![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
All animals (except _____) use anetwork of nerves to process & integrateinformation
|
sponges
|
|
|
Nervous system links 2:
|
• Sensory receptors
• Motor effectors |
|
|
What is Sensory receptors
|
detect stimulus
|
|
|
What is Motor effectors
|
respond to it
|
|
|
Nervous system consists of ____ and _____ cells
|
neurons and supporting cells
|
|
|
only major phylum withoutnerves
|
sponges
|
|
|
Who has the simplest nervous system?
|
Cnidarians
|
|
|
simplest animals withassociative activity
|
flat worms
|
|
|
Peripheral Nervous System
• _____ & responds • Sensory & motor neurons • Somatic NS stimulates skeletal muscles • Autonomic NS stimulates smooth& cardiacmuscles & glands |
-Collects
|
|
|
Central Nervous System
• ____ & Spinal cord • _____ center |
-Brain
-command |
|
|
Vertebrates have 3 types of Neurons
|
-Sensory neurons, motor neurons, interneurons
|
|
|
1. Sensory neurons: (______neurons)carry impulses to ______ nervous system(CNS)
|
-afferent
-central |
|
|
2. Motor neurons: (_____ neurons) carry impulses from CNS to effectors (____ and ____)
|
-efferent
- muscles and glands |
|
|
3. Interneurons: (______ neurons) provide more complex reflexes and associative functions (_____ and ____)
|
-association
-learning and memory |
|
|
Peripheral Nervous System
• Consists of ____ & _____ • Receive info from the enviro. • Conveys it to the CNS & tocarry responses to effectorssuch as muscle cells |
nerves, ganglia
|
|
|
what is ganglia
|
a bunch of nerves together
|
|
|
Somatic Nervous System
Somatic motor neurons stimulate theskeletal _____ to contract • Response to conscious ____ or ____ actions |
-muscles
-command or reflex |
|
|
____ Nervous System
• Composed of the sympathetic ¶sympathetic divisions & medullaoblongata |
autonomic
|
|
|
Autonomic Nervous System
In both, _fferent motor pathway has 2neurons named: |
-efferent
– Preganglionic neuron – Postganglionic neuron |
|
|
– ___ganglionic neuron – exits the CNS and synapses at an autonomic ganglion
|
Preganglionic
|
|
|
– ___ganglionic neuron – exits the ganglion and regulates visceral effectors
|
Postganglionic
|
|
|
Where do the preganglionic neurons start on the Sympathetic division located on spine?
|
thoracic & lumbar regions
|
|
|
Where do the pregangliontic neurons start on the Parasympathetic division located on spine?
|
brain & sacral regions
|
|
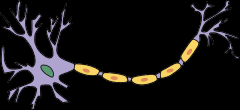
name cell body, dendrites, axon
|
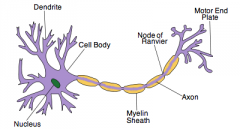
|
|
|
What does the neuroglia do
|
Support neurons both structurally &functionally
|
|
|
Nerve ImpulseTransmission
• There’s a potential difference across everycell’s plasma membrane – Negative pole – _____ side – Positive pole – ___ ___ side |
-cytoplasmic
-extracellular fluid |
|
|
When a neuron is not being stimulated, itmaintains a ____ potential
|
resting
|
|
|
Nerve Impulse Transmission
The inside of the cell is more ___ charged than the outside 1. Sodium–potassium pump 2. Ion leakage channels |
negatively
|
|
|
What is Ligands
|
hormones or neurotransmitters
|
|
|
Axon has a large diameter
• Less resistance to current flow – Found primarily in invertebrates – Axon is myelinated • Action potential is only produced at thenodes of Ranvier • Saltatory conduction |
read
|
|
|
Synaptic (2)
|
• Presynaptic •Postsynaptic
|
|
|
What synapsis cell transmits action potential
|
Presynaptic
|
|
|
What synapsis cell receives it
|
Postsynaptic
|
|
|
2 types of synapsis
|
Electrical, chemical
|
|
|
What part of the nervous system is the brain connected to?
|
central
|

