
|
What are some consequences of too much apoptosis? How about too little? |
Alzheimer's, Parkinson's // Tumors, Cancer |
|
|
What does a nuclear response at the transcription factor create, and what in turn does that regulate? |
mRNA, regulates protein synthesis. |
|
|
What are the three causes of apoptosis? |
Internal damage/signal, external signals, oxidative stress. |

