![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Respiration |
Breaks down fuel particles to produce ATP. |
|
|
3 Pathways of Respiration |
☆Glycolysis ☆Citric Acid Cycle ☆Oxidative Phosphorylation |
|
|
Fermentation |
A catabolic process that partially degrades sugars and other organic fuels in the absence of oxygen (therefore it is an anaerobic process) ● the Electron transport chain is not used in this process. But is used in Anaerobic Respiration. |
|
|
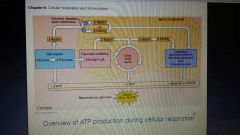
Aerobic Respiration |
More efficient process than fermentation ; oxygen is consumed as a reactant along with some form of organic fuel.
● most eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells carry aerobic respiration. |
|
|
Cellular Respiration |
Results in the relocation of electrons in organic molecules, which in turn causes a release of energy. |
|
|
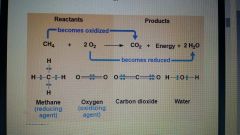
Glucose is broken down in a series of steps |

Electrons travel through the process bonded to proton H+
The electrons are not transferred to direct oxygen rather their pass first to an electron carrier a coenzyme called NAD +
NAD plus is an electron acceptor and can easily alternate between NAD plus an nadh during respiration. |
|
|
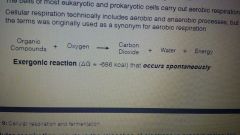
, the most important redox reaction to a cell |
Oxidation of glucose and other molecules in food |
|
|
The transfer of electrons from nadh to water releases... |
Energy that is used for the production of ATP. ● the transfer of electrons from hydrogen to oxygen causes a release of energy as they "fall" closer to the more electronegative oxygen atom. |
|
|
Electron transport chain |

● the electron transport chain consists of a number of molecules, mostly proteins built into the inner membrane of the mitochondria( and plasma membrane of prokaryotes)
● electrons move from the "top" of the chain (higher energy) to the bottom of the chain (lower energy) where they are along with H+ nuclei picked up by O2 forming water. |
|
|
Citric acid cycle |
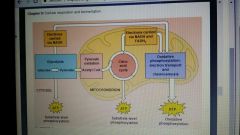
Acetyl COA enters, the breakdown is of glucose to CO2 is completed here |
|
|
Oxidative phosphorylation |
The electron transport chain accepts electrons from the breakdown products of the first two stages |
|
|
Glycolysis |
Occurs in the cytosol; Begins the degradation process by breaking down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate.
Then pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl COA. |
|
|
This account for approximately 90% of ATP production in the cell |
Oxidative phosphorylation |
|
|
Substrate level phosphorylation |
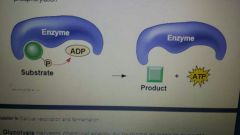
And mechanism which holds glycolysis and the citric acid cycle to produce a smaller amount of ATP.
Occurs when an enzyme transfers a phosphate group from a substrate molecule to ADP rather than adding and inorganic phosphate to ADP as in oxidative phosphorylation |
|
|
Further steps of glycolysis |

Glucose, a six carbon sugar, is split into two three carbon sugars.
These smaller sugars are then oxidized and the remaining atoms are rearranged to form two molecules of pyruvate. |
|
|
Two phases of glycolysis |
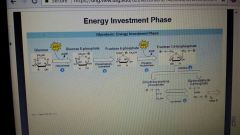
energy investment
energy payoff |
|
|
Citric acid cycle continued |
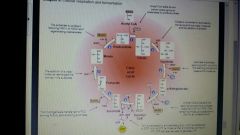
The citric acid cycle acts as a metabolic furnace that oxidizes organic fuel from pyruvates.
The citric acid cycle generates one molecule of ATP per turn by substrate-level phosphorylation, but most of the chemical energy is transferred from NAD + and a related electron carrier, the coenzyme fad (Flavin adenine dinucleotide) during redox reaction.
The reduced coenzymes nadh and fadh2 shuttle their electrons to the electron transport chain. |
|
|
Prosthetic groups and Cytochrome in the Electron transport Chain. |
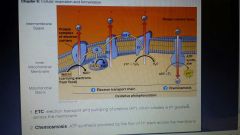
Prosthetic Groups: are tightly bound to the complexes ( the multi protein complexes that are the components on the chain.) and crucial for the catalytic functions of certain enzymes.
Cytochromes: make up several of the proteins in the electron transport chain their prosthetic group is a heme group that contains an iron atom that accepts and donates electrons. |
|
|
Electron Transport Chain continued... |
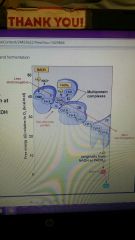
●Fadh2 adds electrons to the chain at a Lower energy level ( complex 2) than Nadh ( complex 1)
●The chain does not create ATP directly, it frees up energy for chemiosmosis.
● Chain moves electrons from less Electronegative space to a more electronegative space down a gradient. Through proteins conplexes. |
|
|
Chemiosmosis |
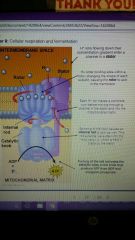
The process by which energy stored in the form of a hydrogen ion gradient is used to drive cellular work, such as the synthesis of ATP.
● in general terms, it is an energy coupling mechanism that uses energy stored in the form of an H+ gradient across a membrane to drive cellular work |
|
|
ATP Synthase |
A protein complex that makes ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate these complexes line the inner membrane of the mitochondria (eukaryotes) or the plasma membrane (prokaryotes). ●uses the energy associated with an ion (H+) gradient to power the synthesis of ATP. |
|
|
2 Fermentation cycles |
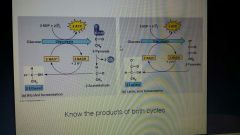
● fermentation is an extension of glycolysis that allows continuous generation of ATP by the substrate level phosphorylation of glucose. ☆Alchohol Fermentation - pyruvate is converted to ethanol (ethyl alcohol) in 2 steps. ☆Lactic Acid Fermentation - pyruvate is produced directly by nadh to form lactate as an end product, with no production of CO2. |

