![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

chromatin
|
IN INTERPHASE
thread-like not visible with a light microscope combination of DNA & proteins that make up eukaryotic chromosomes/contents of the nucleus |
|
|
Why must the nuclear membrane dissolve at the end of prophase?
|
so the sister chromatids can line up in the center of the cell
so the SC can move to opposite poles so it ends up with 2 nuclei in telophase |
|
|
Centrioles
|
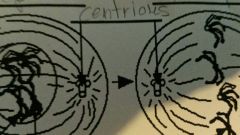
development of spindle fibers in cell division
cylindrical organelle near nucleus (animal cells) in pairs |
|
|
Cancer A
|
No response to growth factors
Signals/cell regulatory checkpoints don't work (some make their own growth factors) |
|
|
Cancer B
|
tumors
Benign tumors remain in place of origin-non-cancerous; may become cancerous in some cells |
|
|
Cancer C
|
-defect gene p53 stops the cell cycle if the DNA is damages, causing the cell to divide uncontrollably
-defect gene p27 stops entry into the S phase if the cell is not ready (may not work in some cancer) |
|
|
Metastasis
|
spread of cancer cells beyond their original site
|
|
|
Cyclins
|
protein signals
regulate cell cycle may not work in some cancerous cells |
|
|
Apopsis
|
destruction of the cell
|
|
|
body cells (Somatic)
|
46 chromosomes from humans
|
|
|
sex cells (Gametes)
|
23 chromosomes from humans
|
|
|
centrioles
|
helps create spindle fibers
|
|
|
chromosomes
|
Thickened structure within the nucleus containing genetic information
made of DNA coiled around proteins |
|
|
Malignant tumors
|
can spread toother parts of the body
|

