![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Are fungi heterotrophic or autotrophic?
|
Heterotrophic |
|
|
What is the study of fungi? |
Mychology |
|
|
What is Mycorrhizae? |
Symbiotic relationship formed between fungi and plants. Fungi attaches to host plant, giving nutrients and water. Plant gives fungus carbohydrates from photosynthesis. |
|
|
What is Chitin? |
A fibrous substance forming the cell walls of fungi. |
|
|
What care Hyphae? |
Each of the branching filaments that make up the mycelium of a fungus. |
|
|
How many species of fungi are there? |
100,000 known, probably more |
|
|
Is fungi more closely related to plants or animals? |
Animals. |
|
|
What is a mycelium? |
Mesh of branched filaments (hyphae). |
|
|
How does a fungus infect humans? |
The mycelium of the fungus can be pathogenic to humans. It enters through a cut or a scrap and develops of mycetoma, a chronic infection. |
|
|
How do fungi absorb nutrients? |
First, exoenzymes are transported out of the hyphae, where they process nutrients in the environment. Then, the smaller molecules produced by this external digestion are absorbed through the large surface area of the mycelium. As with animal cells, the polysaccharide of storage is glycogen, rather than starch, as found in plants. |
|
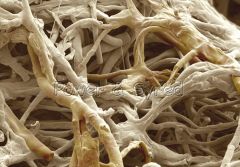
|
Fungus hypha |
|
|
Where do fungi get most of their nutrients? |
Fungi are mostly saprobes organisms that get nutrients from dead decaying matter, mainly plant material |
|
|
What is a mushroom? |
A mushroom is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground on soil or on its food source. |
|
|
Yeast |
Single-celled fungal infection typically on the skin or mucous membranes caused by candida. |
|
|
Fungal asexual reproduction |
Fungi can reproduce asexually by forming spores through mitosis |
|
|
Fungal sexual reproduction |
Fungi can reproduce sexually by fusion of haploid cells followed by meiosis |
|
|
Fungal sexual reproduction 2 |
Plasmogamy: fusion of cytoplasm between two haploid cells. Karyogamy: fusion of the two nuclei to form diploid zygote. |
|
|
Chytridiomycota |
Chytridiomycota is a division in the kingdom Fungi. The name is derived from the Greek chytridion, meaning "little pot", describing the structure containing unreleased zoospores. Oldest kind |
|
|
Zygomycota |
Lives in soil or decaying matter Hyphae lack septae Asexual reproduction thru spores Sexual reproduction- two hyphae |
|
|
Classification |
Chytrids Zygomycota Ascomycota, Sac fungi Basidiomycota, Club Fungi Glomeromycota Deutermycota |
|
|
Glomeromycota |
Glomeromycota is one of seven currently recognized divisions within the kingdom Fungi, with approximately 230 described species. |
|
|
Deuteromycota |
Unknown sexual reproduction Known as mold Fungus in roquefort and Camember cheese |
|
|
Mycorrhizae |
Fungus in or on tree roots |
|
|
Lichens |
Mutualistic relationship between a fungus and an alga or cyanobacterium |
|
|
Endophytic fungi |
Fungi living in other organisms like grass, protecting them from predators |
|
|
What distinguishes fungal reproduction from that of plants and animals? |
There is no embryo produced when fungi reproduce. |
|
|
A zygospore undergoes _________ to produce haploid spores. |
meiosis |
|
|
Yeasts, truffles, and Dutch elm disease belong to which division of Fungi? |
Ascomycota |
|
|
The clublike structure producing the spores of typical mushrooms is called __________. |
Basidia |
|
|
A haploid asexual spore is formed by a haploid mycelium via ________. |
Mitosis |
|
|
What is the tangled mass of branched filaments that typically forms the fungal body? |
Mycelia |
|
|
The mushrooms on the pizza you might have eaten last night belong to the phylum: |
Basidiomycota |
|
|
During sexual reproduction in the Basidiomycota and the Ascomycota, _______ produces _______ spores, which give rise to a new mycelium. |
meiosis; haploid During sexual reproduction, when DNA has been combined from two organisms, meiosis is required to reduce the number of chromosomes to give haploid spores which will produce a haploid mycelium |
|
|
The spores of chytrids are unique because they are: |
flagellated |
|
|
What is a zygospore? |
A zygospore is a diploid reproductive stage in the life cycle of many fungi and protists. |
|
|
Mycorrhizae commonly involving Glomeromycetes in which the fungal hyphae penetrate the cell walls of the plant root cells (but not the cell membranes)? |
Arbuscular Mycorrhizae |
|
|
Symbiotic relationship in which one member benefits while the other member is not affected? |
Commensalism |
|
|
Reproductive sac that contains spores. |
sporangium |
|
|
Fusion of nuclei? |
Karyogamy |
|
|
What is mycosis? |
Fungal infection |
|
|
Mycorrhizae in which the fungal hyphae do not penetrate the root cells of the plant? |
Ectomycorrhizae |
|
|
Clusters of algal cells and mycelia that allow lichens to propagate. |
Soredia |

