![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
All living organisms share 5 fundamental characteristics |
1. Energy (all organisms acquire and use energy) 2. Cells (all organisms are made up of membrane bound cells 3. Information (all organisms process hereditary info encoded in genes and info from the enviro) 4. replication (all organisms are capable of reproduction) 5. Evolution (populations of organisms are continually evolving) |
|
|
How is biology studied? Scientific Method
|
Bottom up: 1. Observation (about the surrounding) 2. questions (about the phenomenon being observed) 3. hypothesis (tentative explanation to the question) 4. Testing ( perform tests to determine the accuracy of their hypothesis) 5. explanation - it is a hypothesis that has passed the widest and most comprehensive series of tests - still subject to review and consideration - may be elevated to a theory = well demonstrated principle and theory |
|
|
Theories:
|
(scientific theory is an explanation for a very general class of phenomena or observations that are supported by a wide body of evidence) |
|
|
Two components of a Theory
|
1. Pattern: Something that occurs in the natural world 2. Process: what drives or explains the pattern |
|
|
Two theories that form the framework for modern biological science:
|
1. Cell theory: what are organisms made of? 2. The theory of evolution by natural selection: Where do organisms come from? |
|
|
The Cell Theory |
- the cell is the lowest level of organization that can perform all activities required for life - a cell is a highly organized compartment bounded together by a plasma membrane and containing concentrated chemicals in an aqueous solution -the cell is the fundamental structure unit in all living organisms |
|
|
The Cell Theory: Louis Pasteur's Experiment
|
Louis Pasteur's hypothesis: cells arise from cells -cells do not arise from spontaneous generation - |
|
|
Prediction |
is measurable or observable result that must be correct if a hypothesis is valid
|
|
|
Implications of the cell theory
|
1. because all cells come from preexisting cells - all individuals in a population of single-celled organisms are related by common ancestry 2. all of the cells present in a multicellular organism - have descended from prexisting cells - are connected by common ancestry |
|
|
The continuity of life is based on heritable information in the form...
|
DNA Cells genetric material - chromosomes *DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) -DNA is the substance of genes |
|
|
Chromosomes |
Chromosomes are thread-like molecules that carry hereditary information for everything from height to eye color. They are made of protein and one molecule of DNA, which contains an organism’s genetic instructions, passed down from parents. In humans, animals, and plants, most chromosomes are arranged in pairs within the nucleus of a cell. Humans have 22 of these chromosome pairs, called autosomes.
|
|
|
Genes |
are the units of inheritance that transmit information from parents to offspiring
|
|
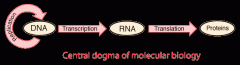
The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology |
- genes control protein production indirectly -DNA is transcribed into RNA then translated into a protein Nucleotide: sequences 3 billion - an orgnaism's genome is its entire set of genetic instructions (nucleotide sequences of DNA base pairs), it's proteome (all of its proteins) enables its functions (amino acid sequences) |
|
|
Proteome |
The proteome is the entire set of proteins expressed by a genome, cell, tissue, or organism at a certain time. More specifically, it is the set of expressed proteins in a given type of cell or organism, at a given time, under defined conditions. The term is a blend of proteins and genome. Proteomics is the study of the proteome.
|
|
|
Evolution accounts for the ______ and _______of life
|
unity and diversity - unity underlies the diversity of life (DNA- universal genetic language) |
|
|
The theory of Evolution by natural selection
|
- 1858, Darwin/Wallace made two claims regarding the natural world: - all speicies are related by a common ancestor (PATTERN) - characteristics of species can be modified from generation to generation - Descent with modification (PROCESS) - Evolution *Natural selectionexplains how evolution occurs |
|
|
Steps of the Theory of Evolution
|
1. Overpopulation: produce more offspring than can survive 2. Variation: individuals of a population have many characteristics that differ 3. Selection: some individuals survive longer and reproduce more than others 3. Adaption: the traits of those individuals that survive and reproduce will become more common in a population |
|
|
Fitness |
the ability of an individual to produce offspring (individuals with higher fitness produce many more surviving offspring than do others in the population |
|
|
Adaptation |
is a trait that increases the fitness of the individual in a particular enviro
|
|
|
Evolutionary change occurs when
|
- if certain heritable traits lead to increased sdesuccess in producing offspring (fitness) - these traits become more common in the population over time - the population's characteristics change (evolve) as a result to natural selection acting on individuals |
|
|
Natural Selection act on _________________ Evolutionary change occurs in _______________ |
1. Individual 2. Population |
|
|
What do the Cell Theory and Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection Imply?
|
- that all speices come from preexisting species - and all species, past and present, trace their ancestry back to a single common ancestor |
|
|
Speciation |
the divergence process in which natural selection has caused populations of one speices to diverge to form new species
|
|
|
Phylogeny |
Genealogical relationship or "Tribe source"
|
|
|
Phylogenetic Tree |
- is used to show the relationships between species - branches that share a recent common ancestor represent species that are closely related |
|
|
Carl Woese? |
1. rRNA : small subunit ribosomal RNA, he used this to understand evloutionary changes 2. rRNA is a molecule found in all orgnaisms (part of the ribosomes) and is comprised of 4 chemical units called ribonucleotides (symbolized by letters A, U, C, and G) |
|
|
Ribosomes |
There are two major types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Ribosomes are cell organelles that consist of RNA and proteins. They are responsible for assembling the proteins of the cell. Depending on the protein production level of a particular cell, ribosomes may number in the millions.
|
|
|
if the evolution theory is correct then...
|
rRNA sequences should be very similar in closely related organisms but less similar in organisms that are less closely related. Species that are part of the same evolutionary lineage, like the plants, should share certain changes in rRNA that no other species have
|
|
|
Taxonomy |
is the effort to name and classify organisms a taxon (taxa, plural) is a named group Domain- Kingdom- Phylum- class- Order- family-genus- Species (dirty kinky people cry out for good sex) Why important? ability to collaborate w/ others- common language |
|
|
DNA is universal |
we all have the same 4 nucleotides that translate to same 23 amino acids
|
|
|
Three Domain system
|
1. Prokayotes - domain Bacteria - Domain Archaea 2. Eukaryotes - Domain Eukarya |
|
|
Eukaryotic cell |
had membrane- enclosed organelles - nucleus is usually the largest - plants, animals, fungi, and all othe forms of life |
|
|
Prokaryotic Cell |
is similar to eukaryotic and usually smaller - doe not conatin a nucleus or other membrane enclosed organelles - Bacteria and Archaea |
|
|
Linnaeus' Taxonomic System of Classification
|
- est system used today in 1735 - each organism is given a unique two-part scientific name 1. consists of the genus and the species - a genus is made up of a closely related group of species - a species is individuals that regularly breed together (BSC) or individuals whose characteristics are distinct from those of other speices |
|
|
Rules of Nomenclature |
an orgnaisms genus and species designation is called its scientific name or latin name - Scientific names are always intalicized orunderlined - Genus names are always capitalized - species names are not capitalized example: C. sinensis |
|
|
Hypothesis Based Science
|
Hypothesis testing is a two-part process - state the hypothesis as precisly as possible and lost the predictions it makes - design an observational or experiment study that is capable of testing those proedictions |
|
|
Null Hypothesis |
specifies what we chould observe if the hypothesis being tested does not hold
|
|
|
Expiremental Design
|
1. expirements allow researchers to test the effect of a single, well defined factor or variable on a particular phenomeno 2. Controlled Experiment compares an experimental group/treatement with a control group/treatement 3. idealy only one variable of interest differs between the control and the experimental treatments. 4. a controlled experiment means that control groups/treatments are used to cancel the effects of unwanted variables |

